Autotrophs and Heterotrophs
Summary
TLDRThe video script explores the fascinating world of autotrophs and heterotrophs, delving into how organisms obtain energy and nutrients. It explains that plants, as autotrophs, produce their own food through photosynthesis, while heterotrophs like animals consume organic matter. The script also introduces chemoautotrophs, which use chemicals for energy, and photoheterotrophs, which rely on light but consume organic matter. The video highlights the complexity and diversity of life's nutritional strategies, encouraging viewers to appreciate the beauty of biology.
Takeaways
- 🐔 The speaker had various favorite animals as a child, including silkie bantam chickens, which might still be a favorite.
- 📚 A key interest was collecting facts about different animals, including their diet and habitat.
- 🌿 Most animals, including the speaker's favorites, are heterotrophs, meaning they consume organic matter for energy.
- 🌱 In contrast, plants are generally autotrophs, producing their own food from inorganic substances using light or chemical energy.
- 🌞 Plants, including carnivorous ones, primarily produce their food through photosynthesis, even if they also consume insects.
- 🌐 Some organisms, like Euglena, can be both autotrophs and heterotrophs, switching modes based on the availability of light.
- 🔬 Autotrophs obtain carbon from inorganic sources, while heterotrophs derive it from the organic matter they consume.
- 🌌 Photoautotrophs, like plants, use light as their energy source, whereas chemoautotrophs, such as certain bacteria, use chemical energy.
- 🍽️ Humans are chemoheterotrophs, relying on organic matter for both food and energy, unlike photoheterotrophs which use light energy.
- 🧬 The video script highlights the diversity of nutritional strategies among organisms and the fascinating exceptions in biology.
Q & A
What are heterotrophs?
-Heterotrophs are organisms that consume organic matter to obtain their carbon and energy. This group includes animals, fungi, some protists, and some bacteria and archaea.
What does it mean for an organism to be an autotroph?
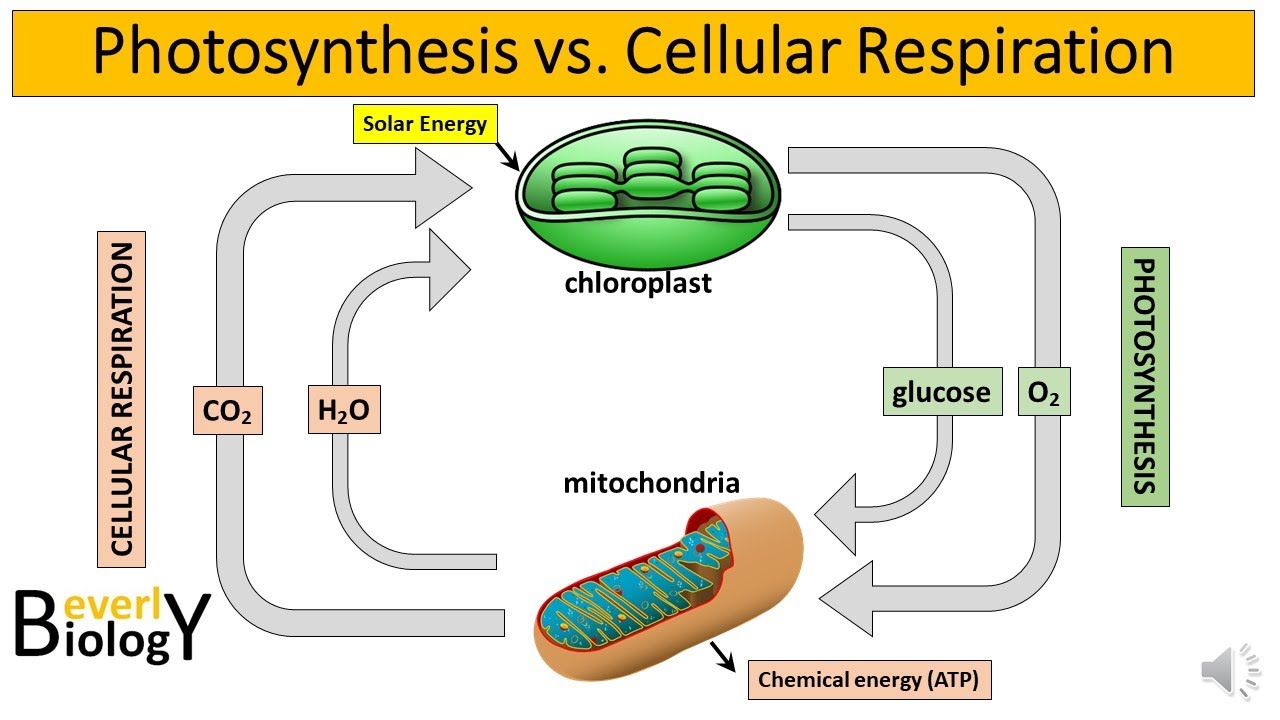
-Autotrophs are organisms that produce their own food by converting inorganic substances into organic substances. For example, plants are autotrophs because they use light energy to create glucose from carbon dioxide and water through photosynthesis.
Can an organism be both an autotroph and a heterotroph?
-Yes, an organism like Euglena can be both. Euglena can perform photosynthesis as autotrophs when light is available but can also consume organic matter as heterotrophs when light is not available.
What is the difference between photoautotrophs and chemoautotrophs?
-Photoautotrophs use light as their energy source to produce organic substances from inorganic substances, while chemoautotrophs use chemical energy from inorganic substances to achieve the same goal.
How do plants obtain their energy and nutrients?
-Plants are photoautotrophs. They use light energy to perform photosynthesis, producing glucose from carbon dioxide and water. They are also capable of producing their own food and are known as producers.
What are photoheterotrophs and where are they found?
-Photoheterotrophs are heterotrophs that use light as their energy source but still consume organic matter for their carbon needs. This mode of nutrition is found in a few types of prokaryotes.
What type of organisms are chemoheterotrophs?
-Chemoheterotrophs, such as humans and other animals, are organisms that consume organic matter for both their carbon and energy needs.
Why do carnivorous plants also perform photosynthesis?
-Carnivorous plants perform photosynthesis to produce their own food, like other autotrophs. However, they also digest insects to obtain nitrogen, which is scarce in the soil where they commonly live.
What is the role of autotrophs and heterotrophs in ecosystems?
-Autotrophs, also known as producers, create organic substances from inorganic ones and provide the base energy for most ecosystems. Heterotrophs, also known as consumers, rely on consuming organic substances, making them integral to the food chain.
How do organisms like chemoautotrophs survive in environments without light?
-Chemoautotrophs survive in environments without light by using chemical energy from inorganic substances, like hydrogen sulfide, to produce organic matter, allowing them to thrive in extreme conditions such as deep-sea vents.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)