BIOLOGI SMA Kelas 11 - Sistem Pernapasan | GIA Academy
Summary
TLDRThis educational video from Gia Academy explores the human respiratory system, detailing the organs involved in breathing and their functions. It explains the process of inhaling oxygen and exhaling carbon dioxide and water vapor, highlighting the roles of the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli. The video also covers the mechanics of breathing, including diaphragm and intercostal muscle actions, and discusses various respiratory diseases. It concludes with a look at the different volumes of air involved in breathing and factors affecting respiration rates.
Takeaways
- 😷 The human respiratory system includes organs such as the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, and lungs.
- 👃 The nasal cavity filters, warms, and humidifies the air, and also detects scents through the olfactory receptors.
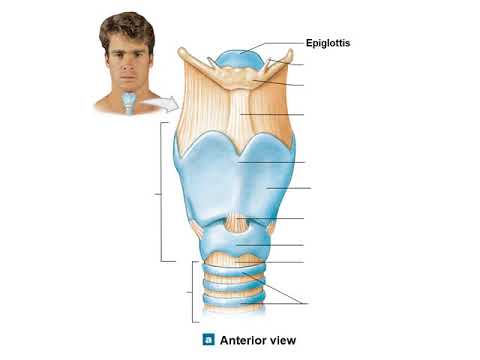
- 🔄 The pharynx serves as a junction between the nasal cavity and the respiratory and digestive tracts, with the epiglottis preventing food from entering the windpipe.
- 🗣️ The larynx contains the vocal cords and the epiglottis, which plays a crucial role in both breathing and swallowing.
- 🌀 The trachea, or windpipe, is a tube that branches into the lungs and is lined with cartilage rings to keep it open.
- 💨 Bronchi and bronchioles are the branching airways within the lungs that end in tiny air sacs called alveoli.
- 🌪️ Alveoli are the site of gas exchange, where oxygen diffuses into the bloodstream, and carbon dioxide diffuses out.
- 🏋️♂️ Breathing is facilitated by respiratory muscles, including the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm, which expand and contract the chest cavity.
- 🔁 The process of inhalation (inspiration) and exhalation (expiration) involves the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, regulated by changes in air pressure within the thoracic cavity.
- 🚑 Common respiratory disorders include asthma, emphysema, lung cancer, pneumonia, and tuberculosis, which can impair the function of the respiratory system.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
-The primary function of the respiratory system is to facilitate the intake of oxygen into the body and the expulsion of carbon dioxide and water vapor from the body.
What are the main organs that make up the human respiratory system?
-The main organs that make up the human respiratory system include the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, and lungs.
How does the nasal cavity contribute to the respiratory process?
-The nasal cavity contributes to the respiratory process by filtering, warming, and humidifying the air that enters the body, and it also detects odors through the olfactory receptors.
What is the role of the epiglottis in the respiratory system?
-The epiglottis plays a crucial role in preventing food from entering the trachea during swallowing by covering the entrance to the larynx.
How does the trachea contribute to the respiratory process?
-The trachea, or windpipe, serves as a conduit for air to travel from the upper airway to the bronchi, which then branch out into the lungs.
What is the function of the bronchi and bronchioles in the respiratory system?
-The bronchi and bronchioles are the branching airways in the lungs that eventually lead to the alveoli, where gas exchange occurs.
What is the significance of the alveoli in the respiratory system?
-Alveoli are the tiny air sacs in the lungs where the actual gas exchange between oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place, allowing oxygen to enter the bloodstream and carbon dioxide to be expelled.
How does the diaphragm muscle assist in the breathing process?
-The diaphragm muscle assists in the breathing process by contracting and relaxing, which changes the volume of the thoracic cavity, thus facilitating inhalation and exhalation.
What is the difference between external and internal respiration?
-External respiration refers to the gas exchange that occurs in the alveoli of the lungs, while internal respiration refers to the gas exchange that occurs within the body's tissues and cells.
What is the role of hemoglobin in the respiratory system?
-Hemoglobin plays a critical role in the respiratory system by binding to oxygen to form oxyhemoglobin, which transports oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues.
What are some common respiratory disorders mentioned in the script?
-Some common respiratory disorders mentioned in the script include asphyxiation, asthma, emphysema, lung cancer, pneumonia, tuberculosis, influenza, and bronchitis.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Microteaching_Kelompok 2_ Pertemuan 1 "Organ Sistem Pernapasan" by A.Tenri Ayu Wulandari

VIDEO PEMBELAJARAN BERDIFERENSIASI

Kurikulum Merdeka Rangkuman IPA Kelas 8 Bab 2: Sistem Pernapasan
Anatomi Sistem Respirasi | Materi Kedokteran Dasar

GRADE 6- The Respiratory System | K12 Lesson Sulong Edukalidad

SISTEM PERNAPASAN MANUSIA | ORGAN PERNAPASAN
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
