Types Of Joints in the Human Body - GCSE PE
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the different types of joints in the human body, detailing fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial joints. Fibrous joints are immovable and include those found in the skull and teeth. Cartilaginous joints, partially movable, are connected by cartilage, like those in the spine. Synovial joints, the most common and highly movable, include hinge, pivot, ball-and-socket, saddle, condyloid, and gliding joints, each allowing specific movements like flexion, extension, rotation, and more. The video also explains the components of synovial joints, such as synovial fluid and cartilage, emphasizing their crucial role in human movement.
Takeaways
- 😀 Joints are points where two or more bones meet in the human body.
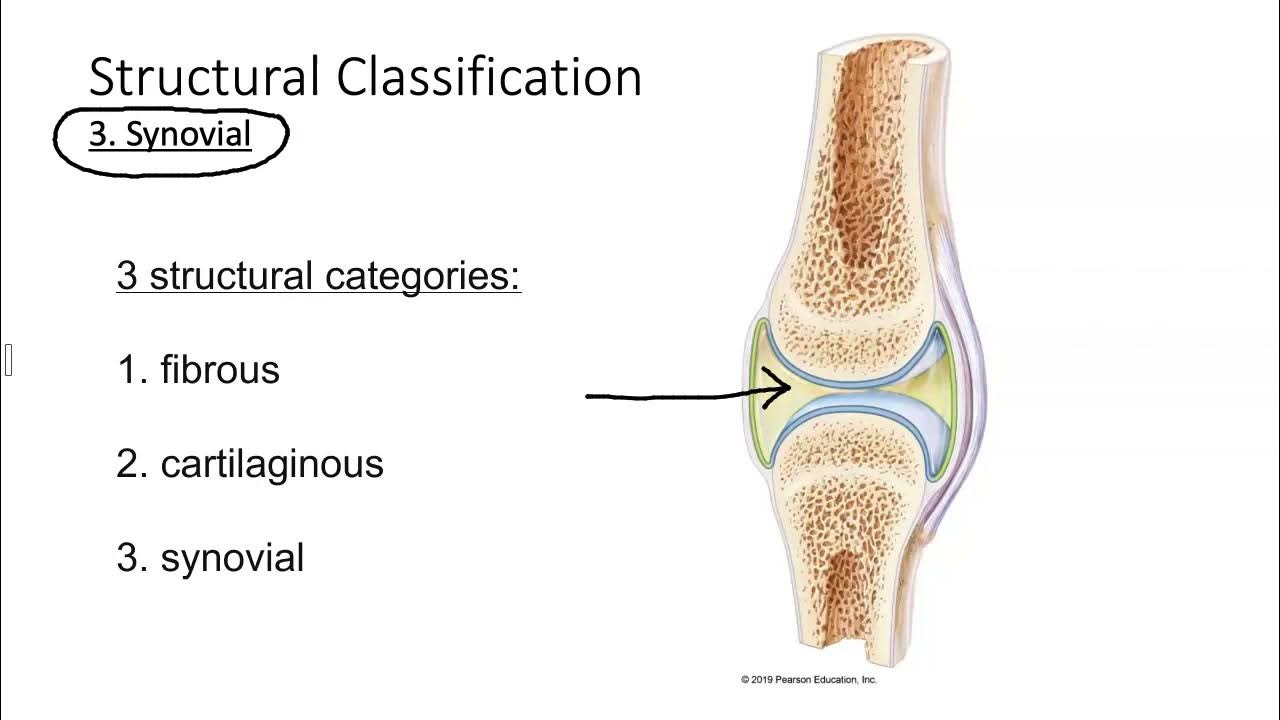
- 😀 There are three main types of joints: fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial.
- 😀 Fibrous joints, also called synarthrosis, are immovable and held together by ligaments.
- 😀 Examples of fibrous joints include the bones in the skull, teeth in their sockets, and the radius and ulna in the elbow.
- 😀 Cartilaginous joints are connected by cartilage and are partially movable.
- 😀 Symphysis joints are connected by fibrocartilage, such as the pubic symphysis and the disks between vertebrae.
- 😀 Synchondrosis joints are temporary and are found in children, like the epiphyseal plates in long bones.
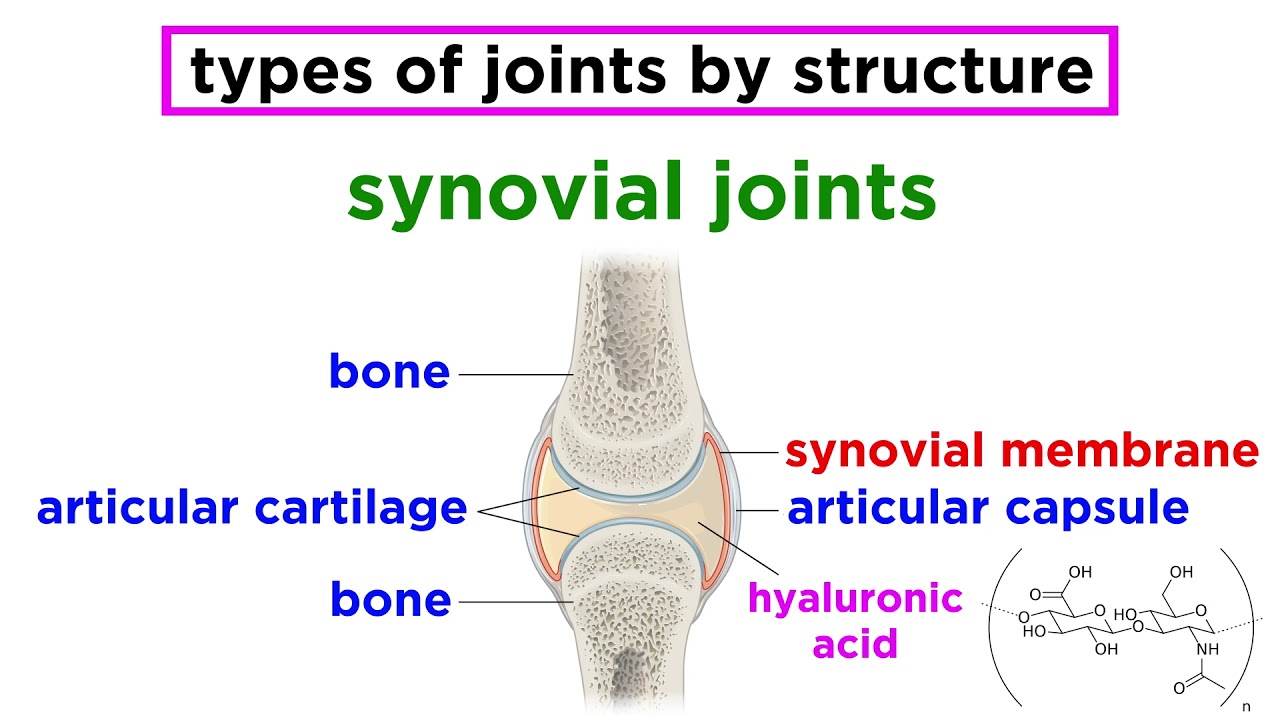
- 😀 Synovial joints are the most common type, allowing for a wide range of movement.
- 😀 Synovial joints have a synovial capsule, synovial membrane that secretes fluid, and hyaline cartilage to protect bones.
- 😀 There are six types of synovial joints: hinge, pivot, ball-and-socket, saddle, condyloid, and gliding joints, each allowing specific movements.
- 😀 Hinge joints, like those in the knee and elbow, allow flexion and extension.
- 😀 Pivot joints, such as the Atlas and Axis in the neck, allow rotational movement.
- 😀 Ball-and-socket joints, like the hip and shoulder, allow a full range of movements, including rotation.
- 😀 Saddle joints, like the MCP joint in the thumb, allow flexion, extension, adduction, and abduction.
- 😀 Condyloid joints, found in the wrist and hand, allow flexion, extension, adduction, and abduction.
- 😀 Gliding joints, like those in the carpal joints of the hand, enable bones to glide against each other.
Q & A
What are the three main types of joints in the human body?
-The three main types of joints in the human body are fibrous joints, cartilaginous joints, and synovial joints.
What is the key characteristic of fibrous joints?
-Fibrous joints are immovable, as the bones are held together by ligaments, and they allow virtually no movement.
Can you provide an example of a fibrous joint?
-Examples of fibrous joints include the joints between the bones in the skull, the connection of teeth to their sockets, and the joint between the radius and ulna in the elbow.
What are cartilaginous joints and what are their two types?
-Cartilaginous joints are where bones are connected by cartilage. The two types are symphysis joints (connected by fibrocartilage) and synchondrosis joints (temporary, found in children until the end of puberty).
What is the role of synovial fluid in synovial joints?
-Synovial fluid lubricates the joint, helping to reduce friction and allowing smooth movement between the articulating bones.
How are synovial joints classified?
-Synovial joints are classified into six types based on the shape of the joint and the available movement: hinge, pivot, ball-and-socket, saddle, condyloid, and gliding joints.
What is an example of a hinge joint and what movement does it allow?
-An example of a hinge joint is the knee or elbow. It allows flexion (bending) and extension (straightening).
What is a pivot joint and where is it found in the body?
-A pivot joint allows one bone to rotate around another. A prime example is the joint between the Atlas and Axis at the top of the neck.
What types of movement does a ball-and-socket joint allow?
-Ball-and-socket joints, found in the hip and shoulder, allow flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation, and circumduction (a circular movement).
What is a saddle joint, and where can it be found?
-A saddle joint allows flexion, extension, adduction, and abduction. It is found in the MCP joint at the base of the thumb.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)