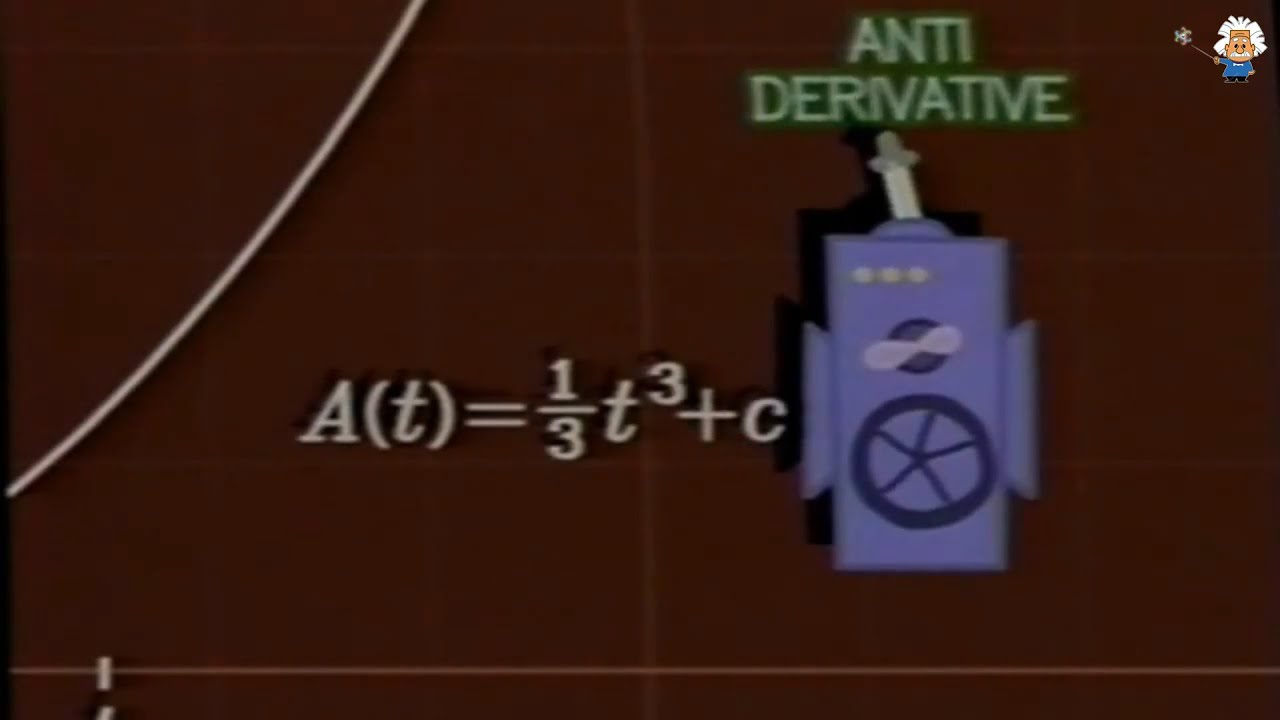The History of Calculus -A Short Documentary | Newton & Leibniz
Summary
TLDRThe history of calculus is a captivating tale that spans over 2,500 years, beginning with ancient Greek mathematicians like Archimedes, who pioneered methods of calculation that resemble early integral and differential calculus. Fast forward to the 17th century, where Isaac Newton and Gottfried Leibniz independently developed the foundations of modern calculus, transforming our understanding of motion and change. Despite controversy over who 'discovered' calculus first, both men are credited with its development. Today, calculus is a fundamental tool in numerous fields, from physics to economics, shaping how we model and solve complex problems involving change.
Takeaways
- 😀 The origins of calculus date back over 2,500 years to ancient Greek mathematicians like Eudoxus and Archimedes, who used methods of exhaustion to calculate areas and volumes.
- 😀 Archimedes developed the method of exhaustion further, deriving formulas for the area of a circle and surface area of a sphere, laying the groundwork for integral calculus.
- 😀 Archimedes also pioneered early forms of differential calculus by calculating the tangent to a curve using a method that involved breaking down motion into radial and circular components.
- 😀 In the 17th century, European mathematicians like Cavaliere, Barrow, Descartes, Fermat, Pascal, and Wallis began discussing derivatives, but the most significant breakthroughs came from Isaac Newton and Gottfried Leibniz.
- 😀 Isaac Newton, in the mid-1600s, developed calculus as a tool to solve problems related to physics, such as motion, gravitation, and planetary orbits.
- 😀 Newton used the concept of the derivative to calculate instantaneous rates of change, referring to it as 'Fluxion.' This concept forms the basis of differential calculus.
- 😀 Newton also discovered that integration is the inverse of differentiation and developed the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, linking the two branches.
- 😀 Integral calculus, as developed by Newton, involves calculating areas under curves by breaking them into thin rectangles, a process that approaches the exact area as the rectangle width approaches zero.
- 😀 Gottfried Leibniz, independently of Newton, developed calculus from a metaphysical perspective, identifying the relationship between integration and differentiation and introducing notation that is still in use today.
- 😀 The controversy over who first discovered calculus between Newton and Leibniz led to both being credited as independent founders, with Leibniz's superior notation being adopted in modern calculus.
- 😀 The advent of calculus revolutionized the way we understand dynamic change and motion in the physical world, impacting fields from physics to economics, medicine, and beyond.
Q & A
What is the method of exhaustion, and how did Archimedes use it?
-The method of exhaustion was an early technique used to find the area or volume of irregular shapes by approximating them with simpler shapes. Archimedes expanded on this method to calculate the area of a circle and the volume of spheres and cones by breaking them down into polygons or smaller segments, leading to more accurate approximations.
How did Archimedes' work foreshadow integral and differential calculus?
-Archimedes’ use of the method of exhaustion and his calculations of areas under curves and tangents to curves resembled integral and differential calculus. His approach to finding the area under a parabola and his method for calculating the tangent to a spiral anticipated later developments in both fields.
What is the significance of Cavalieri's principle in the development of calculus?
-Cavalieri's principle, developed in the 1630s, was an early form of integral calculus. It stated that if two solids of equal height and equal cross-sectional area are placed on the same plane, their volumes are equal. This principle built on Archimedes' work and laid the groundwork for understanding how to calculate areas and volumes using infinitesimally small sections.
How did Isaac Newton contribute to the development of calculus?
-Isaac Newton developed the concept of *fluxions*, or derivatives, as a way to calculate instantaneous rates of change. This allowed him to describe the motion of objects, the acceleration of falling bodies, and planetary orbits, marking a significant breakthrough in both mathematics and physics. He also formulated the fundamental theorem of calculus, which links differentiation and integration.
Why did Newton create calculus, and what specific problem was he trying to solve?
-Newton created calculus to solve problems in physics, specifically to explain the motion of objects under gravity and the orbits of planets. He needed a mathematical framework to describe the changing velocities of falling objects and to understand why planets moved in elliptical orbits, which couldn't be explained by existing mathematical methods.
What was the core difference between Newton's and Leibniz's approaches to calculus?
-Newton’s approach to calculus, called *fluxions*, focused on the rate of change of quantities and used the concept of instantaneous change. Leibniz, on the other hand, introduced the concept of infinitesimally small quantities and used notation that is still in use today, such as the integral sign and the derivative notation (d/dx).
What role did Gottfried Leibniz play in the development of calculus?
-Leibniz independently developed calculus around the same time as Newton but published his work first. He introduced the modern notation for derivatives and integrals and focused on the metaphysical idea of infinitesimal quantities. His contributions were pivotal in formalizing calculus and establishing its standard notation.
What was the controversy between Newton and Leibniz regarding the discovery of calculus?
-The controversy arose because both Newton and Leibniz independently developed calculus but at different times, with Leibniz publishing his work first. A dispute ensued over who deserved credit, with Newton’s followers accusing Leibniz of plagiarism. Eventually, it was acknowledged that both men had made independent and significant contributions to the field.
How did calculus revolutionize mathematics and science?
-Calculus revolutionized mathematics by providing a new way to model and understand dynamic systems and changes in the world, such as motion, growth, and decay. It allowed scientists and engineers to make precise calculations in physics, astronomy, biology, economics, and many other fields, laying the foundation for modern science and technology.
What is the fundamental theorem of calculus, and why is it important?
-The fundamental theorem of calculus states that differentiation and integration are inverse operations. This means that the process of taking a derivative (finding the rate of change) and then integrating it (finding the accumulated quantity) will return the original function. This theorem forms the core of calculus, linking the two main branches and enabling more advanced problem-solving.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)