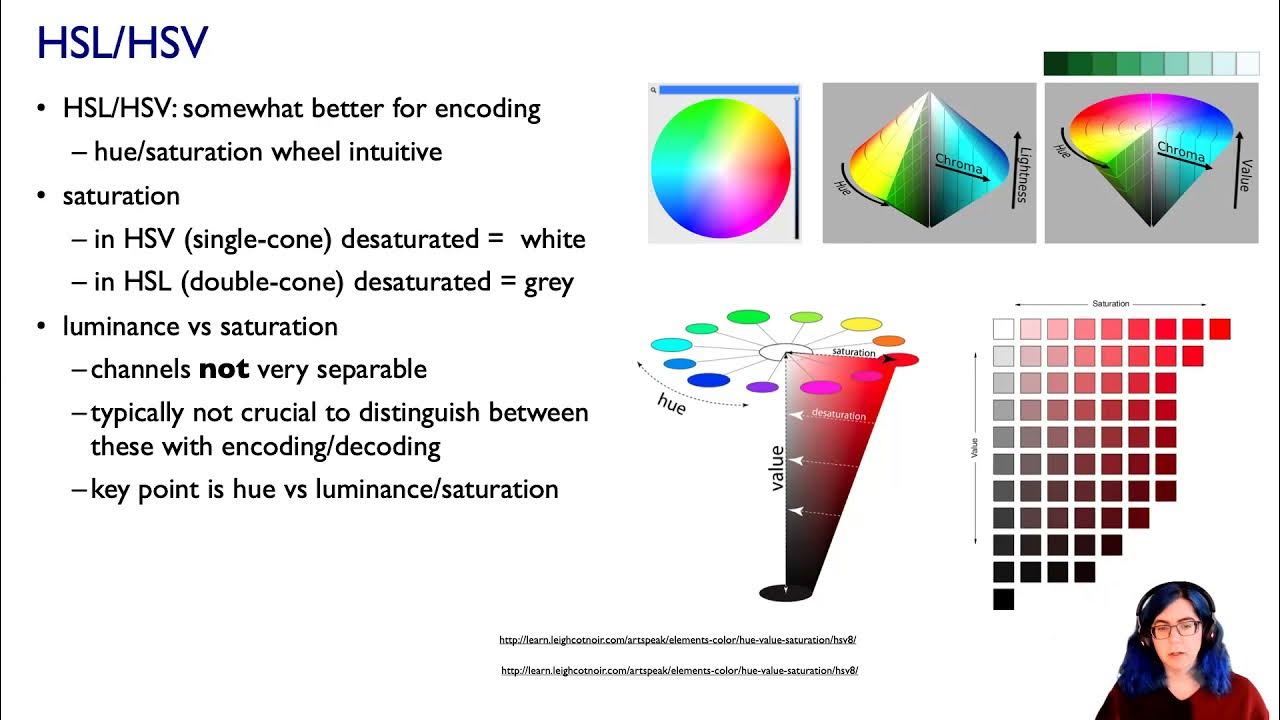
Now You See It: Lessons from Research on Perception for Design of Data Visualizations
Summary
TLDRThe script delves into the complexities of visual perception and its crucial role in data visualization design. It highlights how understanding principles from neuroscience, Gestalt psychology, and cognitive load theory can significantly improve the effectiveness of graphics. Key concepts such as visual illusions, the organization of elements in perception, and the balance between cognitive load and design choices are explored. The script emphasizes the need for thoughtful design to cater to both experts and novices, considering factors like abstraction, familiarity, redundancy, and emotional engagement in visual communication.
Takeaways
- 😀 Effective data graphics should clarify information and support analytical thinking, keeping the viewer's perception in mind.
- 😀 Visual perception is not always what we see, as optical illusions show how our brain actively interprets visual information.
- 😀 The eye-camera analogy breaks down because the brain processes and synthesizes information, rather than just recording it.
- 😀 Gestalt psychology principles, such as similarity, proximity, closure, and good continuation, are key in designing effective visualizations.
- 😀 Cognitive load refers to the mental effort required to process a visualization. It can be influenced by design elements like abstraction and redundancy.
- 😀 A well-designed graphic can reduce cognitive load, especially when it balances familiarity and novelty, and uses redundancy effectively.
- 😀 The cognitive load of a design also depends on its dimensionality, density, and the level of ornamentation used.
- 😀 The effectiveness of a design can vary depending on the audience’s expertise and their ability to recognize patterns specific to their field.
- 😀 Emotional engagement can enhance memory retention, meaning well-crafted ornamentation in designs can sometimes improve long-term understanding.
- 😀 The context and time constraints of presenting information (e.g., a 20-second slide) also influence how much information can be processed by the audience.
Q & A
What is the primary goal of data graphics, and how does it relate to effective communication?
-The primary goal of data graphics is to clarify information and support analytical thinking. Effective communication, including visualization, should always prioritize the perceiver, ensuring that the design helps the viewer understand the data clearly and intuitively.
How does research on visual perception influence graphic design?
-Research on visual perception provides insights into how the brain processes visual information. This knowledge helps designers create graphics that align with how people naturally perceive and interpret visual stimuli, making graphics more effective in conveying information.
Why is the 'eye as a camera' analogy not entirely accurate?
-The 'eye as a camera' analogy breaks down because the brain does not merely record visual data; it actively processes and synthesizes the information. The brain analyzes different aspects of a scene (e.g., color, location, and movement) through parallel pathways, and prior experiences influence how we perceive things.
What role do Gestalt principles play in visual perception and design?
-Gestalt principles highlight how the brain organizes visual information, emphasizing that the whole is greater than the sum of its parts. Principles like similarity, proximity, closure, and good continuation guide how we group elements and interpret visual scenes, making them essential for effective graphic design.
Can you explain the Gestalt principle of closure with an example?
-The principle of closure suggests that we tend to perceive incomplete shapes as whole. For example, in a broken triangle shape, the brain fills in the gaps, leading us to perceive it as a complete triangle, even if parts of the border are missing.
How does cognitive load impact the effectiveness of a data visualization?
-Cognitive load refers to the mental effort required to process information. If a design imposes too much cognitive load, it can overwhelm the viewer, making it harder for them to understand the data. Proper design should aim to balance cognitive load to facilitate easier comprehension.
What are the six dimensions of cognitive load in data visualization design?
-The six dimensions of cognitive load are: 1) Concrete vs. abstract design, 2) Familiar vs. original graphical forms, 3) Information density (light vs. dense), 4) Dimensionality (2D vs. multi-dimensional), 5) Redundancy (strategic vs. non-redundant), and 6) Decoration (adorned vs. unadorned).
Why does cognitive load depend on the audience's expertise?
-Cognitive load varies depending on the audience's familiarity with the subject. Experts can process information more quickly and recognize patterns, while novices may find the same information more overwhelming due to a lack of familiarity and pattern recognition.
What does the term 'common fate' refer to in Gestalt psychology, and how is it applied in design?
-Common fate refers to the tendency to perceive elements that move in the same direction as belonging together. In design, this principle can be used to group related elements that share movement or direction, helping to visually organize data and guide the viewer's attention.
How does emotion influence perception and understanding of data visualizations?
-Emotion plays a key role in how we attend to and process information. Some studies suggest that ornamentation in designs can enhance emotional engagement and improve long-term memory of the information, suggesting that visual design can influence not only cognition but also emotional responses.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)