Distribution of Oceans and Continents | Animated Summary | Fundamentals of Physical Geography Ch 4
Summary
TLDRThis video summarizes Chapter 4 of the Grade 11 NCERT text, 'Distribution of Oceans and Continents.' It covers the Continental Drift Theory proposed by Alfred Wegener, evidence supporting the theory, and the forces behind drifting. It also delves into post-drift studies, ocean floor configuration, sea-floor spreading, plate tectonics, and the various plate boundaries. The video highlights the major and minor plates, explains the different types of plate movements, and explores the movement of the Indian Plate and its impact on Earth's topography, including the formation of the Himalayas and Deccan traps.
Takeaways
- 😀 Alfred Wegener's Continental Drift Theory suggests that all continents were once part of a supercontinent called Pangaea.
- 😀 Pangaea split into two major parts: Laurasia (north) and Gondwanaland (south).
- 😀 Key evidence supporting continental drift includes the jigsaw fit of continents, similar rock ages across oceans, and tillite (glacial deposits) found globally.
- 😀 Placer deposits, like gold in Ghana with source rocks in Brazil, also support the theory of continental drift.
- 😀 Fossils of Mesosaurus, found in Brazil and Africa, indicate that these continents were once connected.
- 😀 Two forces driving continental drift are the Pole Fleeing Force from Earth's rotation and the tidal force from the Sun and Moon's gravitational pull.
- 😀 Post-drift studies include the Convection Current Theory, which suggests that mantle currents caused by radioactive elements create thermal differences.
- 😀 Mapping of the ocean floor revealed that oceanic rocks are much younger than continental rocks, further supporting continental drift.
- 😀 The ocean floor is segmented into three major parts: Continental Margins, Abyssal Plains (deep-sea basins), and Mid-Ocean Ridges.
- 😀 The Sea Floor Spreading Hypothesis proposes that constant volcanic eruptions at mid-ocean ridges cause crust rupture and expansion.
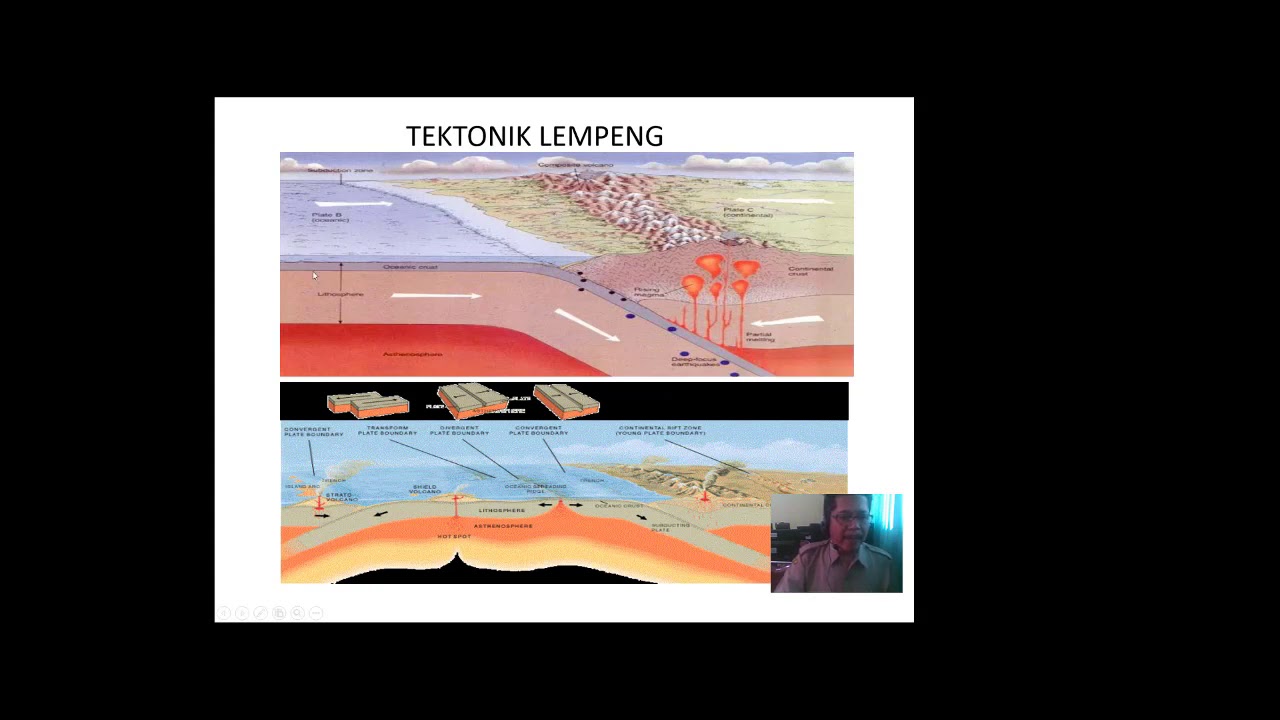
- 😀 The Plate Tectonic Theory states that Earth's lithosphere is divided into major and minor plates, which move over the Earth's mantle.
- 😀 Earthquake and volcanic activity are most common at plate boundaries, such as the Pacific Ring of Fire.
- 😀 Plate movement happens at three types of boundaries: Divergent (plates pull apart), Convergent (plates collide), and Transform (plates slide past each other).
- 😀 Plate movement rates vary, with the Arctic Ridge moving slowly and the East Pacific Rise moving the fastest.
- 😀 The movement of the Indian Plate led to the formation of the Himalayas and the Deccan Traps, as India collided with Eurasia.
Q & A
What is the Continental Drift Theory, and who proposed it?
-The Continental Drift Theory, proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1912, suggests that continents were once joined together as a supercontinent called Pangaea and later drifted apart over time.
What evidence supports the Continental Drift Theory?
-Evidence includes: 1) Continents fitting together like a jigsaw puzzle, 2) Similar-aged rocks across oceans, 3) Tillite deposits from glacial activity found worldwide, 4) Placer deposits of gold in Ghana and Brazil, and 5) Fossils of Mesosaurus found in both Brazil and Africa.
What are the two forces responsible for the drifting of continents?
-The two forces are the Pole Fleeing Force, caused by the Earth's rotation, and the tidal force, which is generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun.
What is the Convectional Current Theory, and how does it relate to continental drift?
-Arthur Holmes' Convectional Current Theory explains that thermal differences in the Earth's mantle, caused by radioactive decay, create currents that drive the movement of tectonic plates, thus contributing to continental drift.
What are the three divisions of the ocean floor?
-The ocean floor is divided into three parts: 1) Continental margins, which transition from continental shores to deep-sea basins, 2) Abyssal plains or deep-sea basins, which are flat plains between continental margins and mid-ocean ridges, and 3) Mid-ocean ridges, the longest submerged mountain chains.
What is Sea Floor Spreading, and what evidence supports this hypothesis?
-Sea Floor Spreading suggests that volcanic eruptions at mid-ocean ridges push apart oceanic crust, causing the sea floor to spread. Evidence includes volcanic eruptions along ridges, similar rock composition equidistant from the ridges, and younger oceanic rocks compared to continental rocks.
What are the three types of plate boundaries?
-The three types of plate boundaries are: 1) Divergent boundaries, where plates pull apart and new crust is formed, 2) Convergent boundaries, where plates collide and one is subducted beneath the other, and 3) Transform boundaries, where plates slide horizontally past one another.
What is the role of the Ring of Fire in relation to plate tectonics?
-The Ring of Fire refers to the area around the Pacific Ocean where frequent volcanic eruptions and earthquakes occur due to active tectonic plate boundaries. It is known for having a large number of volcanoes and seismic activity.
How do the rates of plate movement vary across the globe?
-The rates of plate movement vary, with the slowest movement occurring at the Arctic Ridge and the fastest near the East Pacific Rise, close to Chile.
How did the movement of the Indian Plate affect the Earth's geography?
-The movement of the Indian Plate towards the Eurasian Plate led to the formation of the Himalayas and the Deccan Traps, as India collided with Asia around 225 million years ago, significantly altering the region's geography.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

GEO XI. 1. Indonesia Sebagai Poros Maritim Dunia (Letak & Luas Wilayah Indonesia).

Distribution of Oceans and Continents - Chapter 4 Geography NCERT Class 11

BENUA DAN SAMUDERA |PROSES TERBENTUKNYA BENUA & SAMUDERA|

Unit 3. My Study Habits ~ Chapter 4. My School Activities ~ English for Nusantara Grade VII
IPS KELAS 9 MATERI TEORI TERBENTUKNYA BENUA

Kurikulum Merdeka Rangkuman IPS Kelas 8 Tema 1: Keragaman Alam Indonesia
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
