Pricing and billing
Summary
TLDRGoogle Cloud offers per-second billing for services like Compute Engine, Google Kubernetes Engine, Dataproc, and App Engine flexible environment VMs. It provides sustained-use discounts for long-running instances and custom VM types for cost optimization. Users can set budgets and alerts to manage expenses, with visual reporting tools available in the Google Cloud Console. Quotas, including rate and allocation types, prevent over-consumption of resources, ensuring both account and community protection.
Takeaways
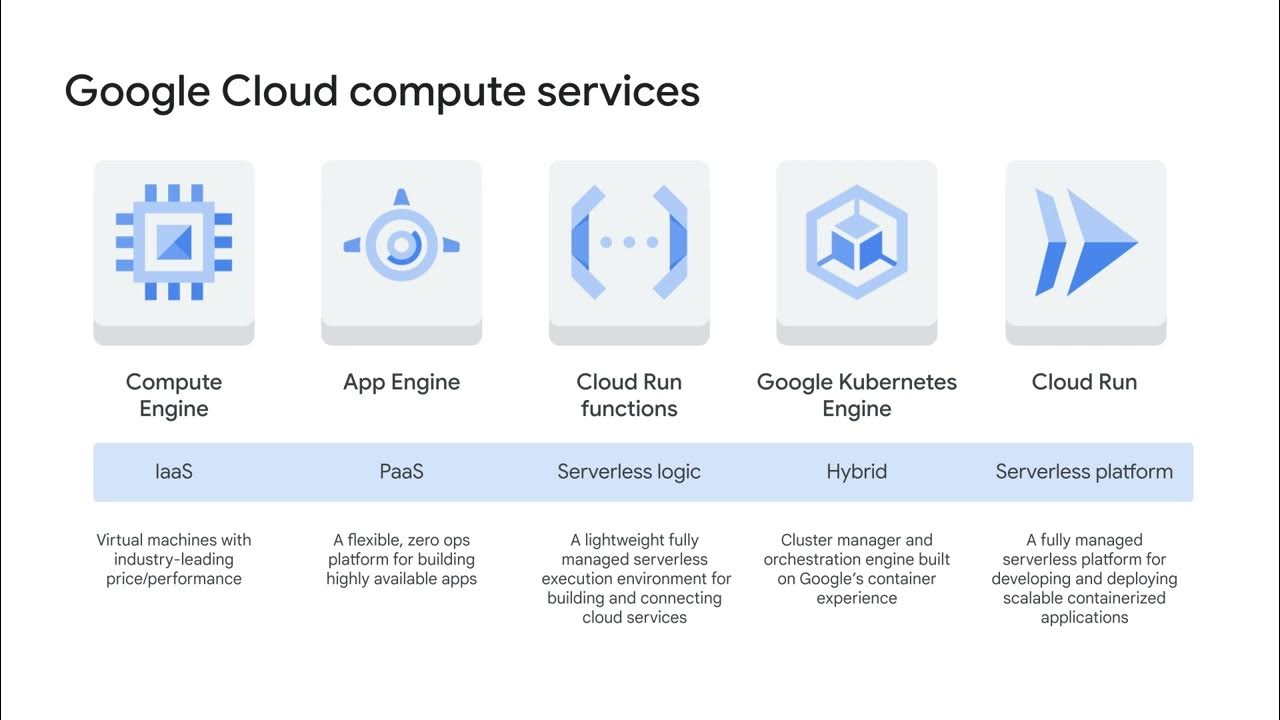
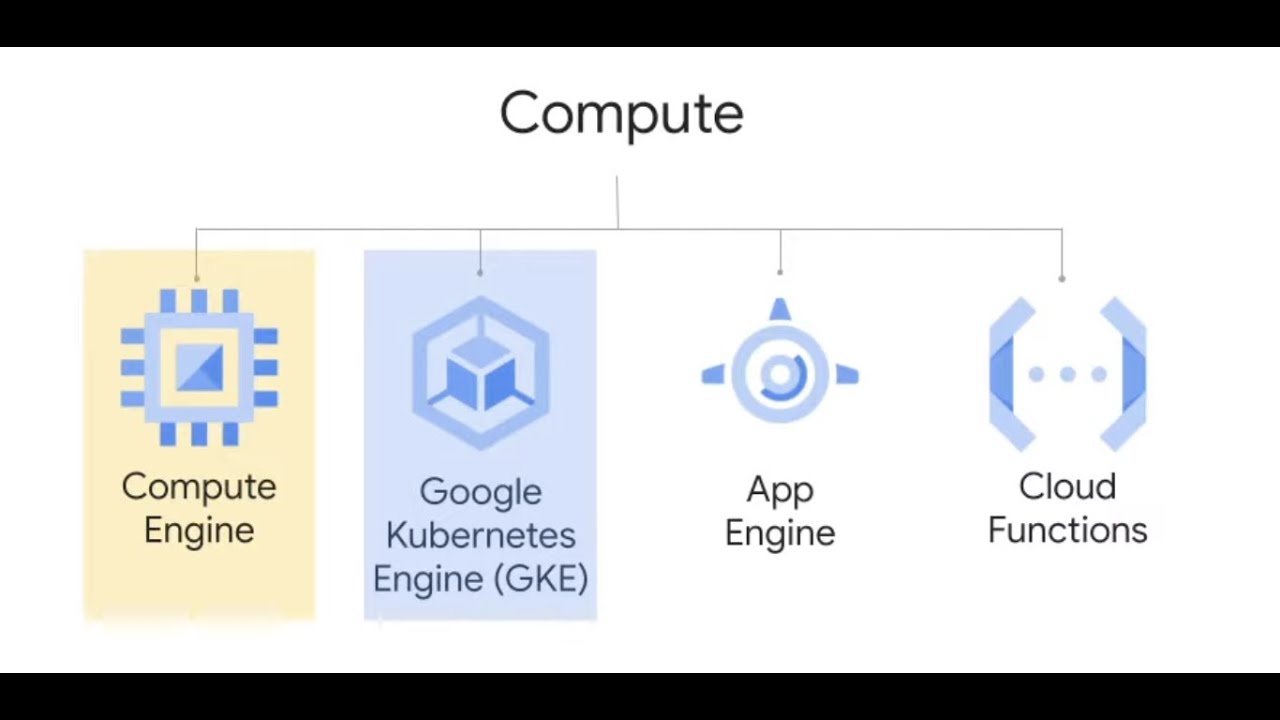
- 💲 Google Cloud was the first to offer per-second billing for its Compute Engine, Google Kubernetes Engine, Dataproc, and App Engine flexible environment VMs.
- ⏱️ Compute Engine provides sustained-use discounts automatically when a virtual machine runs for more than 25% of the billing month.
- 🛠️ Custom virtual machine types in Compute Engine allow for fine-tuning of vCPU and memory to optimize pricing for specific workloads.
- 💡 Google's online pricing calculator is available to estimate costs at cloud.google.com/products/calculator.
- ⚠️ To prevent unexpected high bills, Google Cloud allows setting budgets at the account or project level, with alerts for when costs approach the limit.
- 🔔 Budget alerts can be customized and are typically set at 50%, 90%, and 100% of the budget limit.
- 📊 The Reports tool in Google Cloud Console visually tracks expenditure based on projects or services.
- 🚦 Quotas in Google Cloud are in place to prevent over-consumption of resources, protecting both users and the platform from errors or attacks.
- 🔄 Rate quotas in Google Cloud reset after a specific time period, such as 3,000 API calls every 100 seconds for GKE.
- 📈 Allocation quotas limit the number of resources per project, like a maximum of 15 Virtual Private Cloud networks by default, but can be adjusted by request.
Q & A
What is the significance of Google being the first major cloud provider to offer per-second billing?
-Google's introduction of per-second billing for its services such as Compute Engine, Google Kubernetes Engine, Dataproc, and App Engine flexible environment VMs allows for more granular and cost-effective billing, benefiting users by charging only for the exact amount of time they use the services.
What are sustained-use discounts in Google Cloud's Compute Engine?
-Sustained-use discounts are automatic discounts applied when a virtual machine instance is run for more than 25% of a billing month. For every incremental minute beyond this threshold, the user receives a discount, encouraging longer-term usage of resources.
How do custom virtual machine types in Compute Engine help users?
-Custom virtual machine types enable users to configure virtual machines with specific amounts of vCPU and memory tailored to their application needs, allowing for optimal performance and cost efficiency.
What is the purpose of Google Cloud's online pricing calculator?
-The online pricing calculator is a tool that helps users estimate their costs for using Google Cloud services, providing a clear understanding of potential expenses and aiding in budget planning.
How can users prevent unexpected high costs on Google Cloud?
-Users can define budgets at the billing account or project level and set alerts at specific thresholds, such as 90% of the budget limit, to receive notifications before reaching their spending limit.
What is the role of the Reports tool in Google Cloud Console?
-The Reports tool is a visual aid that allows users to monitor their expenditure based on projects or services, helping them to keep track of their spending and make informed decisions about resource usage.
What are the two types of quotas implemented by Google Cloud, and how do they work?
-Google Cloud implements rate quotas and allocation quotas. Rate quotas limit the number of requests to an API within a specific time frame and reset after that period. Allocation quotas control the total number of resources a project can have, such as the default limit of 15 Virtual Private Cloud networks per project.
How can users request an increase in the default quotas set by Google Cloud?
-Users can request an increase in quotas by reaching out to Google Cloud Support, which will consider the request and potentially adjust the limits based on the user's needs and usage patterns.
Why are quotas important in Google Cloud's service structure?
-Quotas are crucial as they prevent over-consumption of resources due to errors or malicious attacks, ensuring that the platform remains stable and secure for all users while also protecting account owners from unexpected high costs.
What is the default rate quota for the GKE service in terms of API calls?
-The default rate quota for the Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) service allows for 3,000 calls to its API from each Google Cloud project every 100 seconds before resetting.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)