Organel Sel - Kelas XI
Summary
TLDRThis biology lesson focuses on the structure and function of cells, exploring key components such as the plasma membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and organelles like the Golgi apparatus and mitochondria. It delves into the differences between plant and animal cells, explaining their unique organelles and functions. The lesson also highlights processes such as protein synthesis, digestion, and cellular respiration. The video emphasizes the role of various cell structures in maintaining cell function and life processes, with a particular focus on how these systems support cell metabolism and growth.
Takeaways
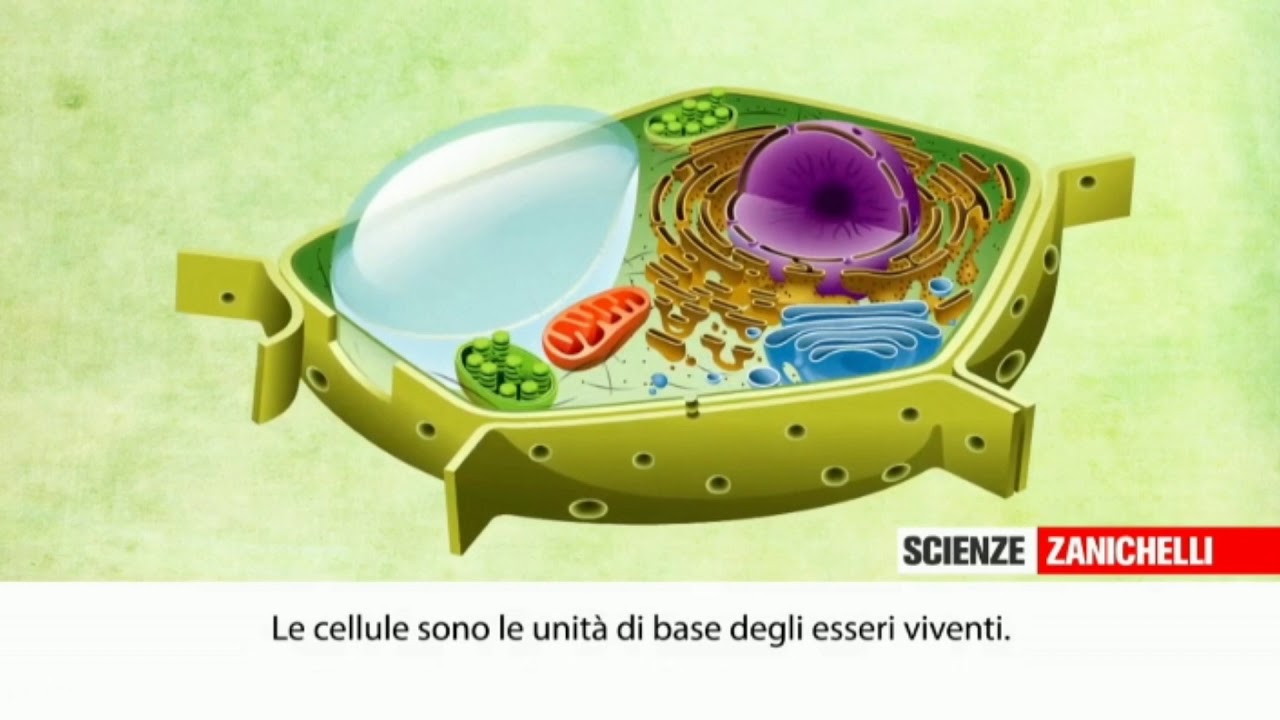
- 😀 Cells contain various organelles with distinct structures and functions, which can be studied through cell fractionation.
- 😀 The cell membrane, composed of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates, serves as a barrier and controls the entry and exit of substances.
- 😀 The fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane explains its dynamic nature, where lipid molecules and proteins can move like liquid.
- 😀 The nucleus controls protein synthesis, stores genetic information in the form of DNA, and regulates cell metabolism.
- 😀 Cytoplasm, the fluid inside the cell, supports organelles, facilitates cellular movement, and stores organic molecules.
- 😀 Ribosomes are crucial for protein synthesis, existing as free or bound ribosomes depending on the destination of the proteins.
- 😀 The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) plays a key role in lipid synthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, and protein synthesis, with both smooth and rough types.
- 😀 The Golgi apparatus is responsible for sorting, packaging, and delivering cell products, including the formation of acrosomes in sperm cells.
- 😀 Lysosomes contain enzymes for intracellular digestion and play a role in processes like autophagy and autolysis, helping break down macromolecules.
- 😀 Mitochondria are energy producers, involved in cellular respiration, and are semi-autonomous due to their own DNA and protein synthesis mechanisms.
- 😀 Plastids, found only in plant cells, are involved in material storage and contain types like leucoplasts and chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
-The cell membrane's primary function is to control the entry and exit of substances into and out of the cell, protect the contents of the cell, and act as a receptor for stimuli from the external environment.
What is the fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane?
-The fluid mosaic model, proposed by J. Singer and G. Nicolson in 1972, describes the plasma membrane as a dynamic structure where lipid molecules and proteins move fluidly like a liquid, with proteins embedded in a bilayer of lipids.
How are the phospholipids in the plasma membrane structured?
-Phospholipids in the plasma membrane have a hydrophilic (water-attracting) phosphate head and hydrophobic (water-repelling) fatty acid tails, arranged in a bilayer with the hydrophilic heads facing outward and the hydrophobic tails facing inward.
What is the function of ribosomes in the cell?
-Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis. They can be free in the cytosol or bound to the endoplasmic reticulum. Free ribosomes synthesize proteins that function in the cytosol, while bound ribosomes synthesize proteins for secretion, incorporation into membranes, or packaging in organelles like lysosomes.
What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in the cell?
-The Golgi apparatus acts as the cell's production center for sorting, packaging, and shipping proteins and lipids. It modifies macromolecules and produces vesicles containing enzymes for secretion, as well as forms acrosomes in sperm cells.
What is the significance of the mitochondria in the cell?
-Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell, responsible for cellular respiration. They generate ATP, the energy currency of the cell, through metabolic processes, particularly in cells with high energy demands like muscle cells.
What is the difference between smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum?
-The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) lacks ribosomes and is involved in lipid synthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, and detoxification, while the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) has ribosomes on its surface and is responsible for protein synthesis.
What are lysosomes, and what is their function?
-Lysosomes are small organelles filled with hydrolytic enzymes that digest macromolecules, such as nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids. They play a crucial role in intracellular digestion, phagocytosis, and recycling damaged organelles (autophagy).
How do peroxisomes function in the cell?
-Peroxisomes contain enzymes like oxidase and catalase that break down fatty acids, neutralize alcohol toxins, and other harmful compounds in liver cells. In plants, they help convert fatty acids into sugars during seed germination.
What is the function of the vacuole in plant cells?
-In plant cells, the vacuole serves several functions, including storing water, organic compounds, inorganic ions, pigments, and toxic substances. It also helps maintain turgor pressure, which is important for cell structure, and serves as a waste disposal system.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)