aula DNA RNA 1
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the structure and function of DNA, focusing on how genetic information is stored in cells. It introduces nucleotides as the building blocks of DNA, consisting of a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base. These bases (adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine) pair up to form the DNA double helix. The script also discusses the concept of complementary strands, where adenine pairs with thymine, and guanine with cytosine, ensuring proper DNA structure. The video touches on different DNA structures, such as cruciform and triple helix, and emphasizes the importance of base pairing and molecular structure in genetic information storage.
Takeaways
- 😀 DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) stores genetic information in cells.
- 😀 RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) is similar to DNA but uses ribose instead of deoxyribose.
- 😀 The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, which consist of a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base.
- 😀 Nucleotides form a long chain through chemical bonds, creating the DNA molecule.
- 😀 DNA's sugar can be ribose or deoxyribose; deoxyribose is missing a hydroxyl group.
- 😀 Nitrogenous bases are classified into purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (cytosine, thymine, and uracil).
- 😀 A nucleotide forms when a nitrogenous base attaches to a sugar and phosphate group.
- 😀 DNA strands are antiparallel, meaning they run in opposite directions (5' to 3' and 3' to 5').
- 😀 Adenine pairs with thymine (A-T), and guanine pairs with cytosine (G-C) through hydrogen bonds.
- 😀 DNA's double helix structure is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between base pairs, maintaining its integrity.
- 😀 The DNA molecule can adopt different structural forms, like the double helix, triplex, or cruciform, depending on the sequence.
Q & A
How is it possible for the sperm and egg cells store information about the characteristics of both the father and mother?
-The sperm and egg cells store genetic information through their DNA, which contains the instructions for the development of a new organism. This genetic material is inherited from both parents and determines the traits of the offspring.
What are the key molecules involved in storing genetic information?
-The key molecules involved in storing genetic information are DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). These molecules carry genetic instructions and are essential for cellular functions.
Why is DNA referred to as a 'twisted ladder'?
-DNA is referred to as a 'twisted ladder' because its structure resembles a helical shape, often depicted as a double helix. This structure consists of two strands twisted around each other, connected by base pairs.
How does the structure of DNA help it store genetic information?
-DNA stores genetic information through its sequence of nucleotides, which are the basic building blocks. The specific order of these nucleotides encodes the genetic instructions necessary for cell functions and organism development.
What are nucleotides made of?
-Nucleotides are composed of three components: a pentose sugar (either ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (which can be a purine or a pyrimidine).
What is the difference between ribose and deoxyribose in the context of nucleotides?
-Ribose and deoxyribose are both sugars found in nucleotides, but ribose has a hydroxyl group (-OH) on the second carbon atom, while deoxyribose lacks this hydroxyl group, which is why it is called 'deoxy'.
What are purines and pyrimidines?
-Purines and pyrimidines are types of nitrogenous bases in nucleotides. Purines include adenine and guanine, which have a double-ring structure, while pyrimidines include cytosine, thymine, and uracil, which have a single-ring structure.
What happens when nucleotides link together in DNA?
-When nucleotides link together in DNA, they form a chain through phosphodiester bonds between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the sugar of the next, creating a long, continuous strand of DNA.
What is the significance of the antiparallel structure of DNA strands?
-The antiparallel structure of DNA means that the two strands run in opposite directions. This alignment ensures that the complementary base pairs (adenine with thymine, and guanine with cytosine) can properly form hydrogen bonds, maintaining the stability of the double helix.
How do the base pairs in DNA interact with each other?
-Base pairs in DNA interact through hydrogen bonds: adenine pairs with thymine via two hydrogen bonds, and guanine pairs with cytosine via three hydrogen bonds. These interactions hold the two DNA strands together.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
生命科學(一) Ch7-3 A Tour of the Cell

Transcription and Translation: From DNA to Protein

Genetica molecular. Replicación, transcripción y traducción. 4º ESO - Bio[ESO]sfera

2 hubungan gen dna kromosom
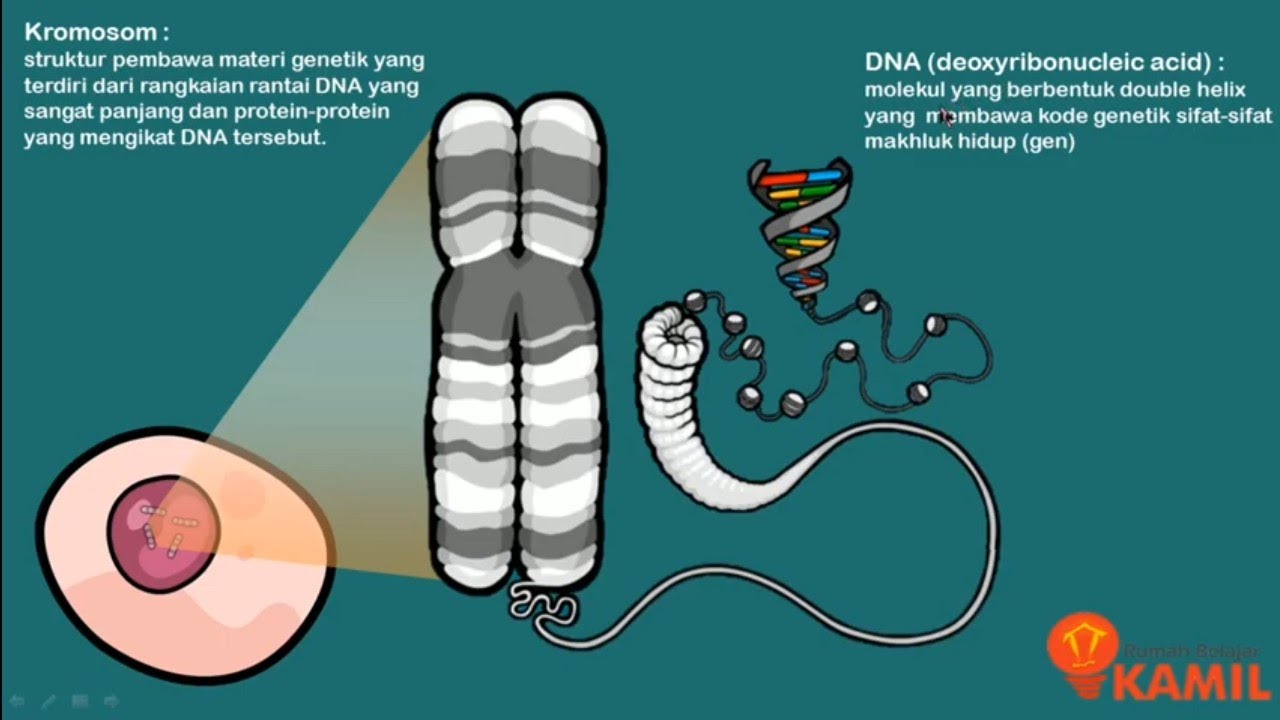
IPA Kelas 9 : Pewarisan Sifat I (Materi Genetik : Kromosom, DNA dan RNA)

A1.2 Structure of DNA and RNA [IB Biology SL/HL]
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
