Leopold's Maneuver | Return Demonstration
Summary
TLDRIn the video, Sripayna Aquino Maranga demonstrates Leopold's maneuver, a non-invasive method used to determine the position and engagement of a fetus in the uterus after 36 weeks of gestation. The procedure involves four specific maneuvers to palpate the uterus and locate the fetal back and heart tones. The video provides a step-by-step guide, emphasizing the importance of patient comfort, proper handwashing, and infection control. The outcome of the demonstration indicates a cephalic presentation with the baby's head engaged, ideal for labor, and a normal fetal heart rate of 125 beats per minute.
Takeaways
- 🤰 Leopold's maneuver is a systematic palpation technique used to determine the position and presentation of a fetus in the uterus.
- 👩⚕️ It is typically performed after 36 weeks of gestation to prepare for labor and assess the need for a cesarean section.
- 🧼 The procedure requires hand washing and preparation of equipment such as a pillow, towel, and stethoscope to ensure hygiene and comfort.
- 🛌 The patient is positioned supine with a pillow under her head and a towel under her hip to facilitate the examination.
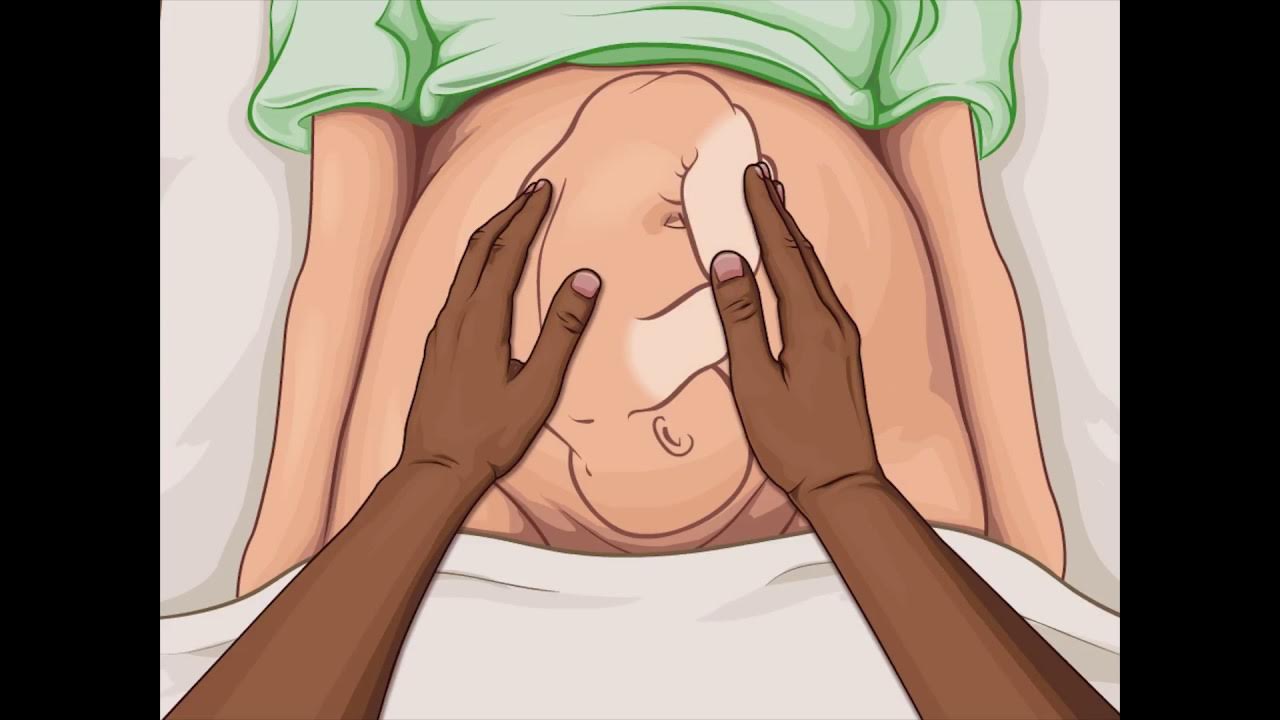
- 🤲 The maneuver consists of four steps: fundal grip, umbilical grip, pollux grip, and pelvic grip, each revealing different aspects of fetal position and engagement.
- 👶 The fundal grip helps to identify if the fetal head or breech is in the upper part of the uterus.
- 🔍 The umbilical grip involves palpating the lateral uterine surface to locate the fetal back or extremities.
- 🤝 The pollux grip is used to determine if the fetal head has engaged in the pelvis.
- 🔎 The pelvic grip confirms the findings of the pollux grip and identifies the presenting part in the hypogastrium.
- 💓 After the maneuvers, the fetal heart tone is located and listened to for at least one minute to assess the baby's well-being.
- 📝 The procedure concludes with the nurse covering the patient, ensuring comfort, and documenting the findings.
Q & A
What is Leopold's maneuver and why is it performed?
-Leopold's maneuver is a systematic palpation technique used to determine the position, presentation, and engagement of the fetus inside the uterus. It is performed after 36 weeks of gestation to help prepare for labor and to assess the need for a cesarean section.
What are the necessary equipment and preparations before performing Leopold's maneuver?
-The necessary equipment includes a pillow, a towel, and a stethoscope. Preparations involve hand washing to prevent infection and ensuring the patient's comfort by having her void before the procedure.
Why is it important to void before Leopold's maneuver?
-Voiding before the maneuver is important as an empty bladder promotes comfort and allows for a more productive examination. A distended bladder can obscure the fetal contour and may slightly deviate the uterus.
How does the patient need to position herself during Leopold's maneuver?
-The patient should be positioned supine with one pillow under her head and a flexed knee, with a towel placed beneath her hip to displace the uterus off the inferior vena cava and aorta, preventing supine hypotensive syndrome.
What is the purpose of the fundal grip in Leopold's maneuver?
-The fundal grip is the first maneuver, where the uterine fundus is palpated to determine which part of the baby is at the upper part of the uterus, such as the fetal head or breech.
How does the umbilical grip help in Leopold's maneuver?
-The umbilical grip involves palpating the lateral uterine surface to determine the fetal back or extremities by applying gentle but deep pressure.
What is the purpose of the pollux grip in the maneuver?
-The pollux grip is used to grasp the lower uterine segment and determine if the fetal head is engaged, providing information about the baby's position in the birth canal.
What does the pelvic grip reveal during Leopold's maneuver?
-The pelvic grip is performed to confirm the findings of the pollux grip and to determine the presenting part in the hypogastrium of the mother, as well as the fetal head position (flexed or extended).
Why is it important to locate the fetal back and listen for the fetal heart tone after the maneuvers?
-Locating the fetal back and listening for the fetal heart tone are important to confirm the baby's position and to ensure the baby's well-being, with a normal heart rate being around 120-160 beats per minute.
What is the significance of the cephalic position mentioned in the script?
-A cephalic position indicates that the baby's head is at the lower part of the uterus and is engaged, which is the ideal position for labor, suggesting a potentially easier delivery.
What is the normal fetal heart rate and what does it indicate?
-A normal fetal heart rate is between 120-160 beats per minute. In the script, a rate of 125 beats per minute indicates that the baby's heart rate is within the normal range, suggesting good fetal health.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

PREFORMING LEOPOLD'S MANEUVERS | SKILLS DEMO
Leopold's Maneuvers - Fundamentals of Fetal Health Surveillance

How to do Obstetric Examination? Leopold Maneuvers | Obs-Gyne Full Course Launched
Fundal Height Measurement by Weeks Nursing Maternity Lecture NCLEX

Video Learning: Pemeriksaan Fisik Ibu Hamil
FERTILISASI DAN PERKEMBANGAN EMBRIO
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
