Vasopressor Drugs (Medical Definition) | Quick Explainer Video
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces vasopressor drugs, medications that increase blood pressure by inducing vasoconstriction, and are crucial for treating hypotension in critically ill patients. It highlights common vasopressors like epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine, and dobutamine, each with distinct mechanisms of action on heart and blood vessels. The importance of cardiovascular drugs in respiratory care is emphasized, as respiratory therapists also manage heart conditions. The video provides a brief overview, encouraging further exploration of related topics through additional resources, making it a helpful educational tool for those studying pharmacology and respiratory therapy.
Takeaways
- 😀 Vasopressor drugs are medications that increase blood pressure by inducing vasoconstriction.
- 😀 Respiratory therapists are trained to care for both heart and lung conditions as these organs work together to deliver oxygenated blood to the body.
- 😀 Vasopressors are typically used to treat moderate to severe hypotension, especially in critically ill patients.
- 😀 Common vasopressor drugs include epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine, and dobutamine.
- 😀 Epinephrine is the vasopressor of choice during CPR and acts on beta 1, beta 2, and alpha receptors to increase heart rate, stroke volume, and cardiac output.
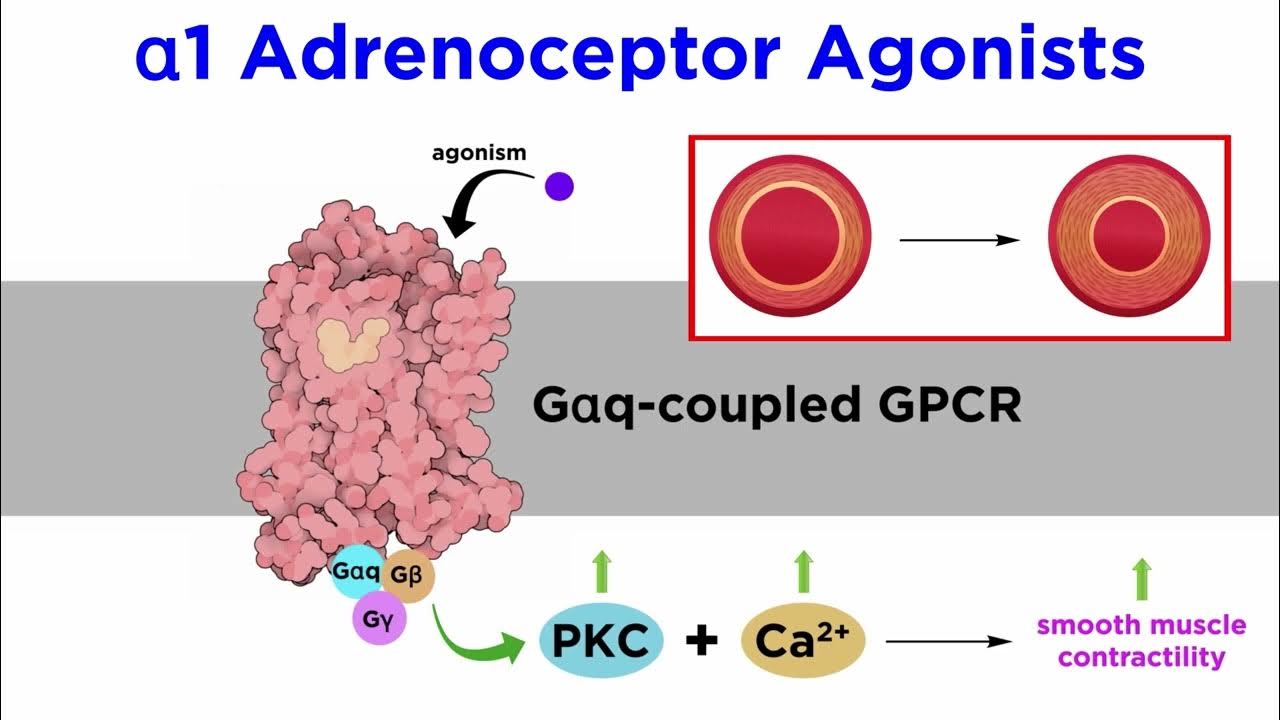
- 😀 Norepinephrine primarily acts on alpha receptors to raise and maintain blood pressure.
- 😀 Dopamine, when administered in high doses, stimulates alpha receptors to cause vasoconstriction and is used for managing shock and bradycardia.
- 😀 Dobutamine stimulates beta receptors to increase stroke volume and cardiac output, promoting vasoconstriction indirectly, but its effect on blood pressure is often unpredictable.
- 😀 Vasopressor drugs can have differing effects on blood pressure due to their varied mechanisms of action on alpha and beta receptors.
- 😀 The video is for educational purposes and encourages viewers to visit respiratorytherapyzone.com for study guides and further resources.
Q & A
What are vasopressor drugs and how do they work?
-Vasopressor drugs are medications that increase blood pressure by inducing vasoconstriction, which helps in raising the blood pressure in patients with hypotension, especially those who are critically ill.
Why is it important for respiratory therapists to understand cardiovascular drugs?
-Respiratory therapists need to understand cardiovascular drugs because the heart and lungs work together to pump oxygenated blood to the body. A dysfunction in one can affect the other, making it essential to be knowledgeable about medications that affect both systems.
What condition are vasopressor drugs typically used to treat?
-Vasopressor drugs are typically used to treat moderate to severe hypotension, which is often seen in critically ill patients.
Can you give an example of a vasopressor drug used during CPR?
-Epinephrine is the vasopressor of choice during CPR. It works by acting on beta and alpha receptors to increase heart rate, stroke volume, and cardiac output.
How do epinephrine and norepinephrine differ in their mechanism of action?
-Epinephrine acts equally on both alpha and beta receptors, resulting in a wider range of effects, while norepinephrine primarily acts on alpha receptors to increase and maintain blood pressure.
What role does dopamine play in managing shock and bradycardia?
-Dopamine, when administered in high doses, stimulates alpha receptors to cause vasoconstriction. It is used for the management of shock and in patients with bradycardia who do not respond to atropine.
Why is dobutamine considered unpredictable in its effect on blood pressure?
-Dobutamine stimulates beta receptors to increase stroke volume and cardiac output. However, it also causes systemic vasodilation, which makes its effect on blood pressure unpredictable, though it is still effective in maintaining mean arterial pressure in hypotensive patients.
What are some other types of cardiovascular drugs that respiratory therapists should be familiar with?
-Other types of cardiovascular drugs that respiratory therapists should be familiar with include inotropic agents, antiarrhythmic agents, vasodilators, and anti-anginal drugs.
What resources are available for those looking to learn more about cardiovascular drugs?
-For those looking to dive deeper into cardiovascular drugs, the video suggests visiting respiratorytherapyzone.com, which offers free study guides, practice questions, and other helpful resources.
What is the main purpose of the video in terms of educating respiratory therapists?
-The main purpose of the video is to provide a brief overview of vasopressor drugs and their importance in treating hypotension and cardiovascular issues, helping respiratory therapists expand their understanding of medications affecting both the heart and lungs.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)