Menghitung Hambatan total / pengganti rangkaian listrik seri paralel majemuk
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial explains how to calculate total or equivalent resistance in both series and parallel electrical circuits. It covers the principles of combining resistances in series, where they are added together, and in parallel, where the inverse of the total resistance is the sum of the inverses of individual resistances. Various examples are provided to demonstrate these concepts, guiding viewers through complex calculations step by step. The video aims to help students understand and solve problems involving series and parallel resistances, preparing them for more advanced electrical circuit analysis.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video explains how to calculate total or equivalent resistance in series and parallel electrical circuits.
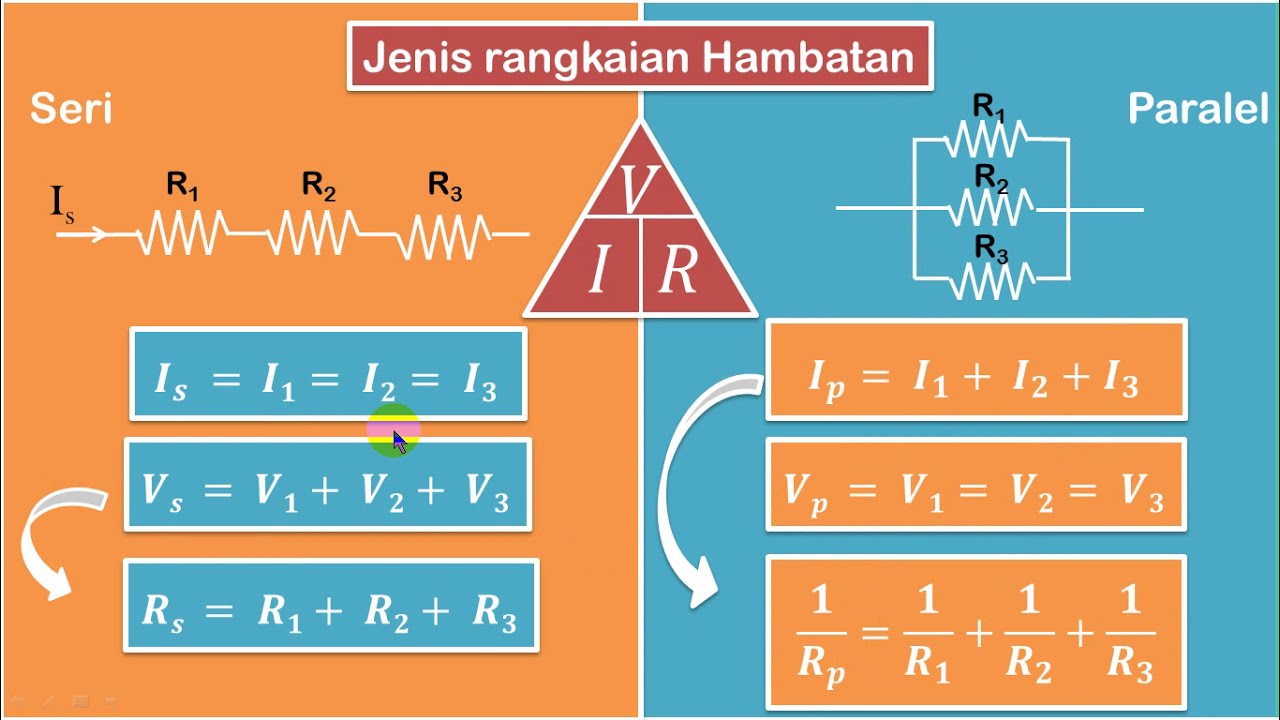
- 😀 In a series circuit, components are connected in a straight line, while in a parallel circuit, components are connected at branching points.
- 😀 For parallel circuits, the reciprocal of the total resistance is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistances.
- 😀 The resistance for two parallel resistors is calculated as the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of their resistances (1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2).
- 😀 Series circuits result in a total resistance that is simply the sum of the individual resistances (R_total = R1 + R2).
- 😀 If resistors are connected in series, the total resistance increases. If connected in parallel, the total resistance decreases.
- 😀 A key example in the video involves finding the equivalent resistance of a network of resistors by applying both series and parallel rules.
- 😀 The script walks through detailed calculations, showing step-by-step how to solve for total resistance in different circuit configurations.
- 😀 The video highlights common mistakes, such as mixing up parallel and series configurations, and emphasizes the importance of identifying junction points correctly.
- 😀 The content also introduces more complex networks, showing how combinations of series and parallel resistors can be simplified to a single equivalent resistance.
- 😀 The concept of equivalent resistance is fundamental in understanding how electrical current behaves in different circuit configurations, especially when determining the power distribution across components.
Q & A
What is the primary difference between a series and a parallel circuit?
-In a series circuit, resistors are connected end to end, and the total resistance is the sum of the individual resistances. In a parallel circuit, resistors are connected at junction points, and the total resistance is found by taking the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of each resistance.
How do you calculate total resistance in a series circuit?
-In a series circuit, the total resistance (R_total) is calculated by adding the resistances of all individual resistors together: R_total = R_1 + R_2 + ... + R_n.
What formula is used to calculate total resistance in a parallel circuit?
-In a parallel circuit, the total resistance is calculated using the reciprocal formula: 1/R_total = 1/R_1 + 1/R_2 + ... + 1/R_n. After summing the reciprocals, take the reciprocal of the result to find the total resistance.
What happens when resistors in a parallel circuit have the same resistance value?
-When resistors in a parallel circuit have the same resistance value, the total resistance is equal to the resistance of one resistor divided by the number of resistors. For example, for two resistors of 5Ω in parallel, the total resistance is 5Ω/2 = 2.5Ω.
How is the total resistance of a combination of series and parallel resistors calculated?
-To calculate the total resistance of a combination of series and parallel resistors, simplify the circuit step by step. First, calculate the equivalent resistance for parallel resistors, then treat the result as a single resistor and add it to any series resistors.
How do you handle circuits with multiple branches or junctions?
-For circuits with multiple branches or junctions, identify the parallel resistors (those sharing a branch point) and use the parallel resistance formula. Series resistors (those not sharing a branch point) are added directly to the total resistance.
In the example where resistors 6Ω and 3Ω are in parallel, how is the total resistance calculated?
-For resistors 6Ω and 3Ω in parallel, the total resistance (R_total) is calculated using the formula: 1/R_total = 1/6 + 1/3. After summing the reciprocals, R_total = 2Ω.
Why is it important to convert fractions when calculating parallel resistances?
-It is important to convert fractions when calculating parallel resistances to have a common denominator, making it easier to sum the reciprocals of the resistances before taking the reciprocal of the total.
What steps should you follow to simplify a complex circuit with both series and parallel resistors?
-To simplify a complex circuit, start by identifying parallel resistors and calculating their equivalent resistance using the reciprocal formula. Then, treat this equivalent resistance as a single resistor and add it to any resistors in series. Repeat this process until you have a single equivalent resistance for the entire circuit.
Can the equivalent resistance in a parallel circuit ever be greater than the individual resistances?
-No, the equivalent resistance in a parallel circuit is always less than the smallest individual resistance. This is because the parallel connection provides additional paths for current, reducing the overall resistance.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
Hambatan Pengganti Rangkaian Seri, Paralel Dan Campuran

Listrik Dinamis-Rangkaian Listrik (Hukum Ohm) (Part 3)

Electrical Engineering: Basic Laws (18 of 31) Finding the Equivalent Resistor Ex. 3
How to use a Resistor - Basic electronics engineering
Electrical Engineering: Basic Laws (17 of 31) Finding the Equivalent Resistor Ex. 2
IPA Kelas 9 : Listrik Dinamis 3 (Rangkaian Hambatan Seri dan Paralel)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
