Statistik : Penyajian Data - Part 4
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial focuses on explaining frequency distributions, including absolute frequency, relative frequency, and cumulative frequency. It covers the differences between absolute and relative frequencies, how to calculate them, and provides an example using specific data. The video also explains the concept of cumulative frequency, both before and after a given class, and demonstrates how to compute these values. The goal is to help viewers understand the process of organizing and analyzing data using these statistical methods, offering practical examples and step-by-step instructions for calculation.
Takeaways
- 😀 Absolute frequency refers to the actual count of occurrences in each class of data.
- 😀 Relative frequency is calculated by dividing the frequency of a class by the total frequency, and it is often expressed as a percentage.
- 😀 To find the relative frequency, multiply the frequency of each class by 100 and divide by the total number of observations.
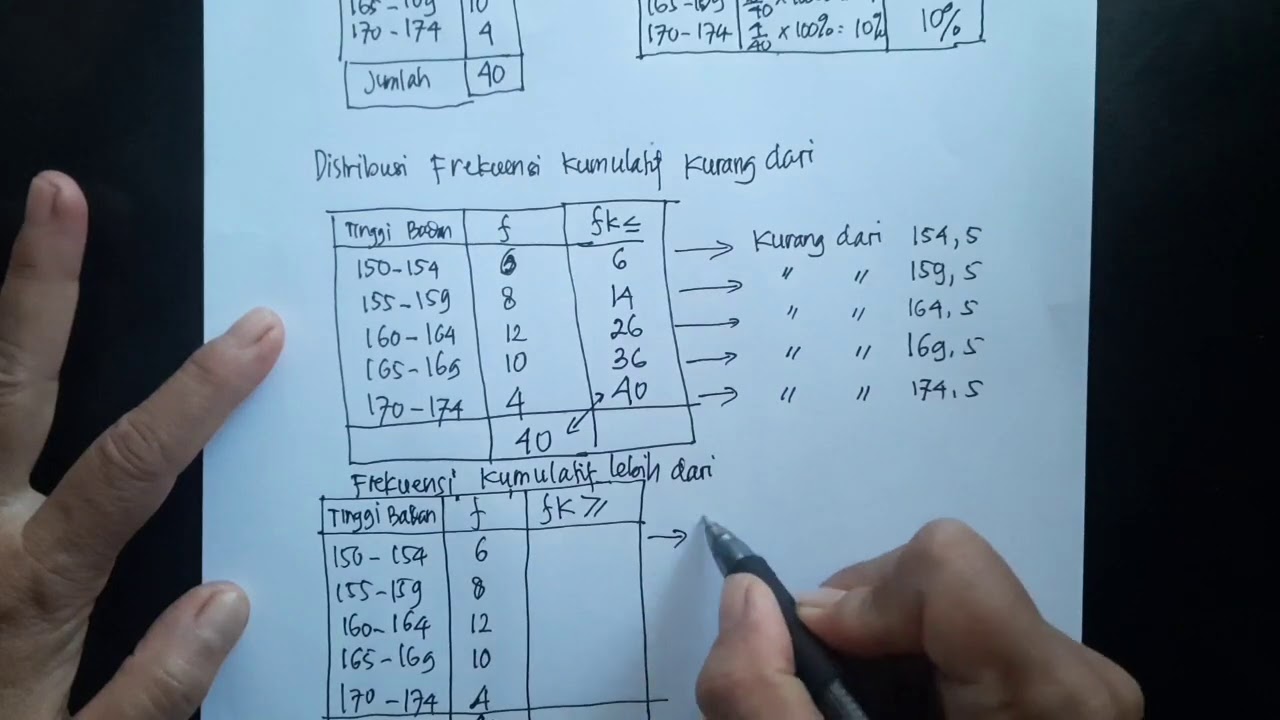
- 😀 Cumulative frequency before (FKB) is the sum of the frequencies up to and including a given class.
- 😀 Cumulative frequency after (FKA) is the sum of the frequencies from a given class onwards, including that class and all subsequent ones.
- 😀 The calculation of relative frequency helps compare how much each class contributes to the overall dataset in percentage terms.
- 😀 The cumulative frequency table includes two types: before and after, depending on whether the sum is from the start of the dataset or from the current class onwards.
- 😀 When calculating cumulative frequencies, for the first class, FKB equals its absolute frequency. For subsequent classes, FKB is the sum of frequencies of all previous classes.
- 😀 For cumulative frequency after (FKA), the last class will have its frequency as the FKA since there are no further classes to add.
- 😀 When calculating FKA for a class, you sum the frequency of that class with all the frequencies from subsequent classes until the last class is reached.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video script?
-The main topic of the video script is about frequency distributions, including absolute and relative frequency, and cumulative frequency distributions.
What is absolute frequency in the context of the video?
-Absolute frequency refers to the total number of occurrences or observations in each class or category in a data set.
How is relative frequency calculated?
-Relative frequency is calculated by dividing the frequency of each class by the total frequency of all classes, then multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage.
What is the difference between absolute frequency and relative frequency?
-Absolute frequency gives the actual count of occurrences in each class, while relative frequency expresses the proportion of occurrences in each class compared to the total number of observations.
What is a cumulative frequency distribution?
-A cumulative frequency distribution accumulates the frequencies from the classes sequentially, showing the total count up to and including each class.
What is the distinction between cumulative frequency before and cumulative frequency after?
-Cumulative frequency before adds the frequencies of a class and all previous classes, while cumulative frequency after adds the frequencies of the class and all subsequent classes.
How do you calculate cumulative frequency before for a given class?
-To calculate cumulative frequency before for a given class, you sum the frequencies from the current class and all previous classes.
How do you calculate cumulative frequency after for a given class?
-To calculate cumulative frequency after for a given class, you sum the frequencies of the current class and all subsequent classes.
What role do frequency tables play in data analysis according to the script?
-Frequency tables are used to organize data, displaying the frequencies for each class, and they are essential for calculating absolute, relative, and cumulative frequencies.
What is the formula for calculating relative frequency from absolute frequency?
-Relative frequency is calculated by dividing the absolute frequency of a class by the total absolute frequency of all classes, then multiplying the result by 100 to get the percentage.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
FREKUENSI RELATIF DAN FREKUENSI KUMULATIF, HISTOGRAM, DAN POLIGON

Distribuição de frequência com classes

TABEL DISTRIBUSI FREKUENSI KUMULATIF DAN RELATIF

Statistika 05 | Distribusi Frekuensi dalam Statistika | Frequency Distribution | Belajar Statistika

Representações Gráficas I | Estatística Básica 03

FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION: Common Terminologies Vid#4 FREE Tutorial | Statistics | EASILY EXPLAINED!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
