Rangkuman Materi Matematika Kelas 2 SD Semester Genap (2) || Kurikulum Merdeka ||
Summary
TLDRThis educational video provides a comprehensive summary of second-grade mathematics lessons for the second semester, based on the Merdeka Curriculum. Topics covered include fractions (1/2, 1/4), measurements of weight and time (including analog and digital clocks), basic arithmetic concepts such as tens and ones, comparing and ordering numbers, and using diagrams (bar and picture charts) to represent data. The video aims to help students understand these concepts in a fun, engaging way, with clear explanations and examples to make learning accessible and enjoyable.
Takeaways
- 😀 Fractions are non-whole numbers expressed as a/b, where 'a' is the numerator and 'b' is the denominator. Examples include 1/2 and 1/4.
- 😀 A fraction like 1/2 represents half of an object or group, such as a pizza divided into two equal parts.
- 😀 When dividing an object into four equal parts, each part represents 1/4, as seen with the example of a pizza divided into four slices.
- 😀 Half of a collection of objects is when the total number is divided into two equal parts. For example, 12 shoes divided into 2 gives 6 shoes per part.
- 😀 Weight comparison can be made using non-standard units such as marbles, coins, or tennis balls, with objects like a banana being compared to the weight of 6 marbles.
- 😀 The standard weight units include kilogram, hectogram, decagram, and gram, with conversions between them based on powers of 10.
- 😀 Time can be measured using analog and digital clocks. Analog clocks show hours, minutes, and seconds, while digital clocks display the time in numbers.
- 😀 In a 24-hour day, the hour hand on an analog clock makes two full rotations, one from midnight to noon, and another from noon to midnight.
- 😀 Simple time calculation can be done by subtracting start and end times. For example, if Mila starts studying at 6:30 PM and finishes at 7:00 PM, the total time is 30 minutes.
- 😀 Place value plays a crucial role in understanding numbers, such as the difference between tens and ones. For example, the number 37 has 3 tens and 7 ones.
- 😀 Comparing and ordering numbers can be done by first comparing the tens place, then the ones place if the tens are the same. For example, 34 > 33 because 34 has more tens.
- 😀 Data visualization can be done using bar charts or pictograms. In a bar chart, each line represents a specific quantity, and in a pictogram, each symbol represents a set number of items.
Q & A
What is a fraction, and how is it represented?
-A fraction represents part of a whole and is written in the form of a/b, where 'a' is the numerator (the number of parts) and 'b' is the denominator (the total number of equal parts).
What is the meaning of 1/2 in fractions?
-1/2 represents dividing a whole into two equal parts. For example, if a pizza is divided into two equal slices, each slice represents 1/2 of the pizza.
How is 1/4 represented, and what does it mean?
-1/4 is a fraction where a whole is divided into four equal parts. For example, a pizza cut into four equal slices represents 1/4 per slice.
What are some examples of non-standard units of measurement for weight?
-Non-standard units of measurement for weight include objects like marbles, coins, or tennis balls. For example, the weight of a banana can be measured by how many marbles it is equivalent to.
How do you convert between different units of weight, such as kilograms to hectograms?
-To convert between units of weight, moving one step down the weight scale multiplies by 10, and moving one step up divides by 10. For example, 1 kg equals 10 hectograms, and 10 hectograms equals 1 kg.
What is the difference between an analog and a digital clock?
-An analog clock uses hands (hour, minute, and second) to display time, while a digital clock shows the time in numerical form. The analog clock involves reading the position of the hands, and the digital clock directly shows the time as numbers.
How do you calculate the duration of an activity using a clock?
-To calculate the duration of an activity, subtract the starting time from the ending time. For example, if Mila started studying at 18:30 and finished at 19:00, the duration of study is 30 minutes.
What do tens and ones represent in number formation?
-In number formation, tens represent groups of 10, and ones represent individual units. For example, the number 37 consists of 3 tens (30) and 7 ones.
What is the method for comparing two numbers using symbols?
-To compare two numbers, first compare the tens place. If the tens are the same, then compare the ones place. Use symbols like '<' for 'less than', '>' for 'greater than', and '=' for 'equal to'.
How are data and quantities represented in a diagram?
-Data can be represented in diagrams like bar graphs and picture graphs. A bar graph uses sticks or lines to represent quantities, while a picture graph uses symbols (like smiley faces) where each symbol represents a specific number of items.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Materi Matematika Kelas X Kurikulum Merdeka!! (Semester 2)

Rangkuman Materi Bahasa Indonesia Kelas 2 SD Semester Genap (2) || Kurikulum Merdeka ||

Rangkuman Materi PJOK Kelas 2 SD Semester Genap (2) || Kurikulum Merdeka ||
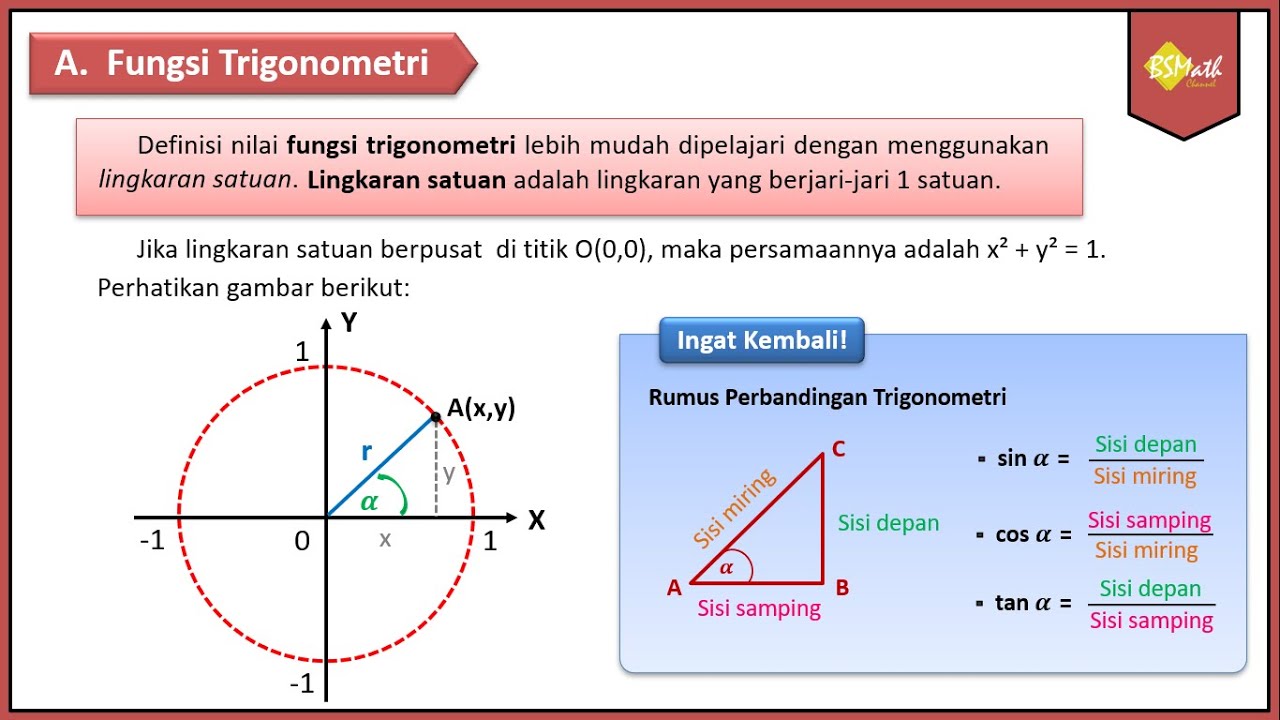
Tanda Fungsi Trigonometri Tiap Kuadran | Matematika Tingkat Lanjut SMA Kelas XI Kurikulum Merdeka

Pengembangan Wilayah, Tata Ruang & Pengaruhnya Terhadap Kebahagiaan #Kurikulum Nasional Geo Klas XII

Pengenalan Materi Pokok Pendidikan Agama Katolik dan Budi Pekerti SMA/SMK Kelas 12 semester 2
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
