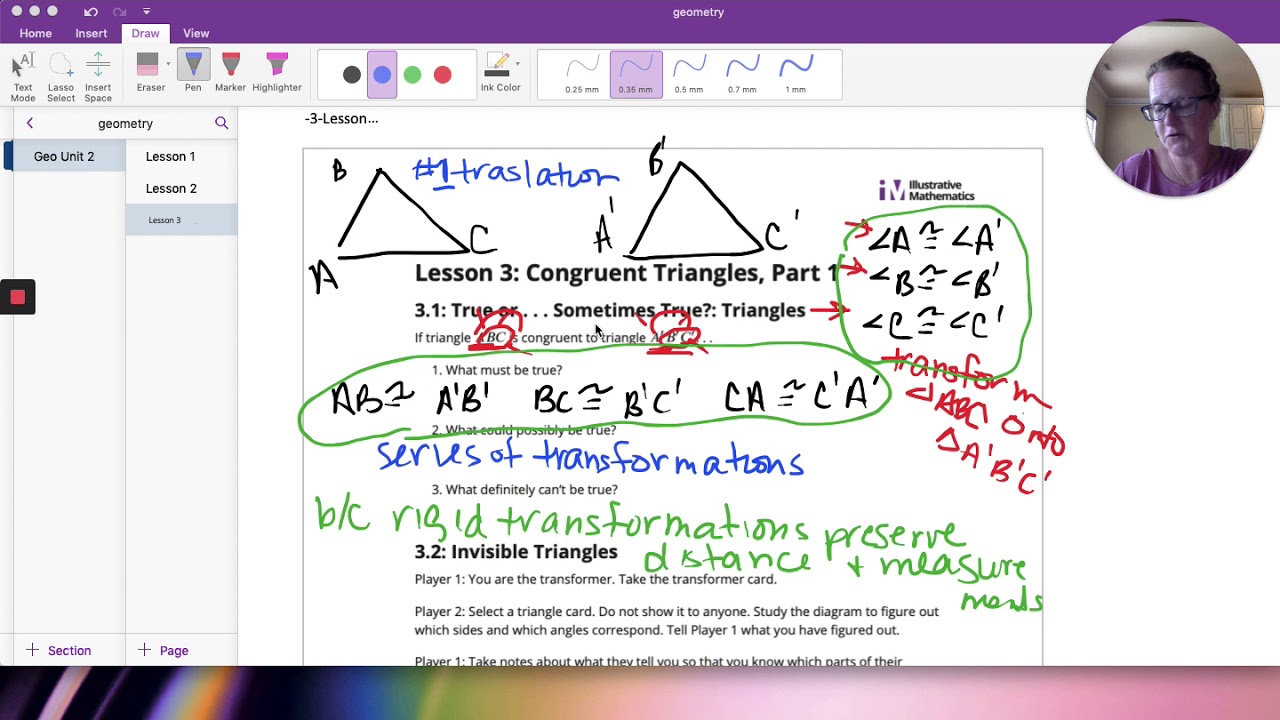
Cara Cepat Memahami Transformasi Geometri [Matematika Kelas IX]
Summary
TLDRThis educational video focuses on the concept of geometric transformations. It covers the definition and types of transformations, including translation, reflection, rotation, and dilation. The video explains each transformation type with visual examples and provides formulas for performing them. It also includes practice problems for better understanding, such as translating points, reflecting shapes across axes, rotating points, and dilating figures. The video aims to help students grasp these key geometric concepts through clear explanations and step-by-step solutions.
Takeaways
- 😀 Geometric transformations involve changing the position, size, or shape of geometric objects.
- 😀 The four main types of geometric transformations are translation, reflection, rotation, and dilation.
- 😀 Translation refers to the shifting of a point or object along a straight line with a specific distance and direction.
- 😀 Reflection involves flipping a point or object over a line, ensuring the distance from the original point to the line is equal to the distance from the reflected point to the line.
- 😀 Rotation refers to rotating a point around a fixed center by a certain angle, with the direction of rotation being either clockwise (negative) or counterclockwise (positive).
- 😀 Dilation is the process of resizing an object, either enlarging or reducing it, by a scale factor.
- 😀 In translation, the formula to find the new coordinates is: (x', y') = (x + a, y + b), where (a, b) is the shift vector.
- 😀 Reflection has several formulas depending on the axis or line of reflection (e.g., reflection over the x-axis, y-axis, or a line y = x).
- 😀 For rotation, common formulas include rotations of 90°, 180°, and 270° in either direction (clockwise or counterclockwise).
- 😀 Dilation uses a scale factor (k) to change the size of the object, and the formula for dilation at the origin is: (x', y') = k * (x, y).
Q & A
What is the definition of geometric transformation?
-Geometric transformation refers to a change in the position or movement of a geometric figure. Specifically, it involves shifting a point or shape from its original position (x, y) to a new position (x', y').
What are the four types of geometric transformations discussed in the script?
-The four types of geometric transformations are translation (shifting), reflection (mirroring), rotation (turning), and dilation (scaling).
How is translation (shifting) defined in geometry?
-Translation is the movement of a point along a straight line in a specific direction and distance, resulting in a new position. The transformation formula for a point P(a, b) translated by a vector (x, y) is P' = (a+x, b+y).
Can you give an example of a translation transformation?
-For example, if point A(3,1) is translated by the vector (3,5), the new point A' would be A'(6,6), obtained by adding 3 to the x-coordinate and 5 to the y-coordinate.
What is the principle behind reflection in geometry?
-Reflection involves flipping a point across a line (the mirror line) such that the distance from the original point to the line is equal to the distance from the reflected point to the line.
How are reflections on different axes or lines expressed in formulas?
-Reflections can be performed across different axes or lines, such as the x-axis, y-axis, or lines like y = x or y = -x. Each type of reflection has a specific transformation formula.
What is the difference between clockwise and counterclockwise rotation?
-Clockwise rotation occurs in the direction of the hands of a clock, while counterclockwise rotation is the opposite. In geometry, clockwise rotations are typically considered negative, and counterclockwise rotations are positive.
What is the formula for rotating a point 90 degrees clockwise?
-The formula for rotating a point (a, b) 90 degrees clockwise is (a, b) → (b, -a).
How does dilation work in geometric transformations?
-Dilation is the process of enlarging or reducing a shape by a scale factor. The scale factor determines how much the distances from the center of dilation are scaled. The formula for dilation is P' = kP, where k is the scale factor.
How do you apply dilation with a given scale factor?
-If point A(3,5) is dilated with a scale factor of 4, the new point A' would be A'(12, 20), obtained by multiplying each coordinate of A by the scale factor (4 * 3, 4 * 5).
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)