Cara Setting IP Address untuk Nembak Wifi dan Topologi Jaringan
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Nanang demonstrates how to set up Mikrotik routers for long-range Wi-Fi connectivity. He explains the importance of correctly configuring IP addresses, subnet masks, and ensuring all routers are on the same network segment for seamless remote management. The video covers essential networking concepts like IP address classes (A, B, C) and provides practical examples of router configuration. With a focus on Mikrotik devices, Nanang guides viewers through setting up and troubleshooting home and outdoor Wi-Fi setups, making the technical aspects accessible for beginners.
Takeaways
- 😀 Understanding IP addresses is crucial for network configuration and troubleshooting.
- 😀 IP addresses are like unique identification numbers for devices in a network, similar to student IDs in a university.
- 😀 The IP address setup is essential for network devices to communicate effectively.
- 😀 Devices need to be on the same IP segment (or subnet) to connect and communicate smoothly.
- 😀 IP classes (A, B, C) determine the size of the network and the range of IP addresses used.
- 😀 Class A IP addresses are used for large networks, while Class C is common for small home or office networks.
- 😀 Subnet masks, like 255.255.255.0 for Class C, specify which part of the IP address is fixed and which part can change.
- 😀 Mikrotik routers can be configured to extend WiFi over long distances, but proper IP addressing is necessary.
- 😀 If devices are in different IP segments (e.g., 192.168.1.x vs 10.10.1.x), they cannot communicate unless properly configured.
- 😀 For seamless communication, all devices on a network should share the same IP range and subnet mask.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video?
-The video primarily focuses on teaching how to configure IP addresses and set up a Mikrotik access point to shoot WiFi over long distances.
Why is understanding IP addresses important for network configuration?
-Understanding IP addresses is essential because it ensures proper communication between devices and routers in a network. Incorrect configuration can lead to issues like being unable to access or configure a router.
What are the two types of IP addresses discussed in the video?
-The two types of IP addresses discussed are IPv4 and IPv6. The video focuses on IPv4, which is commonly used in Indonesia.
What is the difference between IPv4 and IPv6?
-IPv4 is the most widely used addressing system and consists of four sets of numbers separated by dots, while IPv6 uses a longer format with hexadecimal numbers, designed to provide a much larger address space.
What is the significance of subnet masks in IP address configuration?
-Subnet masks define the network portion of an IP address and help in segmenting networks. The subnet mask determines which IP addresses can communicate within the same network.
What is the 'IP class' system in IPv4?
-IPv4 addresses are categorized into different classes (A, B, C, etc.), each with a defined range and usage. For instance, Class A is for large networks, Class B for medium-sized networks, and Class C for smaller networks.
What is the purpose of the Mikrotik access point discussed in the video?
-The Mikrotik access point is used to extend WiFi connectivity over long distances by acting as an outdoor access point, often mounted on a tower to broadcast a signal to a distant target network.
How does one ensure that different routers can communicate with each other in a network?
-To ensure communication between routers, their IP addresses must be within the same network segment or class. This is achieved by configuring them with appropriate subnet masks.
Why can't devices with different IP address classes communicate directly?
-Devices with different IP address classes (e.g., Class A, B, C) cannot communicate directly because they are not in the same network segment. The subnet mask must be consistent for devices to communicate.
What does the term 'segment' mean in IP addressing?
-In IP addressing, a segment refers to a range of IP addresses within the same network class. Devices within the same segment can communicate with each other directly without routing through other networks.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Membuat Wifi Voucheran Tanpa Mikrotik Dengan Tp-Link EAP 110 Omada
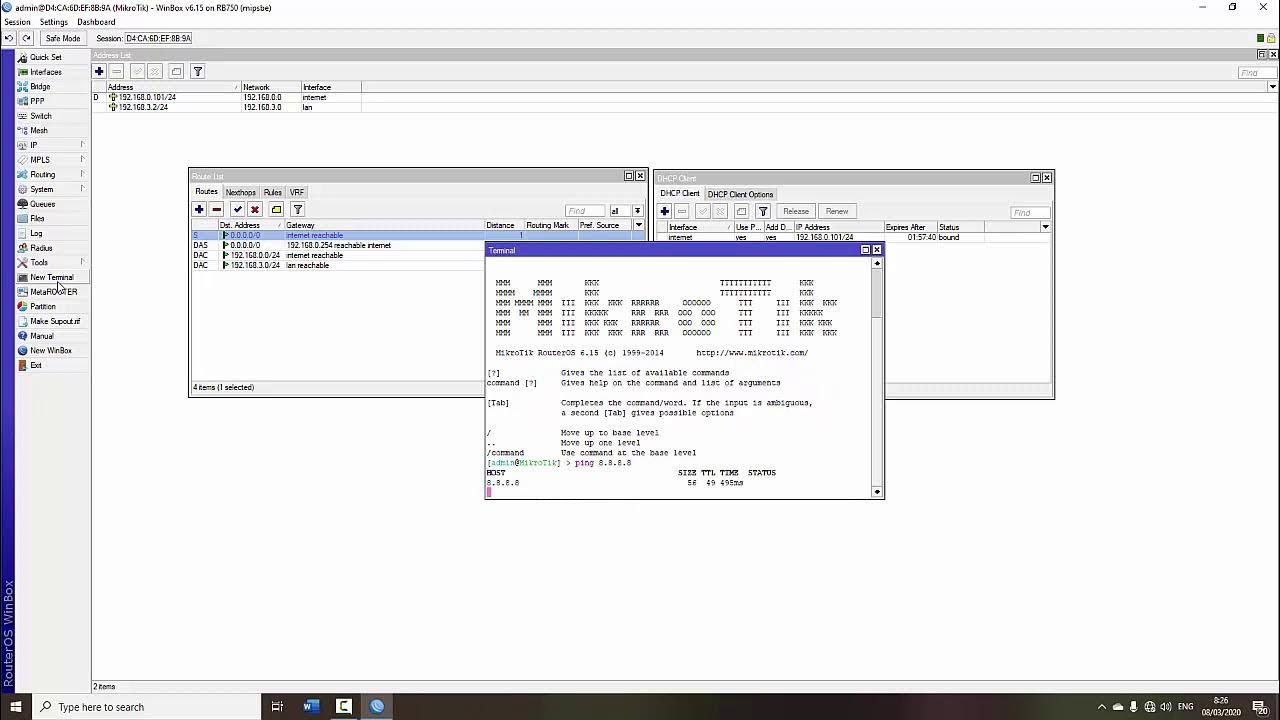
TUTORIAL DASAR MIKROTIK (KONEKSI INTERNET)
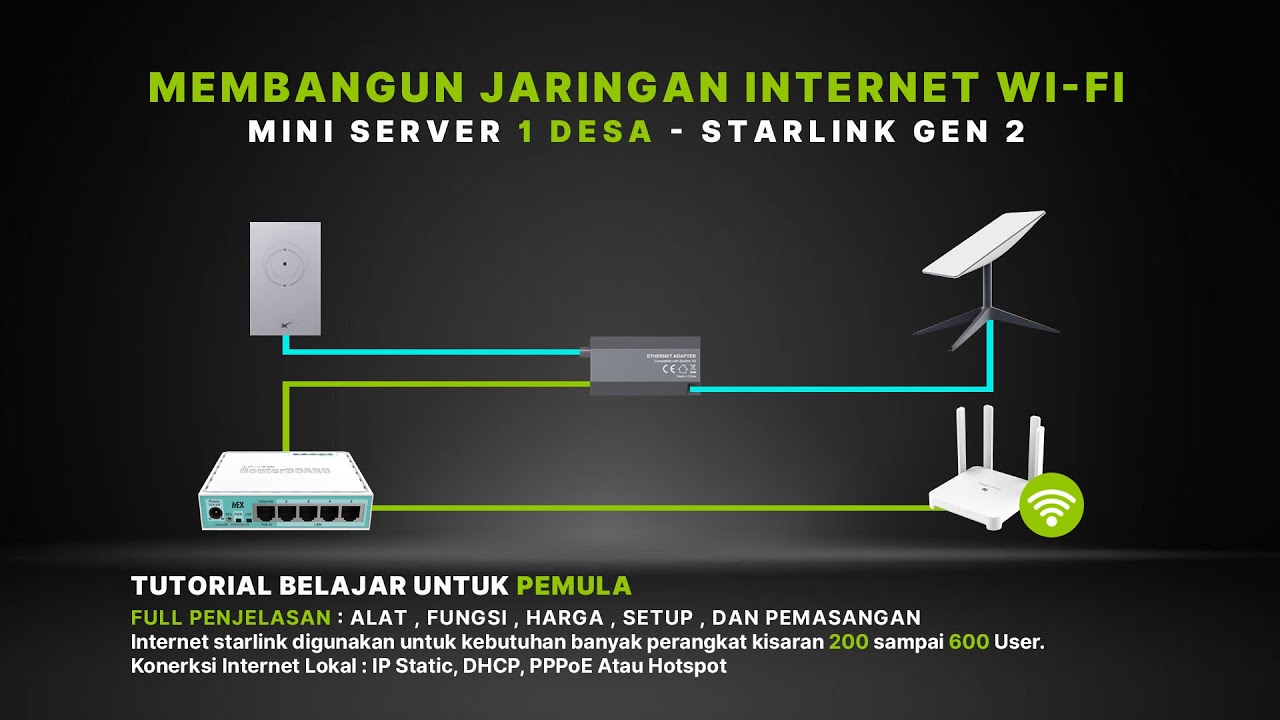
Membangun Jaringan Internet Sekampung dengan Starlink! Begini Caranya!

Istilah Jaringan dalam Setting MikroTik

LOAD BALANCE - Menggabungkan 2 Koneksi Internet dengan MIKROTIK

Share Internet ke Mikrotik VMware #MK2
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
