Benzene Reaction | Nitration Reaction: Reaction Mechanism, Nitration Method, Nitration Application
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the nitration reaction of aromatic compounds is thoroughly explored, focusing on its importance in industries like explosives, dyes, and pharmaceuticals. The process involves electrophilic aromatic substitution, where nitronium ions replace hydrogen atoms on the aromatic ring. Various reagents such as nitric acid and sulfuric acid are used, depending on the conditions. The mechanism includes the formation of the nitronium ion, its attack on the aromatic ring, and the subsequent restoration of aromaticity. The video also covers the effects of substituents on reactivity, as well as practical applications like the production of TNT and pharmaceuticals.
Takeaways
- 😀 Nitration is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction where a hydrogen atom on an aromatic ring is replaced by a nitro group (NO₂).
- 😀 The nitration reaction is used in the synthesis of important compounds like explosives, dyes, and medicines.
- 😀 The most common reagents for nitration are a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and sulfuric acid, which forms nitronium ions (NO₂⁺), the key electrophile.
- 😀 Fuming nitric acid in acetic anhydride and hot concentrated nitric acid are other reagents used, but they have different reaction conditions and rates.
- 😀 The nitration reaction proceeds in three stages: formation of nitronium ions, electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring, and restoration of aromaticity by proton loss.
- 😀 Nitration of aromatic compounds can be influenced by the presence of substituents, which can either activate or deactivate the aromatic ring.
- 😀 Activated aromatic nuclei, like alkyl groups and phenols, react more readily in nitration, while deactivated nuclei, like halobenzene and nitrobenzene, require more specific conditions.
- 😀 The nitration reaction can produce different products depending on the temperature and reagent concentration, such as nitrobenzene, which is a key industrial product.
- 😀 Strongly activated aromatic compounds (e.g., aniline and phenol) may require safer reagents, such as dilute nitric acid, to prevent dangerous reactions.
- 😀 Nitration reactions are critical for producing compounds like TNT (trinitrotoluene) for explosives, synthetic dyes for textiles, and aromatic amines for drugs such as antibiotics and anticancer medications.
- 😀 Understanding the nitration reaction is crucial for applications in chemistry and industry, including the synthesis of various essential compounds.
Q & A
What is the nitration reaction of aromatic compounds?
-The nitration reaction is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction where a nitro group (NO2+) replaces one of the hydrogen atoms on an aromatic ring, such as benzene. This reaction is important for producing compounds used in dyes, explosives, and medicines.
What are the reagents commonly used in the nitration reaction?
-Common reagents for nitration include a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulfuric acid, fuming nitric acid in acetic anhydride, hot concentrated nitric acid, nitric acid in glacial acetic acid, and dilute nitric acid.
Why is a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and sulfuric acid the most commonly used reagent for nitration?
-This mixture is the most commonly used because sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst, protonating nitric acid and facilitating the formation of nitronium ions (NO2+), which are essential for the reaction. It also helps remove water, ensuring a higher concentration of nitronium ions.
What is the role of sulfuric acid in the nitration reaction?
-Sulfuric acid serves two main roles: it acts as an acid catalyst to protonate nitric acid and form nitronium ions, and it also attracts water molecules, ensuring the reaction remains efficient by maintaining high nitronium ion concentration.
What happens during the first stage of the nitration reaction mechanism?
-In the first stage, nitronium ions (NO2+) are formed by the reaction of concentrated nitric acid with concentrated sulfuric acid. These ions are the electrophiles that will later attack the aromatic ring.
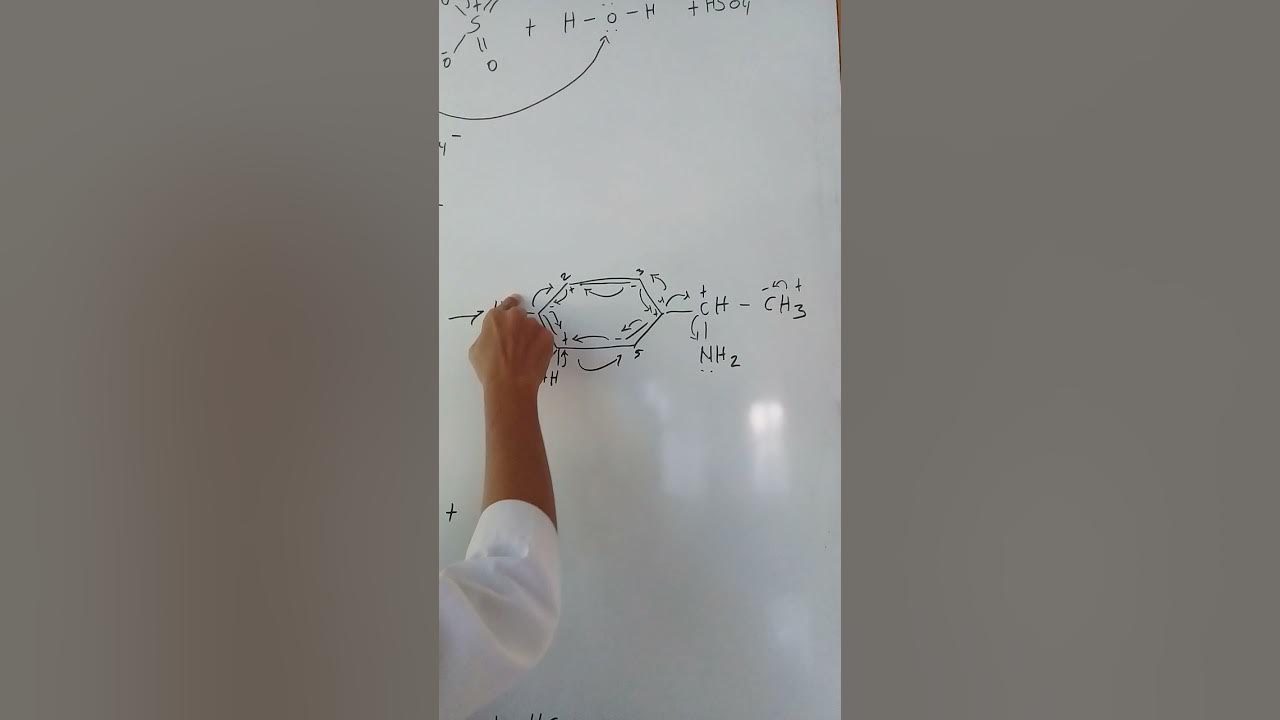
How does the nitronium ion attack the aromatic ring in the second stage of the mechanism?
-The nitronium ion attacks the electron-rich aromatic ring, forming a sigma carbocation complex (arenium ion). This intermediate is unstable as it loses the aromaticity of the ring.
What happens in the third stage of the nitration reaction mechanism?
-In the third stage, the arenium ion releases a proton (H+) to restore the aromaticity of the ring. This results in the formation of the final product, such as nitrobenzene.
How does the presence of substituents on the aromatic ring affect the nitration reaction?
-Substituents on the aromatic ring can either activate or deactivate the ring toward nitration. Activating groups (like alkyl or amide) make the ring more reactive, while deactivating groups (like halogens or nitro groups) make it less reactive.
What is the significance of nitration reactions in industry?
-Nitration reactions are crucial in industries for producing explosives like TNT, synthetic dyes for textiles and food, and pharmaceutical compounds such as antibiotics and anticancer drugs.
Why is nitration of phenol and aniline carried out with dilute nitric acid instead of concentrated nitric acid?
-Phenol and aniline are highly reactive due to their activating groups. Using concentrated nitric acid can lead to uncontrollable reactions. Therefore, dilute nitric acid is preferred to prevent excessive exothermic reactions, such as the formation of explosive compounds like trinitrophenol.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
Proses Sulfonasi Senyawa Aromatik

REAKSI - REAKSI BENZENA

Substitusi Elektrofilik Aromatik: Sulfonasi

REACCIONES DE LOS ALCANOS O HIDROCARBUROS SATURADOS. COMBUSTIÓN. HALOGENACIÓN. NITRACIÓN.

Mecanismo de substituição aromática eletrofílica | Química orgânica | Khan Academy

BENZENA DAN AROMATISITAS [KIMIA ORGANIK]
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
