Kinematics Part 2 (Computations Naman) Physics Explained In Tagalog/Filipino
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script covers fundamental concepts in physics, focusing on velocity and acceleration. It explains the calculation of velocity as displacement over time, using examples to demonstrate how to find velocity in different scenarios, including when direction is specified. The script also delves into acceleration, detailing its computation as the change in velocity over time. Practical examples, such as a car's deceleration when a deer crosses the road, are used to illustrate these principles, making the complex physics concepts accessible and engaging.
Takeaways
- 📏 The formula for calculating velocity is displacement over time, which is used to find the boy's velocity in the video.
- 🕒 The boy's velocity is determined to be one meter per minute to the east, based on a six-meter displacement in six minutes.
- 📉 The script discusses the Cartesian plane and its relevance to physics, emphasizing its use for understanding motion.
- 🔢 The calculation of velocity involves finding the hypotenuse for the displacement and dividing it by time, resulting in 1.2 meters per minute.
- ⏱️ The script explains the conversion of velocity from meters per minute to meters per second, highlighting the importance of time units.
- 📉 The video uses a problem-solving approach to demonstrate how to calculate acceleration, which is the change in velocity over time.
- 🔄 The script clarifies that if acceleration and velocity are in the same direction, the object is accelerating, and if they are in opposite directions, the object is decelerating.
- 🚗 An example of deceleration is given with a car stopping from 60 meters per hour, illustrating how to calculate deceleration.
- 📌 The script emphasizes the importance of direction in vector calculations, noting that direction affects the sign of the calculated values.
- 🎓 The educational content is designed to help viewers understand and apply basic physics concepts related to motion and vectors.
Q & A
What is the formula for calculating velocity?
-The formula for calculating velocity is displacement over time, which can be represented as v = Δx/Δt where v is velocity, Δx is displacement, and Δt is the time taken.
How do you determine the direction of velocity?
-The direction of velocity is determined by the direction of displacement. If the displacement is towards the east, the velocity is positive in the eastward direction. Conversely, if it's towards the west, the velocity is negative or westward.
What is the velocity of the boy who took six minutes to reach a box 6 meters away?
-The boy's velocity is 1 meter per minute since he covered a displacement of 6 meters in 6 minutes.
How is the Cartesian plane used in physics?
-The Cartesian plane is used in physics to represent positions and movements in a two-dimensional space. It helps in understanding and solving problems involving coordinates and directions.
What is the velocity of an object moving 1.2 meters per minute in a positive direction?
-The velocity is 1.2 meters per minute, with the positive sign indicating the direction is towards the positive x-axis or to the right.
How do you convert velocity from meters per minute to meters per second?
-To convert velocity from meters per minute to meters per second, you divide the velocity by 60 since there are 60 seconds in a minute.
What is the formula for calculating acceleration?
-Acceleration is calculated using the formula a = Δv/Δt where a is acceleration, Δv is the change in velocity, and Δt is the time over which the change occurs.
If an object's velocity changes from 38 m/s to 68 m/s in 5 seconds, what is its acceleration?
-The acceleration is 6 meters per second squared (6 m/s²) since the change in velocity is 68 - 38 = 30 m/s over 5 seconds.
What is the difference between acceleration and deceleration?
-Acceleration occurs when the velocity of an object increases, while deceleration occurs when the velocity decreases. Both are measured using the same formula, but the direction of the change in velocity determines whether it's acceleration or deceleration.
If a car decelerates from 60 meters per hour to a stop in 25 seconds, what is its deceleration?
-The deceleration is -0.007 meters per second squared (-0.007 m/s²) since the change in velocity is from 60 m/h (which is 60/3.6 ≈ 16.67 m/s) to 0 m/s over 25 seconds.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

FISIKA KELAS X: GERAK LURUS (PART 1) Jarak, Perpindahan, Kelajuan, Kecepatan, Percepatan

Position/Velocity/Acceleration Part 1: Definitions

MATERI KINEMATIK kelas 11 bag 1 PENGERTIAN GERAK, JARAK & PERPINDAHAN K Merdeka
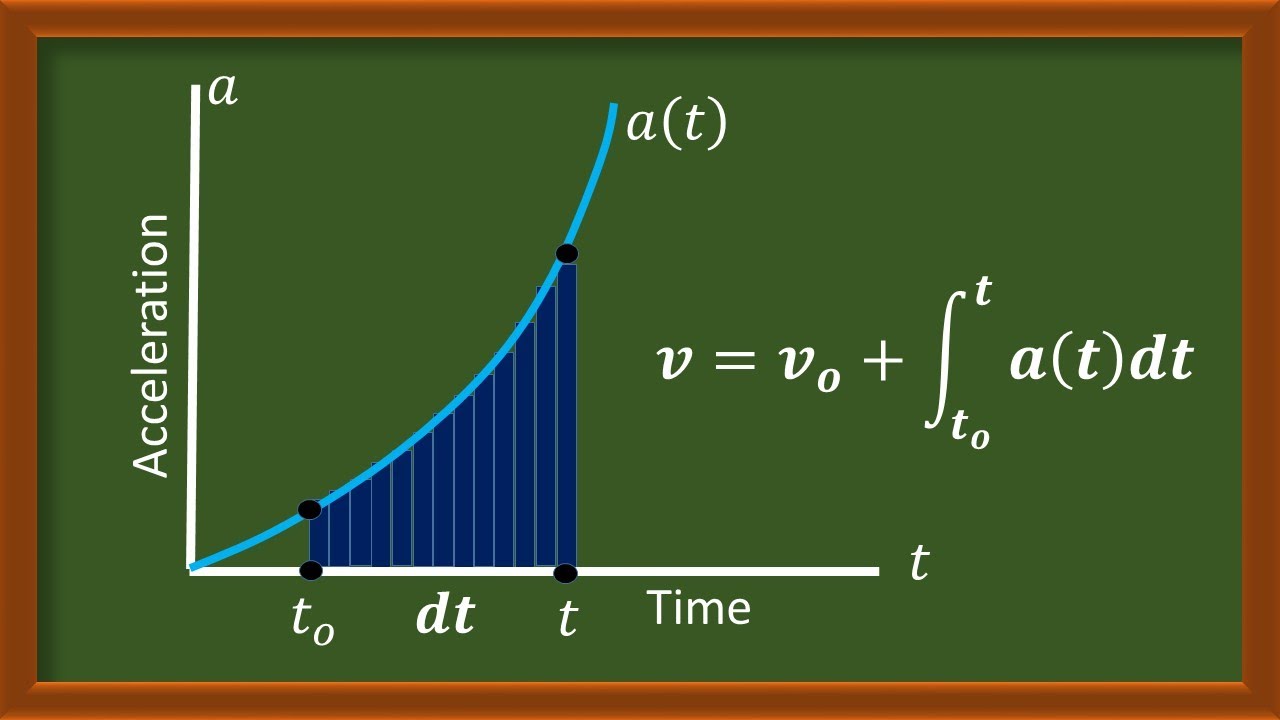
Kinematics: Acceleration Vs Time Graph

BAB 4 : GERAK DAN GAYA | Part 1 : GERAK BENDA | IPA SMP Kelas 7 Kurikulum Merdeka

Distance displacement speed velocity acceleration for IGCSE Physics, GCE O level Physics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
