Anatomi Sistem Saraf: Saraf Pusat & Tepi | Neurologi
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the human nervous system, dividing it into two major components: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain, brainstem, and spinal cord, which coordinate body functions. The brain includes key structures like the cerebrum, cortex, and cerebellum, each with distinct functions. The PNS is made up of cranial and spinal nerves, with specific pathways controlling sensory and motor functions. The video also explains the autonomic and somatic systems, highlighting the nervous system's role in both involuntary and voluntary bodily functions.
Takeaways
- 😀 The nervous system connects and coordinates every step of thought and even the emotions we feel.
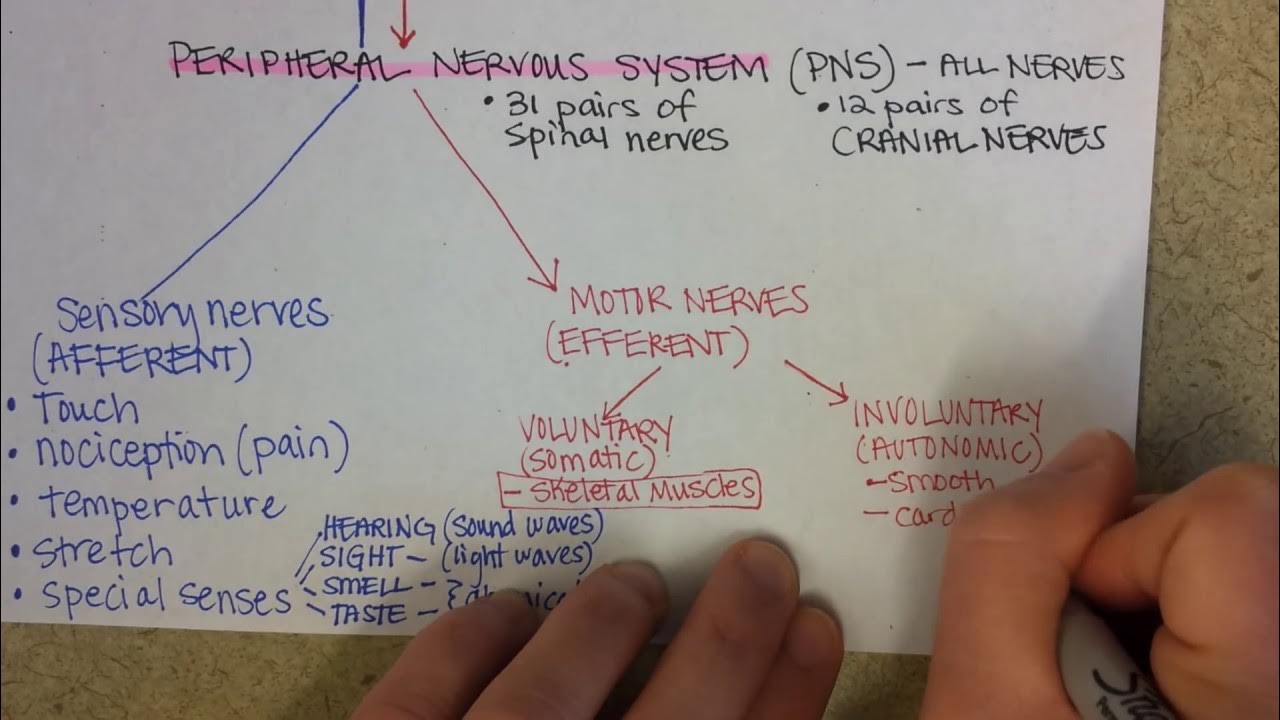
- 😀 The nervous system is anatomically divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
- 😀 The central nervous system includes the brain (encephalon), brainstem (truncus), and spinal cord (medulla spinalis), which function as the body's coordination center.
- 😀 The peripheral nervous system consists of cranial nerves and spinal nerves, linking the CNS to the rest of the body.
- 😀 The peripheral nervous system is further classified into autonomic (unconscious) and somatic (conscious) systems.
- 😀 The brain is protected by the skull and suspended in cerebrospinal fluid, which helps cushion and support it.
- 😀 The outer layer of the brain, the cortex, is composed of ridges (gyri) and valleys (sulci), divided into four main lobes: frontal, temporal, occipital, and parietal.
- 😀 The corpus callosum is a bridge connecting the two hemispheres of the brain.
- 😀 The brain includes important structures like the thalamus, hypothalamus, and cerebellum, which have specific roles in regulating body functions.
- 😀 The spinal cord extends from the brainstem, passing through the vertebrae and extending down the back, transmitting signals to the body.
- 😀 Cranial nerves (12 pairs) provide innervation to the head, neck, thorax, and abdomen, while spinal nerves (31 pairs) extend to different parts of the body, including the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral regions.
Q & A
What are the two main divisions of the human nervous system?
-The two main divisions of the human nervous system are the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
What parts make up the central nervous system (CNS)?
-The central nervous system consists of the brain (encephalon), brainstem (truncus encephali), and spinal cord (medulla spinalis).
How is the brain protected within the human body?
-The brain is protected by the skull, which is supported by cerebrospinal fluid that cushions the brain.
What is the role of the corpus callosum in the brain?
-The corpus callosum connects the right and left hemispheres of the brain, facilitating communication between them.
What are the four main lobes of the cerebrum?
-The cerebrum is divided into four main lobes: frontal, temporal, occipital, and parietal lobes.
What are the primary functions of the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
-The peripheral nervous system connects the central nervous system to the rest of the body, facilitating communication between the brain and muscles, organs, and tissues.
What types of nerves are included in the peripheral nervous system?
-The peripheral nervous system includes cranial nerves (12 pairs) and spinal nerves (31 pairs).
What is the function of cranial nerves?
-Cranial nerves are responsible for sensory and motor functions in areas such as the head, neck, thorax, and abdomen. They include nerves related to vision, smell, and movement of the eyes and face.
How are spinal nerves classified based on their location?
-Spinal nerves are classified into regions based on their location: cervical (C1-C8), thoracic (T1-T12), lumbar (L1-L5), and sacral (S1-S5).
What is the importance of the medulla spinalis in the body?
-The medulla spinalis (spinal cord) serves as a communication pathway between the brain and the rest of the body, transmitting nerve signals to and from the brain.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)