Distribusi Normal • Part 1: Distribusi Peluang Variabel Acak Kontinu
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of continuous random variables and their normal distribution. It contrasts continuous variables with discrete ones, highlighting how continuous variables can take any value within an interval, unlike discrete variables that have fixed integer values. The video explores probability distribution functions, particularly focusing on the normal distribution curve, which is symmetrical and has specific properties such as an area under the curve equal to 1. The tutorial also covers important distinctions between probability statements in discrete versus continuous contexts.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video discusses normal distribution, focusing on probability distribution and continuous random variables.
- 😀 Continuous random variables can take any value within a specified interval, unlike discrete random variables which have specific integer values.
- 😀 Discrete random variables are counted and are always whole numbers (e.g., x = 0, 1, 2), while continuous random variables are measured and can have fractional values.
- 😀 The concept of measuring random variables like body weight, which can be anywhere within a range (e.g., between 50 and 51 kg), demonstrates continuous variables.
- 😀 Continuous random variables are expressed in intervals (e.g., 50 < X < 51), unlike discrete variables which are expressed as exact values (e.g., X = 3).
- 😀 Probability distribution for continuous random variables is represented by a curve, not a bar chart like for discrete variables.
- 😀 The graph of a normal distribution is symmetrical, with a vertical line dividing it into two equal areas, making it different from non-normal distributions which lack symmetry.
- 😀 Normal distribution is characterized by a peak at the center, and the area under the curve represents probability, with the total area being 1.
- 😀 In continuous distributions, the probability of an exact value (e.g., X = 2) is zero, as it is always expressed within an interval (e.g., 1 < X < 2).
- 😀 The probability that a random variable lies within a certain range (X1 ≤ X ≤ X2) is equivalent to the area under the curve between X1 and X2.
- 😀 The integral of the probability density function (PDF) across the entire range equals 1, representing the total probability.
Q & A
What is a continuous random variable?
-A continuous random variable is one that can take any value within a certain interval. It is typically expressed as X1 < X < X2, where X is an element of the real numbers (R).
How is a discrete random variable different from a continuous random variable?
-A discrete random variable takes distinct, countable values, often whole numbers (like X = 0, 1, 2, 3), while a continuous random variable can take any value within a given range and is measured with precision (e.g., X = 50.2, 50.47).
Can you provide an example of a continuous random variable?
-An example of a continuous random variable is body weight, which can be measured as 50.2 kg, 50.47 kg, or 50.714 kg, depending on the precision of the measuring instrument.
What is the probability distribution function (PDF) of a continuous random variable?
-The probability distribution function (PDF) of a continuous random variable is called the probability density function (FX). It is represented graphically as a curve, where the area under the curve between two values represents the probability of the random variable falling within that range.
How does a probability density function (FX) look for a normal distribution?
-For a normal distribution, the graph of FX is symmetrical, with a peak at the mean. A vertical line through the peak divides the curve into two equal halves, reflecting symmetry.
What is the difference between a normal distribution and a non-normal distribution?
-In a normal distribution, the curve is symmetric, with equal areas on both sides of the peak. In a non-normal distribution, the curve may be skewed to the left or right, and does not have symmetry.
What are some key properties of a normal distribution curve?
-Some key properties of a normal distribution curve include: (1) the total area under the curve equals 1, (2) the curve is symmetrical, (3) the probabilities are represented by the areas under the curve, and (4) the probability at any specific point is zero.
How is the probability of a continuous random variable calculated?
-The probability of a continuous random variable falling within a specific interval is calculated by finding the area under the probability density curve between the two values, which is done using an integral.
What does it mean when we say the area under the curve of a probability density function equals 1?
-This means that the total probability of all possible outcomes of the random variable is 1, which is a fundamental property of probability distributions.
How do we interpret the notation PX ≤ X1 or PX = X1 in the context of continuous random variables?
-In continuous random variables, the probability of X being less than or equal to X1 (PX ≤ X1) is the area under the curve up to X1. Unlike discrete variables, where X = X1 is a specific point, in continuous variables, X1 represents an interval and any particular point like X = X1 has zero probability.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Random Variables and Probability Mass/Density Functions
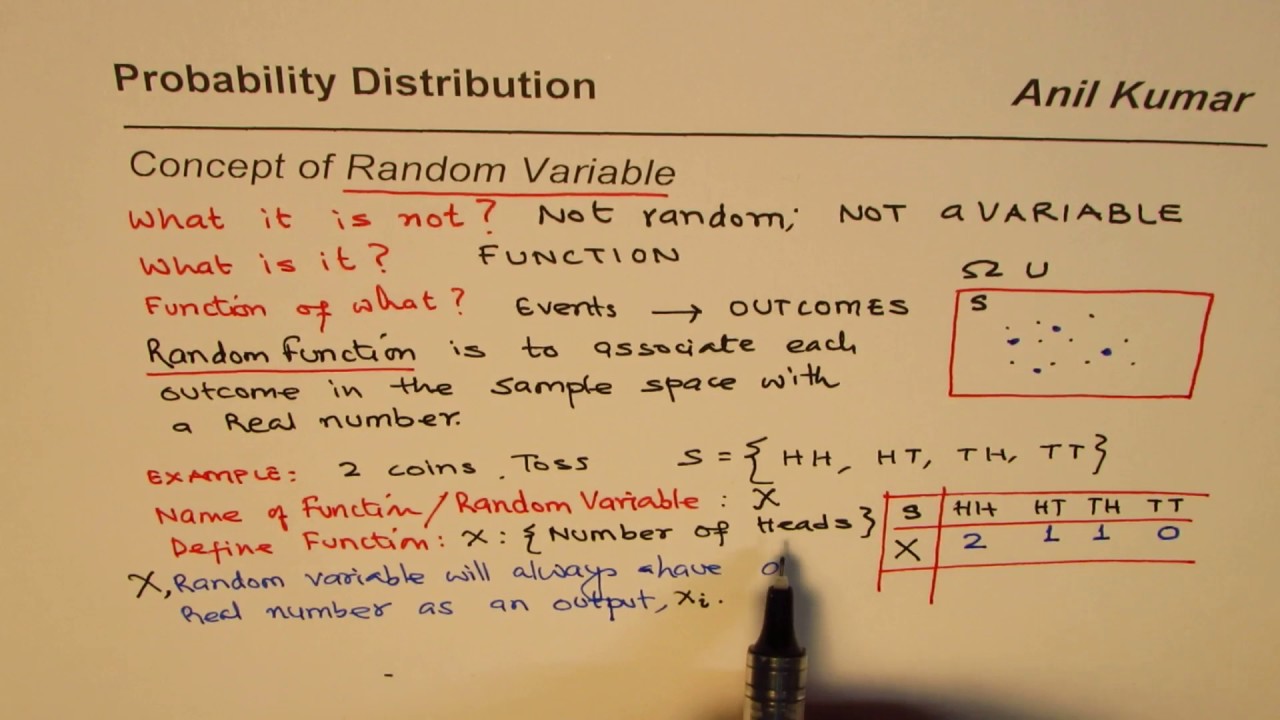
Introduction to Random Variables Probability Distribution

Random Variable, Probability Density Function, Cumulative Distribution Function

Distribusi Binomial • Part 1: Variabel Acak

Econofísica - 5 Momentos Estatísticos
Random Variables - Grade 11 (Statistics and Probability) @MathTeacherGon
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
