Állati és növényi szövetek
Summary
TLDRThis lesson provides a detailed overview of animal and plant tissues, explaining the key differences and functions. Animal tissues are categorized into epithelial, connective, supporting, muscle, and nervous tissues, each playing specific roles like protection, movement, and coordination. In plants, tissues are divided into dividing and permanent types, with functions ranging from growth and protection to transport and storage. The video covers the evolution of tissue types across organisms, highlighting their unique structures and roles in survival, from simple colonial organisms to complex vertebrates and plants.
Takeaways
- 😀 Tissues are sets of cells with similar shape, origin, and function, working together for a common goal in both plants and animals.
- 😀 Algae and mosses represent more primitive forms of plant body structure, as they don't have well-developed tissues like gymnosperms and angiosperms.
- 😀 Sponges in the animal kingdom have pseudotissues, while animals like jellyfish have early forms of real tissues.
- 😀 Animal tissues are categorized into four main types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissues.
- 😀 Epithelial tissue in animals primarily serves a protective function, with variations such as squamous and cylindrical epithelium, and can be single-layered or multi-layered.
- 😀 Connective tissues include blood (which transports hormones and nutrients), adipose tissue (which stores energy and provides insulation), and fibrous tissues (which connect organs and support movement).
- 😀 Supporting tissues in animals, such as cartilage and bone, provide structural support, with bone tissue being both elastic (organic) and hard (inorganic due to calcium and phosphorus).
- 😀 Muscle tissue is crucial for movement, with smooth muscle (found in internal organs), striated muscle (in skeletal muscles), and cardiac muscle (found in the heart).
- 😀 Nervous tissue helps animals perceive and respond to stimuli, with neurons playing a central role in communication within the body.
- 😀 In plants, tissues are divided into dividing tissues (which enable growth) and permanent tissues (which perform specialized functions like protection, transport, and storage).
Q & A
What is the definition of tissue in biological terms?
-A tissue is a group of cells that share a similar shape, origin, and function, working together for a common goal. These cells develop from the same cell during the organism's growth.
Which plants and animals have not developed true tissues, and what is their structural level?
-Among plants, algae and mosses have not developed true tissues and remain at the colonial or filamentous body structure level. Among animals, sponges have a pseudotissue structure, which is similar to the colonial organization seen in primitive plants.
What are the four main categories of animal tissues?
-The four main categories of animal tissues are epithelial tissue, connective and supporting tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue.
What are the main characteristics and functions of epithelial tissue?
-Epithelial tissues consist of closely packed cells with almost no intercellular substance. Their main function is protection, forming coverings for external and internal surfaces of the body. They can be classified by shape (squamous, cuboidal, cylindrical) and by layers (single-layered or multi-layered).
What are the different types of connective tissue and their functions?
-Connective tissues include blood (transports substances and connects organs), adipose tissue (stores energy, insulates heat, and cushions organs), loose fibrous connective tissue (provides elasticity and support in organs), and dense fibrous connective tissue (provides high tensile strength, such as in tendons).
How do cartilage and bone tissues differ in structure and function?
-Cartilage tissue consists of cells in small groups embedded in an elastic matrix, providing flexibility and resilience. Bone tissue contains cells arranged in concentric circles around blood vessels, with organic components for elasticity and inorganic salts (calcium and phosphorus) for hardness, giving structural support and protection.
What are the main types of muscle tissue and their roles?
-There are three types: smooth muscle (found in internal organs, involuntary and slow-moving), striated or skeletal muscle (voluntary, strong, and quickly tiring, responsible for movement), and cardiac muscle (found only in the heart, strong and fatigue-resistant, capable of self-stimulation through the sinus node).
What is the function and composition of nervous tissue?
-Nervous tissue detects, processes, and responds to stimuli. It is composed of neurons (nerve cells that transmit impulses) and glial cells (supporting cells that protect and nourish neurons).
What are the two main categories of plant tissues and their general functions?
-Plant tissues are divided into dividing (meristematic) tissues, responsible for growth and forming new cells, and permanent tissues, which specialize in specific functions such as protection, transport, photosynthesis, and storage.
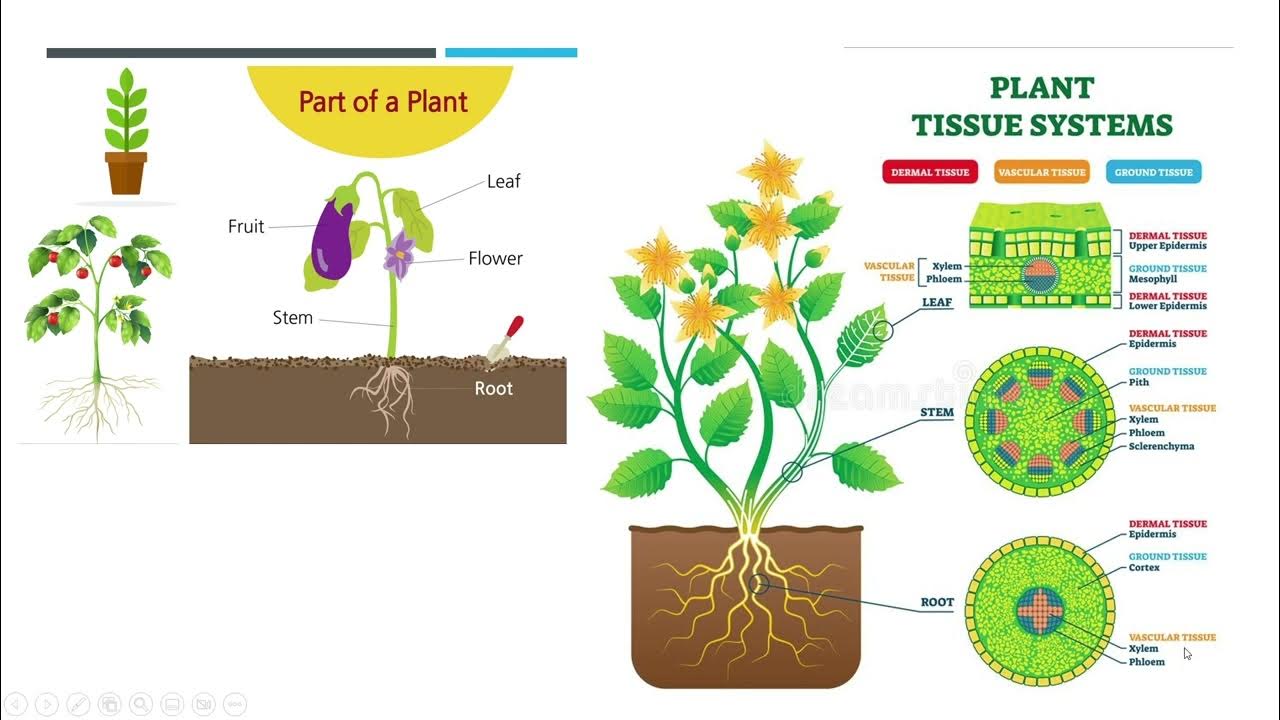
What are the main types of permanent plant tissues and their roles?
-Permanent plant tissues include: skin tissue (protects and allows gas exchange through stomata), transport tissue (xylem transports water and minerals upward; phloem transports organic nutrients), and ground tissue (performs photosynthesis, stores nutrients, provides support, or secretes substances like nectar).
What is the role of the cambium in plants?
-The cambium is a ring of dividing tissue responsible for secondary growth in plants, increasing thickness and forming annual rings in tree trunks.
How do gas exchange openings (stomata) function in plant skin tissue?
-Stomata, controlled by green guard cells, regulate gas exchange by allowing oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass in and out. During the day, plants photosynthesize (taking in CO₂ and releasing O₂), while at night, they primarily respire (taking in O₂ and releasing CO₂).
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

General Biology 1. Cell Types of Plant and Animal Tissues

JARINGAN PADA HEWAN DAN TUMBUHAN | SISTEM ORGANISASI KEHIDUPAN

MERISTEMATIC TISSUE | Characteristic | Apical | Intercalary | Lateral meristem
Module 6: Cell Modifications- General Biology I

GENERAL BIOLOGY 1: Cell Types and Cell Modifications

BAGIAN BAGIAN PENYUSUN SEL TUMBUHAN DAN FUNGSINYA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
