Jaringan pada Hewan dan Tumbuhan | Struktur dan Fungsi Jaringan Hewan dan Tumbuhan - IPA kelas 7
Summary
TLDRThis video covers the structure and function of animal and plant tissues. It explains how multicellular organisms rely on specialized networks of cells to perform vital functions. In animals, tissues like epithelial, connective, muscle, and neural networks serve roles in protection, movement, and communication. Plant tissues, including meristematic and permanent tissues like epidermal, parenchyma, and vascular tissues, support growth, protection, and nutrient transport. The video also delves into how these tissues interact within organisms to ensure their survival, highlighting key functions and examples of each tissue type.
Takeaways
- 😀 Cells in multicellular organisms depend on each other, working together to ensure the organism's survival.
- 😀 Tissues are groups of similar cells that work together to perform specific functions, but cannot be seen with the naked eye.
- 😀 Epithelial tissue protects underlying tissues from mechanical damage, UV radiation, and bacterial attack, and lines body cavities and organs.
- 😀 Connective tissues include supportive, binding, fibrous, and hematopoietic tissues that help provide structure, strength, and immune function.
- 😀 Muscle tissue consists of smooth, skeletal, and heart muscle, each with unique functions in the body, such as movement and circulation.
- 😀 Neural tissue, made up of neurons, is responsible for transmitting electro-chemical signals throughout the body.
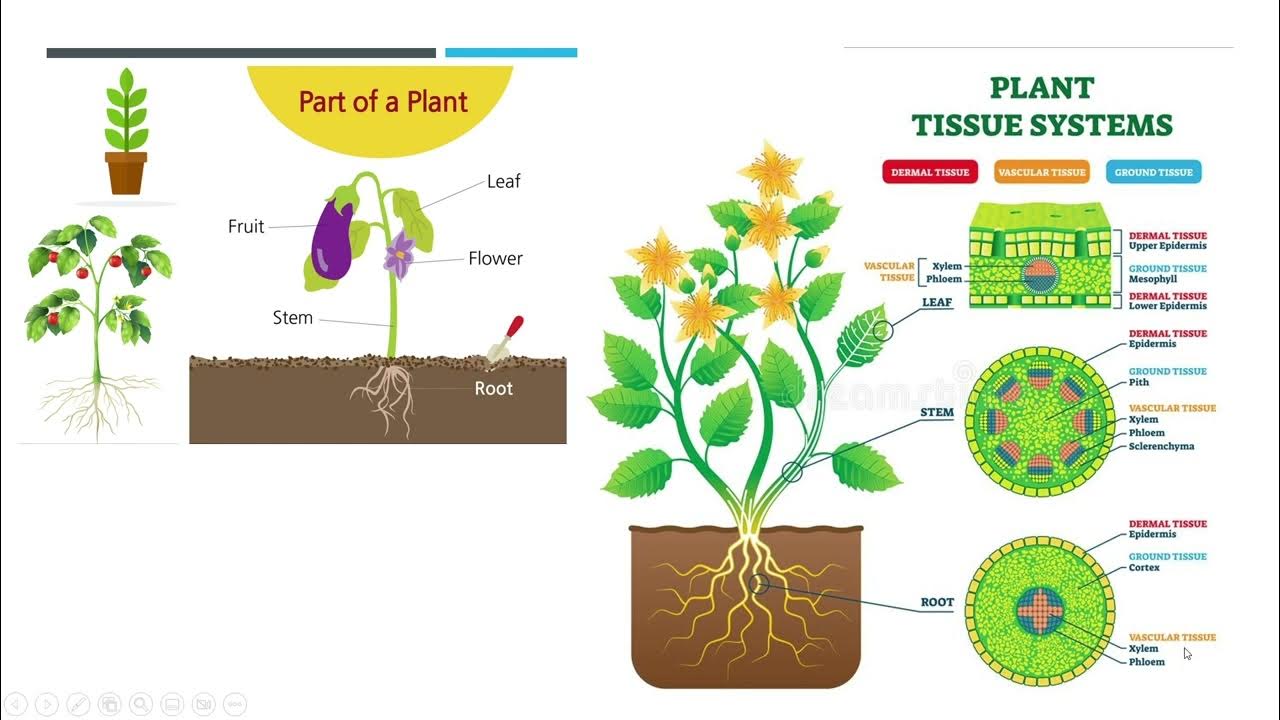
- 😀 Plant tissue is divided into meristem tissue, which is actively dividing, and permanent tissue, which includes protective and supportive types.
- 😀 Meristem tissue is crucial for growth, found at the tips of roots and stems, and helps the plant grow vertically and horizontally.
- 😀 Permanent plant tissues include epidermal tissue for protection, collenchyma and sclerenchyma for support, and parenchyma for storage and photosynthesis.
- 😀 Xylem and phloem are plant transport tissues that carry water, minerals, and nutrients, as well as photosynthetic products, throughout the plant.
Q & A
What is the role of tissue networks in multicellular organisms?
-In multicellular organisms, tissue networks consist of cells grouped together to perform specific functions. Cells depend on each other to maintain the organism's survival and proper function.
How do single-celled organisms carry out their life functions?
-Single-celled organisms perform all their life functions within that single cell. Unlike multicellular organisms, these cells do not rely on other cells for survival.
What is epithelial tissue and where is it found?
-Epithelial tissue consists of tightly packed cells arranged in flat layers. It covers body surfaces, lines cavities, and forms the skin. It also protects underlying tissues from damage.
What are the main types of connective tissue?
-Connective tissue includes various types such as supporting connective tissue (e.g., cartilage), binding connective tissue (e.g., tendons), fibrous connective tissue (e.g., muscle membranes), and hematopoietic tissue (e.g., spinal cord for blood cell production).
What function does muscle tissue serve in animals?
-Muscle tissue is responsible for movement. There are three types: smooth muscle (lines hollow organs), skeletal muscle (moves bones and other body parts), and cardiac muscle (makes up the heart).
What are neurons and how do they function in the neural tissue?
-Neurons are specialized cells in the neural tissue that carry electrochemical nerve impulses. They are essential for communication within the nervous system, with connections called axons and dendrites transmitting signals.
What is meristematic tissue in plants, and where is it located?
-Meristematic tissue is responsible for active cell division. It is found at the tips of roots and stems, as well as in the cambium of vessel bundles. It contributes to plant growth both vertically and horizontally.
How do permanent tissues in plants differ from meristematic tissue?
-Permanent tissues are mature tissues that no longer divide. They include protective, supportive, and transport tissues, such as epidermal tissue, sclerenchyma, xylem, and phloem, each with specific functions.
What is the function of xylem tissue in plants?
-Xylem tissue, also called wood tissue, transports water, minerals, and nutrients from the roots to other parts of the plant, especially the leaves.
What is the role of cork tissue in plants?
-Cork tissue, or periderm, replaces the epidermis as a protective layer. It contains suberin, which helps prevent water loss and protects the plant's internal structures.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)