Risk Analysis - CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 - 5.2
Summary
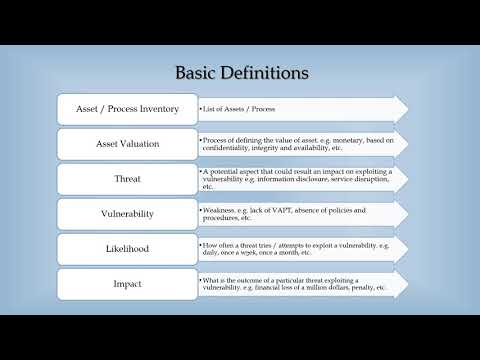
TLDRThis script discusses methods for assessing risk levels, introducing both qualitative and quantitative risk assessments. It explains the use of a traffic light grid to visually represent risk levels and delves into the calculation of Annualized Rate of Occurrence (ARO), Asset Value (AV), Exposure Factor (EF), Single-Loss Expectancy (SLE), and Annualized Loss Expectancy (ALE). The importance of considering life, property, safety, and financial impacts is emphasized, along with the concepts of risk appetite and risk tolerance. The script also highlights the role of a risk register in documenting and managing project risks.
Takeaways
- 📊 Risk assessment involves evaluating various factors and can be done qualitatively or quantitatively.
- 🚦 A qualitative risk assessment uses a traffic light grid to categorize risks as low, medium, or high.
- 🔍 Individual risk factors are assessed for their impact, annualized rate of occurrence, and cost of controls.
- 💡 The overall risk level is determined by combining the individual factors' assessments.
- 💻 Legacy Windows clients are an example where the risk might be medium to high due to the need for updates.
- 📚 Untrained staff is another risk factor, with a low to medium overall risk depending on the impact and occurrence.
- 🛡 Devices without antivirus software pose a high risk due to medium impact and a large rate of occurrence.
- 🔢 Quantitative risk assessment uses specific values like Annualized Rate of Occurrence (ARO) and Asset Value (AV).
- 💰 The Single-Loss Expectancy (SLE) and Annualized Loss Expectancy (ALE) are calculated to determine financial risk.
- 🏢 Risk calculations consider the impact on life, property, safety, and finances.
- 🚦 Likelihood and probability are used to measure the chance of a risk occurring, with qualitative and quantitative measures.
- 🚫 Organizations have a risk appetite and risk tolerance, which define the level of risk they are willing to accept.
- 📋 A risk register documents the risks associated with a project, detailing each risk and providing solutions.
- 🔑 Assigning risk owners and determining risk thresholds are part of managing risks in a project.
Q & A
What is a qualitative risk assessment?
-A qualitative risk assessment evaluates individual risk factors and their criteria, often displayed in broad terms such as low, medium, or high risk.
How can a traffic light grid be used in risk assessment?
-A traffic light grid can be used to show the risk levels (low, medium, high) for different categories, helping to visualize and prioritize areas of concern.
What is the significance of marking the annualized rate of occurrence in red?
-Marking the annualized rate of occurrence in red signifies a high value, indicating that the risk occurs frequently and requires urgent attention.
What does an asset value (AV) represent in risk assessment?
-Asset value (AV) represents the value of an asset to the organization, which may include replacement costs, impact on sales, fines, and other associated costs.
How is a single-loss expectancy (SLE) calculated?
-Single-loss expectancy (SLE) is calculated by multiplying the asset value (AV) by the exposure factor (EF), which represents the percentage of value lost due to a risk.
What does the annualized loss expectancy (ALE) indicate?
-Annualized loss expectancy (ALE) indicates the expected monetary loss over a year, calculated by multiplying the annualized rate of occurrence (ARO) by the single-loss expectancy (SLE).
Why are both qualitative and quantitative risk assessments important?
-Both types of assessments are important because they consider different aspects of risk, with qualitative assessments focusing on broad impacts and quantitative assessments on specific financial costs.
What is risk appetite and how does it differ from risk tolerance?
-Risk appetite is the level of risk an organization is willing to accept, while risk tolerance is the acceptable variance around that appetite. Risk tolerance is usually broader than risk appetite.
How can a risk register be useful in project management?
-A risk register documents individual risks associated with a project, detailing key risk indicators, assigning owners, and providing solutions to manage and mitigate these risks.
What is the purpose of assigning an owner to each risk in the risk register?
-Assigning an owner to each risk ensures accountability and responsibility, helping to manage and mitigate the risk effectively.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)