Introdução ao Sistema Articular - Parte 2
Summary
TLDRThis video lesson explores the structure and classification of synovial joints in the human body. It begins with an introduction to joints, focusing on synovial joints, which allow wide-ranging movement in key areas such as the hips, knees, and shoulders. The lesson covers their characteristics, including cartilage, joint capsules, synovial fluid, and ligaments. It also delves into their functional and morphological classifications, such as uniaxial, biaxial, and triaxial joints, and provides examples like the elbow, wrist, and shoulder. The lesson concludes by discussing exceptions and controversies in joint classification, with particular attention to synovial joints with flat surfaces.
Takeaways
- 😀 Synovial joints are the most mobile type of joint in the human body and include major joints like the hips, knees, shoulders, and elbows.
- 😀 A synovial joint is defined by several key features: articular cartilage covering bone surfaces, a joint capsule, synovial fluid, and ligaments for stability.
- 😀 Some synovial joints contain additional structures like menisci or articular discs that help absorb shock and optimize bone alignment (e.g., knee, TMJ).
- 😀 Synovial bursae are structures that reduce friction between muscles, tendons, and bones, enhancing movement efficiency.
- 😀 Joints can be classified by function based on the number of movement types they allow: uniaxial, biaxial, and triaxial.
- 😀 Uniaxial joints allow only one type of movement, such as flexion and extension (e.g., elbow).
- 😀 Biaxial joints allow two types of movement, including flexion/extension and abduction/adduction (e.g., wrist).
- 😀 Triaxial joints allow three types of movement, such as flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, and rotation (e.g., shoulder, hip).
- 😀 The shape of synovial joints determines their movement capabilities: hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, and ball-and-socket joints.
- 😀 Some synovial joints, like the knee, are classified differently by various authors, either as hinge or biaxial joints depending on the perspective.
- 😀 Flat joints, like those in the wrist or tarsals, allow for sliding or gliding movements, with no distinct rotational or angular motion.
Q & A
What are synovial joints and what are their main characteristics?
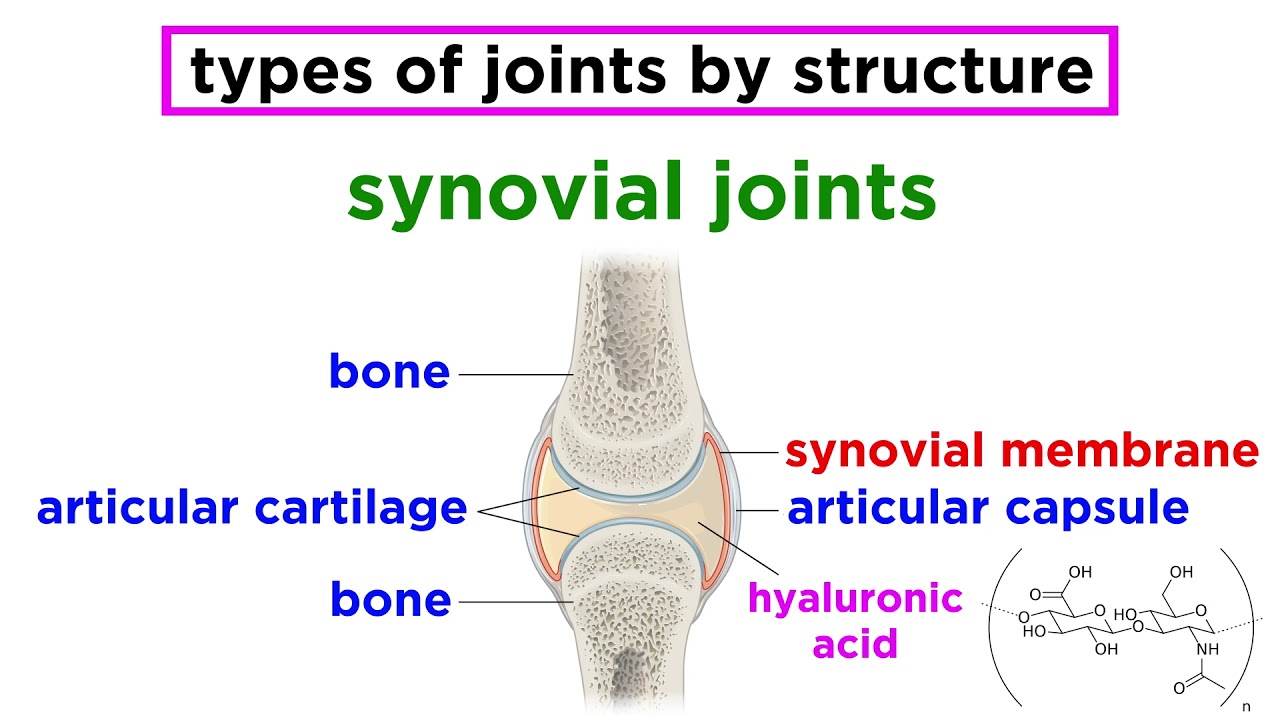
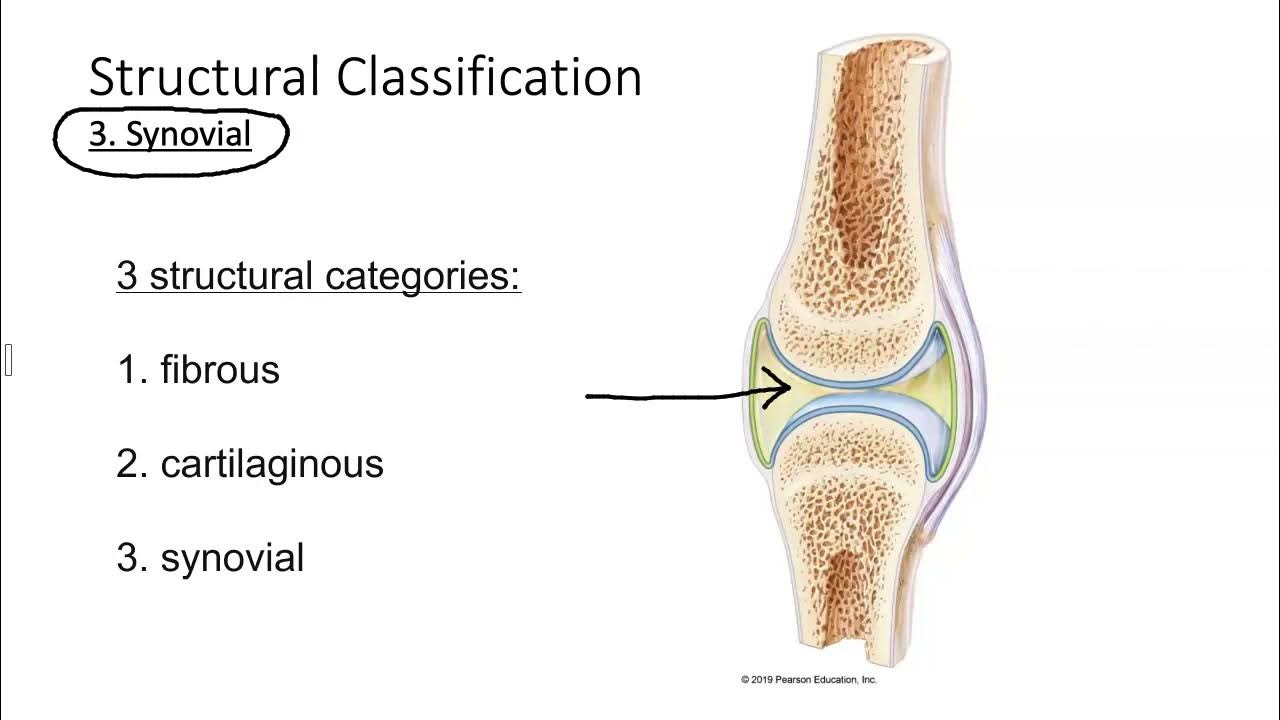
-Synovial joints are the most common type of joints in the body, characterized by having two bones covered with hyaline cartilage, an articular capsule, synovial fluid inside, and ligaments providing stability. They allow for a wide range of movements.
What is the role of synovial fluid in synovial joints?
-Synovial fluid inside the articular capsule acts as a lubricant, reducing friction and providing nourishment to the cartilage, allowing smooth movement between bones.
What are the different types of movements possible in synovial joints?
-The movements in synovial joints include flexion, extension, medial rotation, lateral rotation, adduction, and abduction, depending on the joint and the axis of movement.
How can synovial joints be classified based on movement?
-Synovial joints can be classified into three categories based on the number of movement axes they allow: uniaxial (one movement), biaxial (two movements), and triaxial (three movements).
What is the difference between uniaxial, biaxial, and triaxial joints?
-Uniaxial joints allow movement in one direction (e.g., flexion and extension), biaxial joints allow movement in two directions (e.g., flexion/extension and abduction/adduction), and triaxial joints allow movement in three directions (e.g., flexion/extension, rotation, and abduction/adduction).
Can you provide examples of each type of synovial joint?
-Examples of uniaxial joints include the elbow (hinge joint), biaxial joints include the wrist (ellipsoidal joint), and triaxial joints include the shoulder and hip (ball-and-socket joints).
What is the functional difference between ginglymus (hinge) joints and trochoid (pivot) joints?
-Ginglymus joints (e.g., elbow) allow flexion and extension, whereas trochoid joints (e.g., proximal radioulnar joint) allow rotational movement, like supination and pronation.
What are articular menisci, and what role do they play in synovial joints?
-Articular menisci are fibrocartilaginous structures found in some synovial joints, such as the knee, where they provide shock absorption and improve the fit between bones, optimizing joint function.
What are synovial bursae and their function in the body?
-Synovial bursae are flattened, sac-like structures that are filled with synovial fluid. They reduce friction and act as cushions, facilitating the movement of muscles or tendons over bony prominences.
What is the controversy regarding the classification of the knee joint?
-There is some controversy about the classification of the knee joint, as some authors classify it as a ginglymus (hinge joint), while others classify it as biaxial due to its complex structure and movement capabilities.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)