GCSE Biology - Respiration #21
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the different types of respiration and their importance in energy transfer within living organisms. It explains cellular respiration as an exothermic reaction that releases energy from glucose, highlighting the role of aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration, which requires oxygen, occurs in mitochondria and efficiently produces energy. Anaerobic respiration, occurring without oxygen, is less efficient and produces lactic acid. The video also covers anaerobic respiration in plants and yeast, where glucose is converted to ethanol and carbon dioxide, useful in processes like fermentation for bread, beer, and wine production.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Cellular respiration is an exothermic reaction that transfers energy from glucose, continuously occurring in living cells.
- 🌱 Glucose, which plants produce during photosynthesis, is the primary source of energy for organisms.
- ⚡ Energy from cellular respiration is used to build larger molecules, enable muscular contraction, and maintain body temperature.
- 💡 Metabolism is the sum of all chemical processes in a living organism, including those requiring and not requiring energy.
- 🫁 Aerobic respiration, occurring in the presence of oxygen, is the most efficient way to transfer energy from glucose.
- 🏃♂️ Anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen and results in the formation of lactic acid, which is less efficient and leads to lactic acid buildup.
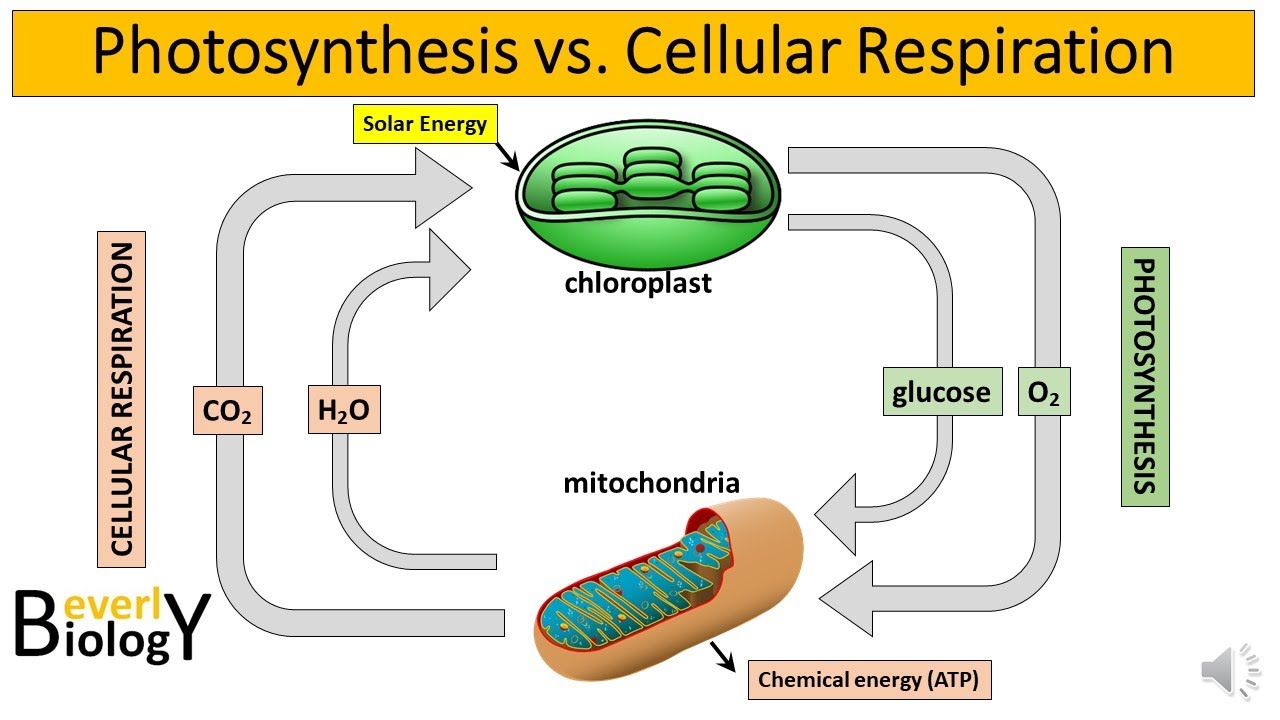
- 🧬 The word equation for aerobic respiration is glucose + oxygen -> carbon dioxide + water, which is the reverse of photosynthesis.
- 🍞 Anaerobic respiration in plants and yeast converts glucose to ethanol and carbon dioxide, a process known as fermentation.
- 🍺 Fermentation in yeast is utilized in the production of bread, beer, and wine due to the carbon dioxide and ethanol it produces.
- 🏋️♀️ Anaerobic respiration is used in situations where oxygen supply is insufficient, such as intense exercise.
Q & A
What is cellular respiration and why is it important?
-Cellular respiration is an exothermic reaction that transfers energy from glucose, which is continuously occurring in living cells. It is important because it provides the energy necessary for various cellular processes.
How is energy from glucose utilized by organisms?
-Energy from glucose is used to build larger molecules from smaller ones, such as combining amino acids to form proteins, for muscular contraction, and for maintaining body temperature.
What is the difference between energy being 'released' and 'made' during respiration?
-During respiration, energy is not made but transferred from glucose molecules. The term 'exothermic' refers to the reaction releasing energy.
What is metabolism?
-Metabolism is the combination of all chemical processes that occur within a living organism to maintain life, including reactions that require energy and those that do not.
What are the two types of respiration?
-The two types of respiration are aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration.
What conditions are necessary for aerobic respiration?
-Aerobic respiration requires the presence of oxygen and is the most efficient way to transfer energy from glucose.
What is the word equation for aerobic respiration?
-The word equation for aerobic respiration is glucose plus oxygen goes to form carbon dioxide plus water.
How is anaerobic respiration different from aerobic respiration?
-Anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen and is less efficient because it results in the incomplete breakdown of glucose, producing lactic acid instead of carbon dioxide and water.
Why do organisms prefer not to use anaerobic respiration?
-Organisms prefer not to use anaerobic respiration because it is inefficient and results in the buildup of lactic acid, which must be removed later.
What is fermentation and how is it utilized in industry?
-Fermentation is the anaerobic respiration process in yeast where glucose is converted to ethanol and carbon dioxide. It is used in industry to produce bread, beer, and wine, with carbon dioxide making bread light and fluffy and ethanol being the alcohol in beer and wine.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Introduction to Bioenergetics | Bioenergetics overview | Class 11
Photosynthesis vs Cellular Respiration

Gaseous Exchange | Chapter # 10 | Biology Class 10th|Lec#1

PIRAMIDA EKOLOGI

Carbohydrates | A type of biological molecule | Functions and Classification

Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration | Week 8 | SCIENCE 9 - QUARTER 1 (MELC 5)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
