Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration | Week 8 | SCIENCE 9 - QUARTER 1 (MELC 5)
Summary
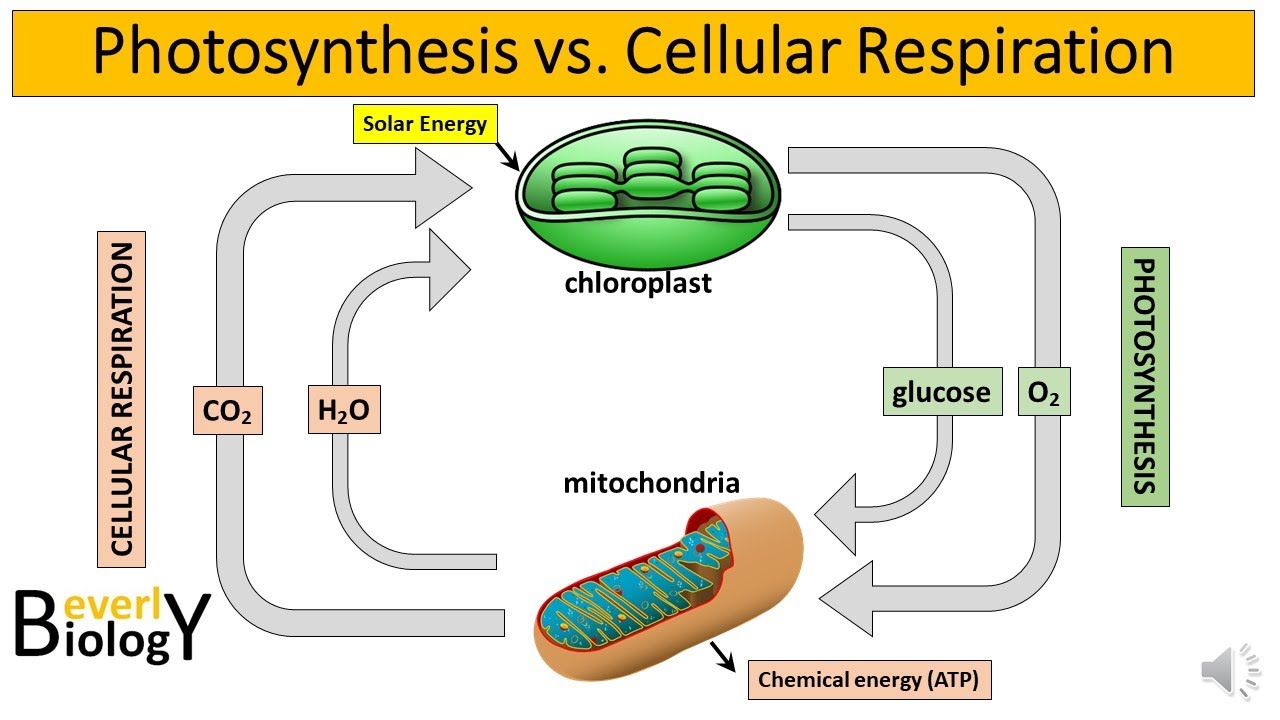
TLDRIn this educational video, Sir Emman, a public school science teacher, explores the fundamental processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration, essential for understanding energy conversion in living organisms. He explains that photosynthesis, occurring in plants, algae, and certain bacteria, uses sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. Cellular respiration, on the other hand, takes place in all living cells, particularly in mitochondria, where glucose and oxygen are broken down to release energy in the form of ATP. The video contrasts these processes, highlighting their significance in sustaining life and the environment.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight into chemical energy in the form of sugar or carbohydrates.
- 🏃♂️ Cellular respiration is the process by which all living organisms break down complex molecules like sugar to release energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
- 🌞 The primary source of energy for life on Earth is the sun, which powers both photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
- 🍃 Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts, the organelles in plant cells that contain the pigment chlorophyll, which absorbs light.
- 🔋 Cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria, often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell, where energy is released from sugar molecules.
- 🌿 Autotrophs, such as plants, are capable of producing their own food through photosynthesis, while heterotrophs rely on consuming other organisms for energy.
- 🔄 Photosynthesis consists of two stages: the light-dependent reaction, which requires sunlight and produces ATP and NADPH, and the light-independent reaction (Calvin cycle), which uses these molecules to produce sugar.
- ♻️ Cellular respiration involves several steps, including glycolysis, pyruvate processing, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain, to convert sugar and oxygen into ATP, carbon dioxide, and water.
- 🌐 Both photosynthesis and cellular respiration are essential for the balance of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the atmosphere, contributing to the Earth's ecosystems.
- 🔬 Understanding these two processes is crucial for learning about energy transfer and the role of plants in sustaining life on Earth.
Q & A
What is the essential learning competency in science for the topic of photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
-The essential learning competency is to differentiate the basic features and importance of photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
What is the primary source of energy required for performing various activities?
-The primary source of energy required for performing activities is the sun, which provides energy through sunlight.
What are autotrophs and how are they related to photosynthesis?
-Autotrophs are organisms, like plants, some bacteria, and algae, capable of making their own food through the process of photosynthesis.
What is the role of chlorophyll in the process of photosynthesis?
-Chlorophyll is the pigment in chloroplasts that absorbs light energy and gives plants their green color; it plays a crucial role in the photosynthesis process.
What are the reactants and products of the photosynthesis process?
-The reactants in photosynthesis are carbon dioxide, water, and light energy, while the products are sugar (glucose) and oxygen.
What are the two stages of photosynthesis and what happens in each?
-The two stages of photosynthesis are the light-dependent reaction, which occurs in the thylakoid membranes and produces ATP and NADPH, and the light-independent reaction (Calvin cycle), which occurs in the stroma and uses ATP and NADPH to produce carbohydrates.
How does cellular respiration differ from photosynthesis in terms of where it occurs?
-Cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria of all living cells, unlike photosynthesis, which occurs in the chloroplasts of plants, algae, and photosynthetic bacteria.
What is the purpose of cellular respiration?
-The purpose of cellular respiration is to break down complex molecules like sugar to release energy in the form of ATP.
What are the reactants and products of the cellular respiration process?
-The reactants in cellular respiration are sugar and oxygen, and the products are carbon dioxide, water, and energy in the form of ATP.
What are the different stages of cellular respiration?
-The stages of cellular respiration are glycolysis, pyruvate processing (oxidation), the Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle), and the electron transport chain.
How do photosynthesis and cellular respiration relate to each other in the context of energy?
-Photosynthesis converts sunlight into chemical energy stored in sugar, while cellular respiration breaks down sugar to release energy in the form of ATP, thus they are complementary processes in the energy cycle.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Grade 9 Science Q1 Ep 8 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Part 2

مسابقة موهوب - (علوم الأحياء): الطاقة الخلوية

ATP - ADENOSINA TRIFOSFATO - ESTRUTURA E FUNÇÃO | Biologia com Samuel Cunha

Science 9: Cellular respiration and its difference from Photosynthesis (Tagalog-English Format)
Photosynthesis vs Cellular Respiration

Introduction to Bioenergetics | Bioenergetics overview | Class 11
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
