Mekanisme Kontraksi Otot Rangka
Summary
TLDRAlfatir, a student from class 2B, explains the mechanism of muscle contraction in the skeletal system. Muscle contraction occurs when muscles receive signals from the nervous system, leading to movement. Muscle fibers contain myofibrils, which are composed of thick (myosin) and thin (actin) filaments. The interaction between these filaments, powered by ATP, results in muscle shortening and movement. The process is regulated by calcium ions, with neurotransmitters like acetylcholine triggering the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. This initiates the contraction cycle, illustrating the complex yet fascinating process of how our muscles enable motion.
Takeaways
- 💪 The script explains the mechanism of muscle contraction in the skeletal system.
- 🏋️♂️ Muscle contraction occurs when muscles tighten or shorten to move bones or the skeleton.
- 🧬 Muscle fibers are composed of many myofibrils, which contain sarcomeres.
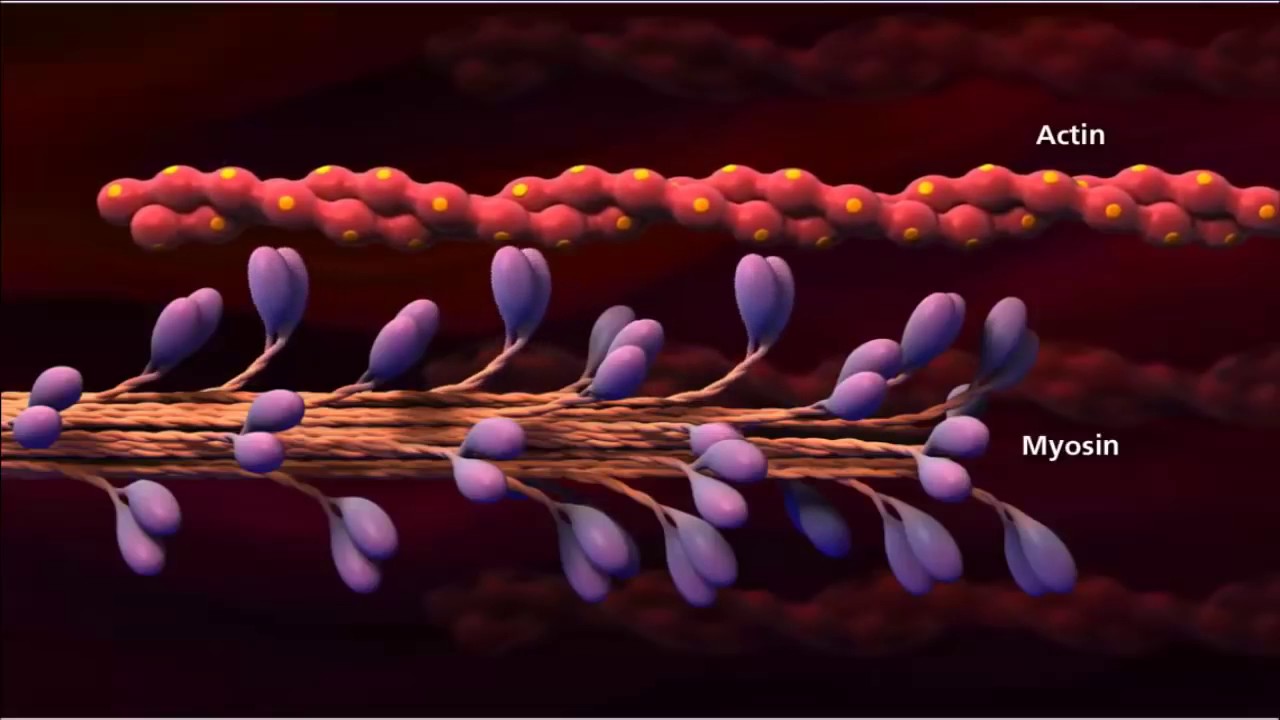
- 🔬 Sarcomeres are made up of thick filaments (myosin) and thin filaments (actin), with the latter also containing regulatory proteins like troponin and tropomyosin.
- 🔋 The contraction process begins when ATP on myosin is hydrolyzed into ADP and a phosphate group, causing myosin heads to bind to actin and form actin-myosin bridges.
- 🔄 This binding and subsequent movement is known as the power stroke, which pulls the thin filaments towards the center of the sarcomere.
- 💡 The release of the phosphate group from myosin allows a new molecule of ATP to bind, enabling the cycle of contraction to continue.
- ⚡ The entire muscle contraction is controlled by calcium ions, which bind to troponin and cause a structural change that activates the myosin heads.
- 🚀 The process is initiated by nerve impulses that cause the release of acetylcholine, leading to the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
- 🧠 The script concludes with a request for corrections if any mistakes are found and a thank you note.
Q & A
What is the process of muscle contraction called?
-The process of muscle contraction is called the 'sliding filament theory', where the actin and myosin filaments slide past each other to cause muscle contraction.
What are the two main types of muscle fibers involved in muscle contraction?
-The two main types of muscle fibers involved in muscle contraction are thick filaments made of myosin and thin filaments made of actin.
What is the role of ATP in muscle contraction?
-ATP (adenosine triphosphate) provides the energy required for the muscle contraction process. It is hydrolyzed to ADP and inorganic phosphate, which leads to the release of energy that powers the muscle contraction.
What is the significance of the Z-line in muscle contraction?
-The Z-line is significant in muscle contraction as it marks the end of one sarcomere and the beginning of another, playing a role in the alignment and structure of the sarcomeres during contraction.
How does the presence of calcium ions affect muscle contraction?
-Calcium ions play a crucial role in initiating muscle contraction by binding to troponin, which then causes a conformational change in tropomyosin, allowing myosin to bind to actin and initiate the contraction process.
What is the role of acetylcholine in the muscle contraction process?
-Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that, when released at the neuromuscular junction, triggers the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which then initiates muscle contraction.
What is the term for the binding of myosin heads to actin filaments during muscle contraction?
-The binding of myosin heads to actin filaments is referred to as 'cross-bridge formation', which is a key step in the muscle contraction process.
What happens to the muscle fibers when they receive a signal from the nervous system?
-When muscle fibers receive a signal from the nervous system, they undergo a change from a relaxed state to a contracted state, which involves the sliding of actin and myosin filaments past each other.
What is the term for the protein that forms the thin filaments in muscle fibers?
-The protein that forms the thin filaments in muscle fibers is called actin, which is part of the sarcomere structure and plays a crucial role in muscle contraction.
How does the power stroke contribute to muscle contraction?
-The power stroke is the phase during muscle contraction where myosin heads pull the actin filaments towards the center of the sarcomere, causing the muscle to shorten and contract.
What is the role of troponin and tropomyosin in the regulation of muscle contraction?
-Troponin and tropomyosin are regulatory proteins that control muscle contraction by blocking or allowing myosin binding sites on actin. Their conformation changes in response to calcium ion binding, which in turn regulates the interaction between actin and myosin.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Sistem gerak pada manusia part 2 - Biologi kelas 11 SMA

CONTRAÇÃO MUSCULAR (FISIOLOGIA DE GUYTON) - FISIOLOGIA DA CONTRAÇÃO MUSCULAR - MÚSCULO ESQUELÉTICO
3. Muscle contraction detail Concept Cell Biology

🫀 FISIOLOGIA DO MÚSCULO CARDÍACO: CONTRAÇÃO DO MÚSCULO CARDÍACO | MK Fisiologia

Cellule musculaire : organisation - SVT - SANTÉ Term spé #7 - Mathrix

Mekanisme Kontraksi Otot Rangka
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
