Neurology - Divisions of the Nervous System
Summary
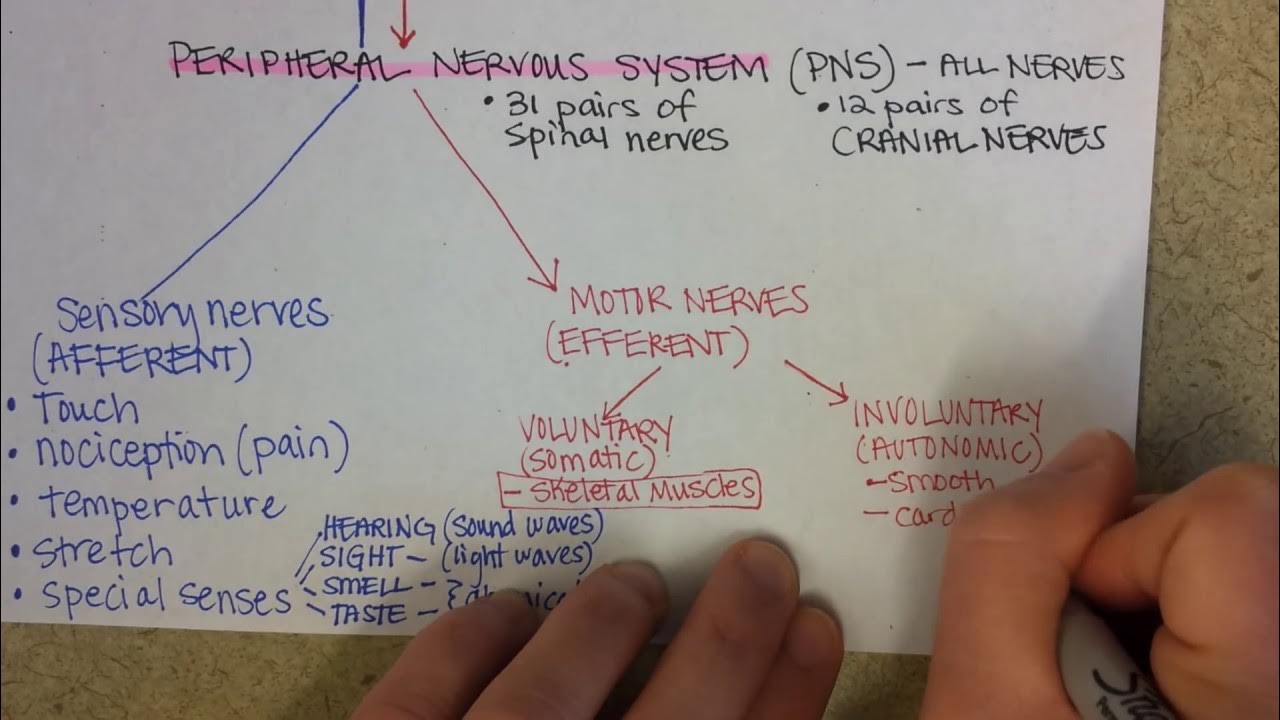
TLDRThis video explains the divisions of the nervous system, highlighting the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), responsible for transmitting signals to and from the CNS. The PNS is divided into the sensory (afferent) division, which brings information to the CNS, and the motor (efferent) division, which sends responses to target cells. The motor division is further split into the somatic nervous system (voluntary control) and the autonomic nervous system (involuntary control), with the autonomic system divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic responses, which have opposing effects on organs like the heart.
Takeaways
- 😀 The nervous system is divided into two main parts: the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
- 😀 The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, where all information is processed and signals are sent to and from the body.
- 😀 The PNS is responsible for bringing information to the CNS and taking signals from the CNS to various parts of the body.
- 😀 The PNS has two major divisions: the sensory (afferent) division, which sends sensory information to the CNS, and the motor (efferent) division, which sends signals from the CNS to target cells.
- 😀 The sensory division is responsible for sensing stimuli such as sight, smell, touch, and pain.
- 😀 The motor division can be divided into two types of neurons: voluntary (somatic nervous system) and involuntary (autonomic nervous system).
- 😀 The somatic nervous system controls voluntary movements, such as moving limbs and muscles.
- 😀 The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary responses, including functions like heart rate and digestion.
- 😀 The autonomic nervous system has two divisions: the sympathetic division, which is active during stress or exercise (fight-or-flight), and the parasympathetic division, which is active during rest (rest-and-digest).
- 😀 The sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions have opposite effects on organs. For example, the sympathetic division increases heart rate, while the parasympathetic division decreases it.
- 😀 Understanding the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic responses is crucial for understanding how the body reacts to different situations and maintains homeostasis.
Q & A
What are the two main parts of the nervous system?
-The two main parts of the nervous system are the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
What does the central nervous system consist of?
-The central nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal cord.
What is the role of the peripheral nervous system?
-The peripheral nervous system brings signals to the central nervous system and takes signals out from the CNS to the target cells.
How is the peripheral nervous system divided?
-The peripheral nervous system is divided into two parts: the sensory division (afferent division) and the motor division (efferent division).
What is the function of the sensory division of the peripheral nervous system?
-The sensory division is responsible for sensing things such as sight, smell, touch, and pain, and sends this information to the central nervous system.
What is the role of the motor division in the peripheral nervous system?
-The motor division takes signals from the central nervous system and sends them to target cells, initiating either voluntary or involuntary responses.
What are the two subtypes of the motor division in the peripheral nervous system?
-The motor division is further divided into the somatic nervous system (voluntary control) and the autonomic nervous system (involuntary control).
What does the somatic nervous system control?
-The somatic nervous system controls voluntary movements by sending signals from the CNS to skeletal muscle cells.
What is the function of the autonomic nervous system?
-The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary responses, such as heart rate, digestion, and glandular function.
What is the difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
-The sympathetic division is active during exercise or stress, often referred to as the 'fight-or-flight' response, while the parasympathetic division is active during rest and digestion, often called the 'rest-and-digest' response. They have opposite effects on target organs, such as the heart.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)