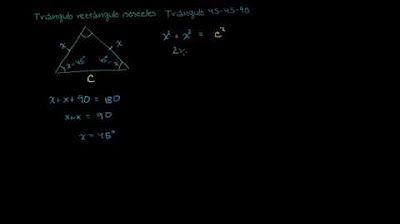Similar Triangles - GCSE Maths
Summary
TLDREste video educativo explora el concepto de triángulos similares, presentando dos tipos de problemas: triángulos conectados y triángulos superpuestos. Se explica cómo determinar la relación de escala constante entre los lados correspondientes de los triángulos y cómo usar la similitud para resolver problemas. Se destacan técnicas como la división de lados en el mismo triángulo y la utilización de fracciones equivalentes. Además, se abordan problemas prácticos con triángulos conectados y superpuestos, y se muestra cómo aplicar la similitud y las proporciones para encontrar longitudes desconocidas en triángulos.
Takeaways
- 🔍 El vídeo trata sobre triángulos similares y cómo resolver problemas donde los triángulos están conectados o se superponen.
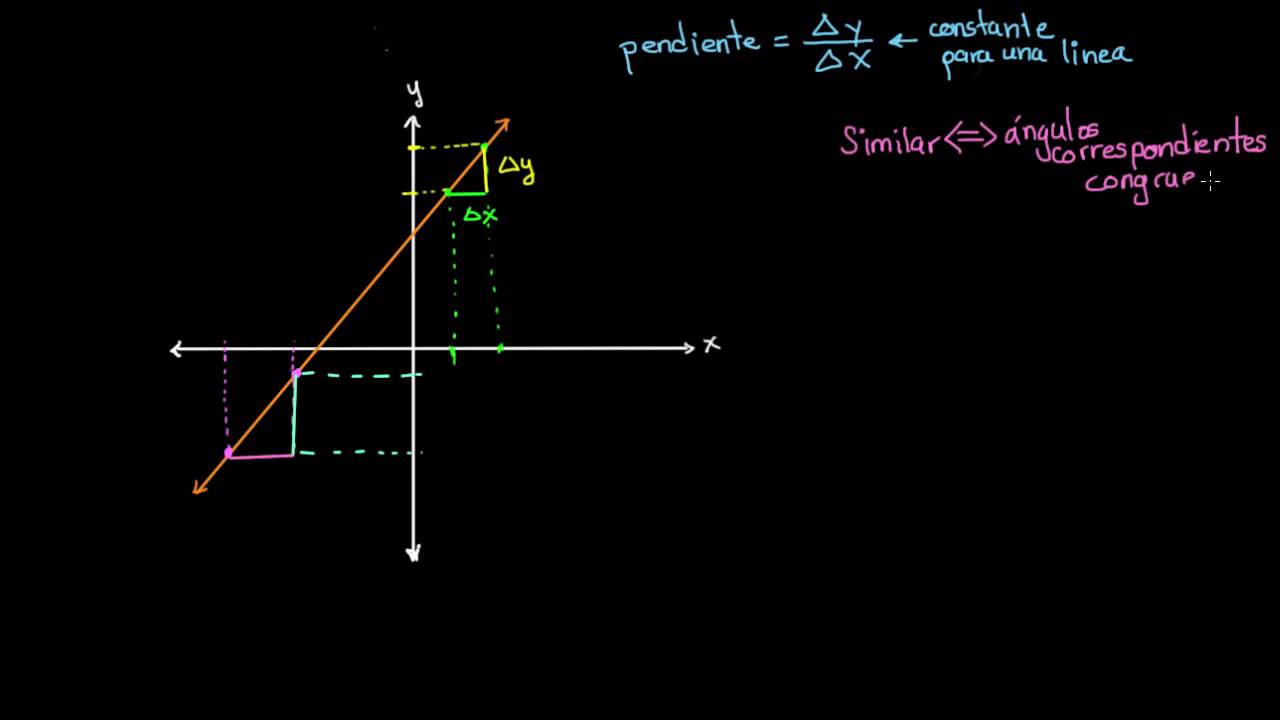
- 🔄 Para que dos triángulos sean similares, deben tener una relación de escalado constante entre sus lados correspondientes.
- 📏 El factor de escala se puede encontrar dividiendo los lados correspondientes de los triángulos, y siempre dará el mismo valor.
- ↔️ El factor de escala también se puede encontrar al dividir los lados dentro del mismo triángulo, siempre que se dividan de manera consistente.
- 🔼 Al resolver problemas con triángulos similares, se pueden utilizar ángulos verticalmente opuestos y ángulos alternos para demostrar la similitud.
- 📐 La similitud de triángulos se puede demostrar al superponer triángulos y comparar los ángulos correspondientes.
- 🔢 Para encontrar valores desconocidos en triángulos similares, se establecen fracciones de lados correspondientes y se resuelven ecuaciones.
- 📏 En problemas donde los triángulos se superponen, se identifican las longitudes de los lados correspondientes y se resuelven ecuaciones para encontrar longitudes desconocidas.
- 💡 Es importante ser consistente al establecer fracciones al inicio de un problema, ya que afecta la resolución de la ecuación.
- 📋 En problemas con ratios dados, se pueden asignar longitudes ficticias a los lados en proporción para facilitar el cálculo de longitudes desconocidas.
Q & A
¿Qué son los triángulos similares y cómo se definen?
-Los triángulos similares son dos triángulos que tienen las mismas proporciones y las mismas formas, pero no necesariamente el mismo tamaño. Se definen por tener un factor de escala constante para la ampliación o reducción de uno a otro, y por tener todos sus ángulos correspondientes iguales.
¿Cómo se determina si dos triángulos son similares?
-Para determinar si dos triángulos son similares, se verifica que sus ángulos correspondientes sean iguales y que la proporción de sus lados correspondientes sea constante. Esto se puede hacer dividiendo los lados correspondientes de uno de los triángulos por los lados correspondientes del otro triángulo y ver si el resultado es el mismo para todos los pares de lados.
¿Qué es el factor de escala de amplificación y cómo se calcula?
-El factor de escala de amplificación es el número por el cual se multiplica el lado de un triángulo para obtener el lado correspondiente en el otro triángulo similar. Se calcula dividiendo un lado del triángulo más grande por el lado correspondiente del triángulo más pequeño.
Si dos triángulos son similares, ¿qué relación tienen sus lados?
-Si dos triángulos son similares, los lados correspondientes están en la misma proporción, lo que significa que si se toma cualquier par de lados en uno de los triángulos y se divide el lado más grande entre el lado más pequeño, el resultado será el mismo que para cualquier otro par de lados en los triángulos.
¿Cómo se resuelven problemas donde los triángulos están conectados?
-Para resolver problemas donde los triángulos están conectados, se identifican los lados correspondientes y se establecen las relaciones de proporción utilizando el factor de escala de amplificación. Luego, se resuelven las ecuaciones para encontrar los valores desconocidos, asegurándose de que los factores de escala se apliquen consistentemente.
En problemas donde los triángulos se solapan, ¿cómo se demuestra que son similares?
-En problemas donde los triángulos se solapan, se demuestran similares al mostrar que tienen todos los ángulos correspondientes iguales, ya sea por ser ángulos alternos o por tener lados paralelos que forman ángulos verticales opuestos.
¿Cómo se utilizan las proporciones para encontrar lados desconocidos en triángulos similares?
-Se establecen fracciones con los lados correspondientes y se resuelven las ecuaciones para encontrar los lados desconocidos. Es importante ser consistente en la selección de lados para las fracciones, ya sea siempre poniendo el triángulo más pequeño en la parte superior o siempre en la parte inferior.
¿Qué sucede si se tiene una relación de longitudes dada en un problema de triángulos similares?
-Si se tiene una relación de longitudes dada, como 5 a 4, se puede asumir una longitud para cada lado en proporción y luego se utilizan estas longitudes para establecer fracciones y resolver las ecuaciones para encontrar los lados desconocidos.
¿Cómo se abordan los problemas donde los triángulos tienen longitudes totales conocidas y partes desconocidas?
-Se identifican las longitudes totales y se establecen ecuaciones para las partes desconocidas, utilizando las proporciones de los lados correspondientes de los triángulos similares. Se resuelven estas ecuaciones para encontrar los valores de las longitudes desconocidas.
¿Cómo se pueden usar las fracciones para resolver problemas de triángulos similares?
-Las fracciones se usan para establecer relaciones de proporción entre los lados correspondientes de los triángulos similares. Se forman fracciones con los lados y se resuelven las ecuaciones resultantes para encontrar los valores desconocidos, asegurándose de que las fracciones sean consistentes en su estructura.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)