The Wet Collodion Process
Summary
TLDRIn 1851, Frederick Scott Archer invented the wet collodion process, revolutionizing photography with detailed negatives and multiple print copies. The process, which dominated from 1851 to 1880, required fast action as the collodion dried quickly. Photographers used portable darkrooms to develop the plates immediately after exposure. The process involved several precise steps, from preparing the glass plates to varnishing the final print. Wet collodion negatives were commonly printed on albumen paper, which became popular for its glossy, detailed prints. This method remained in use until it was eventually replaced by more industrialized processes around 1880.
Takeaways
- 😀 The wet collodion process, invented by Frederick Scott Archer in 1851, revolutionized photography by allowing for finely detailed images on paper and unlimited prints.
- 😀 Unlike earlier photographic methods, the wet collodion process required rapid execution due to the short time window before collodion dried and lost its sensitivity.
- 😀 The process involved several critical steps, including preparing the glass plate, applying a photosensitive collodion mixture, and immersing the plate in silver nitrate to make it light-sensitive.
- 😀 After sensitizing the plate, it was exposed to light inside a camera for a specified time to capture the image.
- 😀 The exposed plate had to be immediately developed in a darkroom, followed by fixing and washing to preserve the image.
- 😀 After development, the plate was varnished to protect the fragile surface and maintain the quality of the image.
- 😀 Albumen prints, made by exposing wet collodion negatives to sunlight, were the most common method of reproducing these photographs.
- 😀 The wet collodion process was dominant from 1851 until about 1880, after which more industrialized photographic methods replaced it.
- 😀 The process required a portable darkroom because collodion dried quickly, and this allowed photographers to develop images immediately after exposure.
- 😀 The wet collodion process was more advanced than previous methods like the daguerreotype and calotype, offering improved image quality and the ability to make multiple prints from a single negative.
Q & A
What was the key invention of Frederick Scott Archer in 1851?
-Frederick Scott Archer invented the wet collodion process, which allowed photographers to create finely detailed negatives on glass plates and produce an unlimited number of prints.
How did the wet collodion process improve upon earlier photographic methods?
-The wet collodion process improved upon the daguerreotype and the calotype by enabling the production of detailed images on paper and the ability to print multiple copies.
Why was the wet collodion process used primarily between 1851 and 1880?
-The wet collodion process was dominant between 1851 and 1880 because it provided superior image quality and allowed for multiple copies to be made, making it the go-to method for photographers in Europe and North America.
What challenge did photographers face when working with the wet collodion process?
-Photographers had to work quickly with the wet collodion process because the collodion would dry and lose its sensitivity after about 10 minutes, requiring the use of portable darkrooms to develop the plates immediately.
What are the critical steps involved in creating a wet collodion image?
-The process involves smoothing and polishing the glass plate, cleaning it, adding a photosensitive mixture to the collodion, dipping it in a silver nitrate bath, exposing it in the camera, developing, fixing, washing, and varnishing the plate.
What chemicals are used in the preparation of the wet collodion plate?
-The preparation of the wet collodion plate involves a mixture of iodides, bromides, ether, and alcohol to make the collodion photosensitive, along with silver nitrate for sensitivity to light.
What is the role of the silver nitrate bath in the wet collodion process?
-The silver nitrate bath makes the collodion-coated plate sensitive to light, allowing it to record the image when exposed inside the camera.
How was the image developed after exposure?
-After exposure, the plate is taken to the darkroom, where it is developed by pouring a developer onto the plate. The development process must be done evenly to avoid leaving marks, and it is then stopped with water.
What is the purpose of varnishing the wet collodion plate?
-Varnishing the wet collodion plate is necessary to protect the fragile image surface from damage, as the plate is heated and a clear coat of varnish is applied.
How were albumen prints made from wet collodion negatives?
-Albumen prints were made by floating photographic paper on a solution of egg whites, then treating it with silver nitrate. After drying, the paper was placed in contact with the wet collodion negative and exposed to sunlight, resulting in a print.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
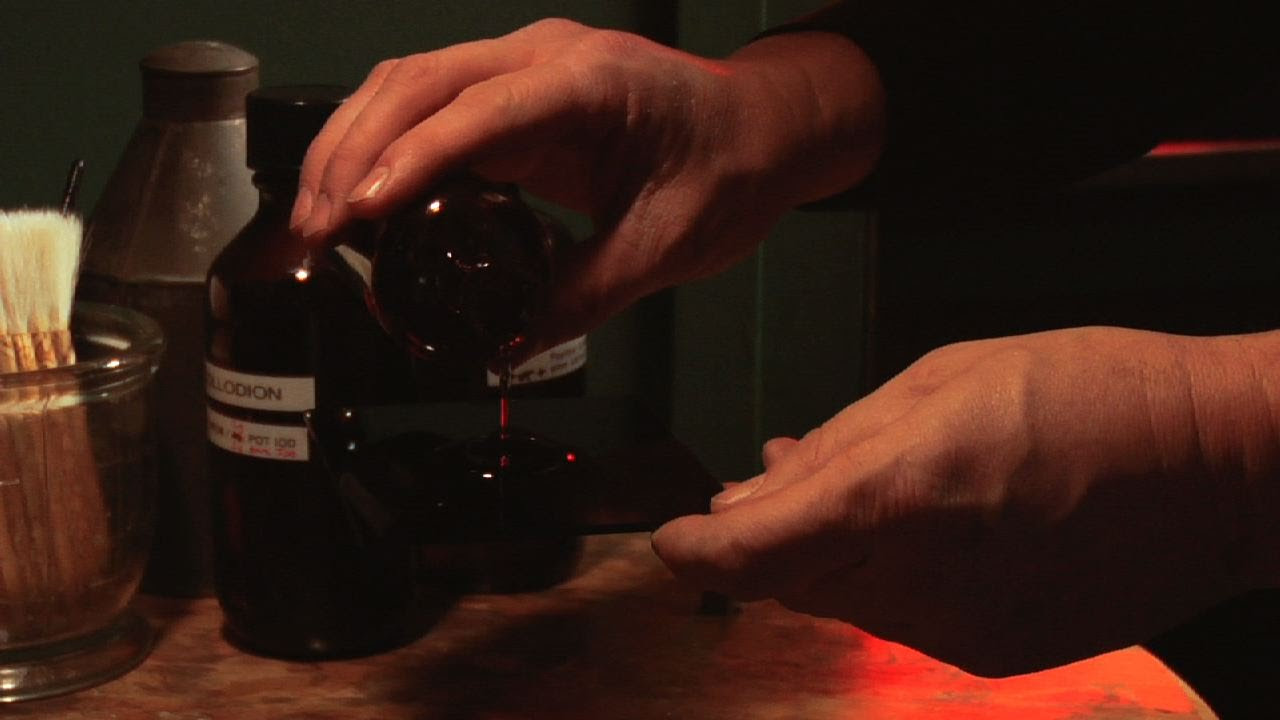

The Collodion - Photographic Processes Series - Chapter 5 of 12
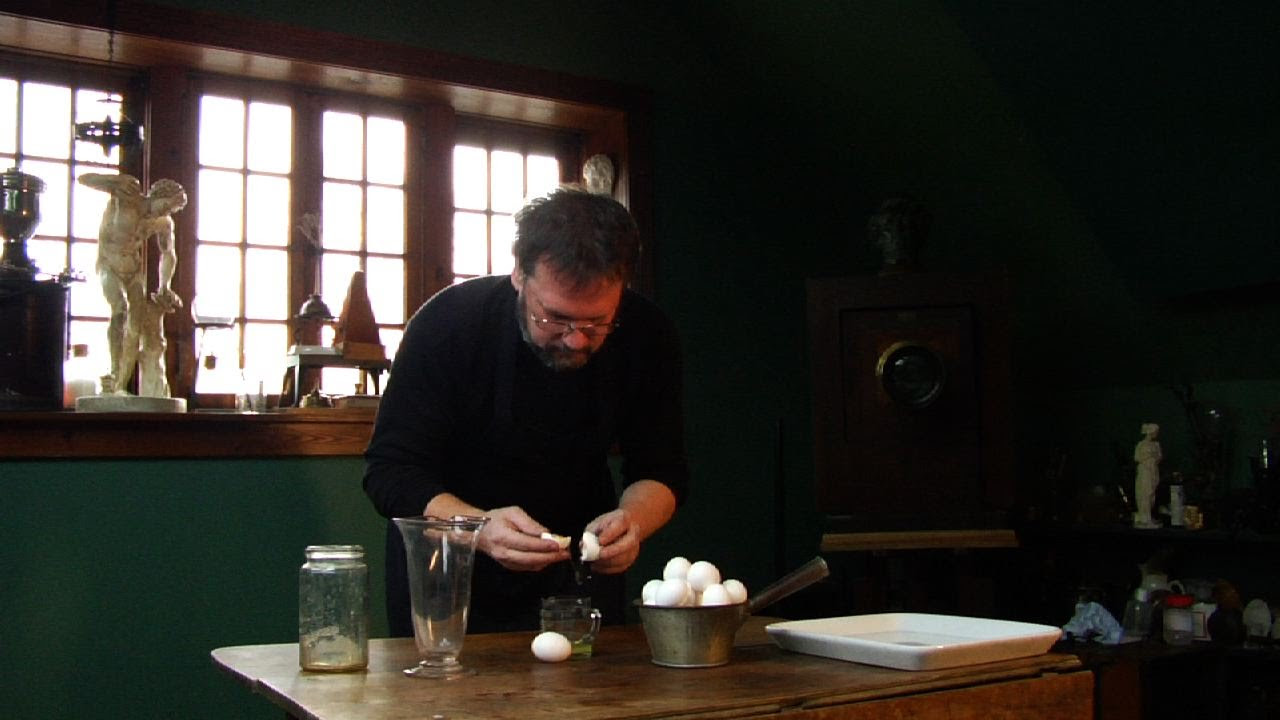

The Albumen Print - Photographic Processes Series - Chapter 6 of 12
Compare and Contrast Same Topic in Different Multimodal Texts
Cara Print Di Laptop Atau Komputer | Ngeprint Dokumen Di Laptop Untuk Pemula

Satellites Use 'This Weird Trick' To See More Than They Should - Synthetic Aperture Radar Explained.
Digital Camera Film Scanning | A how to and look inside fotoScan by Foto Care
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
