A Content Level Comparison of COSO ERM and ISO 31000
Summary
TLDRIn this session, Manos Kval, co-founder and chief risk officer at Risk Spotlight, compares the Koso ERM and ISO 31,000 frameworks, offering insights for both those developing and those reviewing ERM processes. The video highlights key similarities, such as the importance of ERM in achieving organizational objectives and risk management integration with business strategy. It also contrasts the two frameworks on topics like risk definitions, responses, and likelihood analysis. Kval encourages organizations to use the best elements of both standards and cautions against relying solely on consensus-based frameworks for innovation in risk management.
Takeaways
- 😀 The analysis compares the COSO ERM and ISO 31000 frameworks for risk management, focusing on their similarities and differences.
- 😀 There are two main perspectives for the analysis: one for organizations developing new ERM frameworks, and another for reviewing and revising existing frameworks.
- 😀 Both COSO ERM and ISO 31000 emphasize that risk management should align with organizational objectives and be integrated into core business processes.
- 😀 Key similarities between COSO ERM and ISO 31000 include the importance of executive support, stakeholder engagement, and the need for ongoing risk management processes.
- 😀 One significant difference is that ISO 31000 considers both positive and negative consequences as risks, while COSO ERM only considers negative consequences.
- 😀 ISO 31000 provides a broader range of potential risk responses, including responses for increasing or decreasing both likelihood and consequences, while COSO focuses mainly on reducing risks.
- 😀 COSO ERM includes both inherent and residual risk analysis, while ISO 31000 only covers residual risk analysis.
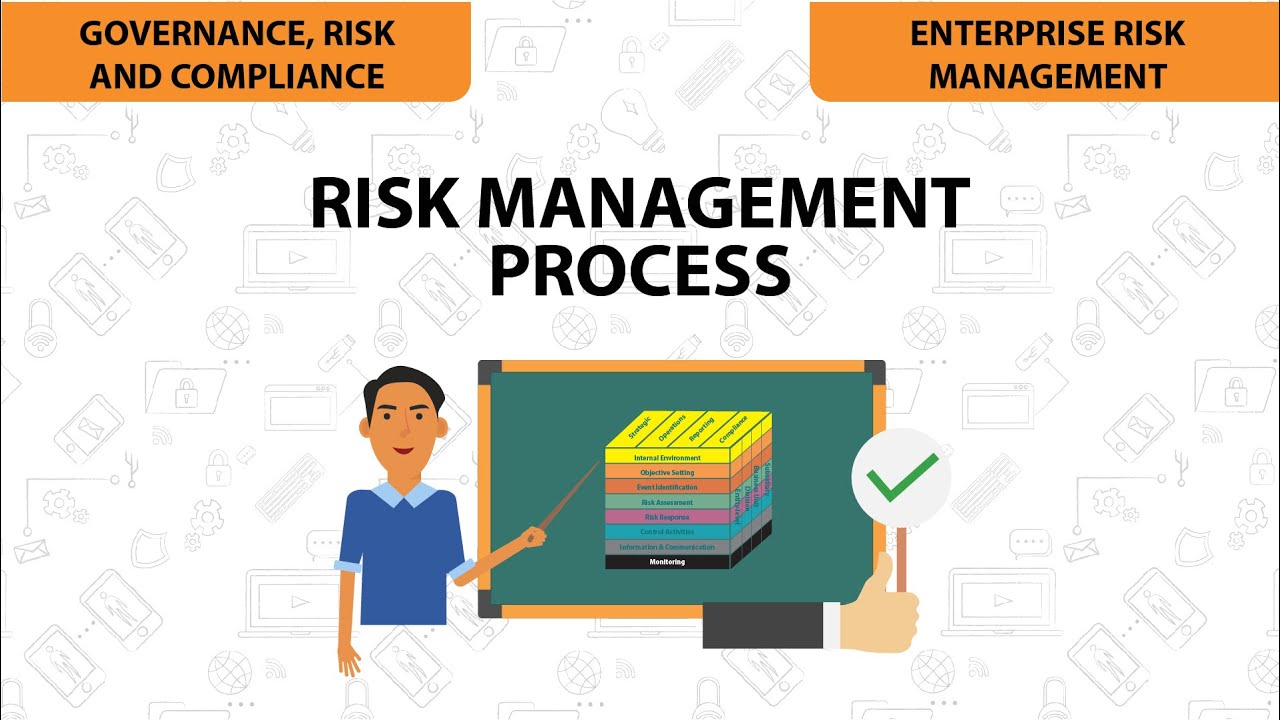
- 😀 In terms of process, ISO 31000 combines risk identification, analysis, and evaluation within a single step, whereas COSO ERM separates risk identification from risk assessment.
- 😀 ISO 31000 recommends conducting likelihood analysis at the consequence level, whereas COSO ERM implies it is done at the event level.
- 😀 ISO 31000 offers more detailed guidance on risk assessment techniques, risk management policies, and defining the ERM framework compared to COSO ERM, which focuses more on risk management processes.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of this session presented by Manos Kval?
-The session focuses on comparing two key risk management frameworks: Koso ERM and ISO 31,000, to help organizations understand their similarities and differences for better implementation of an Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework.
What are the two perspectives mentioned in the session for analyzing ERM frameworks?
-The two perspectives are: (1) Someone responsible for leading the creation of an ERM framework in an organization, often in new or less mature organizations, and (2) Someone responsible for reviewing and revising an existing ERM framework, typically in organizations with established ERM processes.
What do both Koso ERM and ISO 31,000 frameworks emphasize about the role of ERM in organizations?
-Both frameworks emphasize that ERM should facilitate the achievement of organizational objectives, help manage uncertainties, be tailored to the organization's context, be integrated into business strategy, and require executive support for successful adoption.
How do Koso ERM and ISO 31,000 frameworks differ in terms of risk identification and analysis?
-Koso ERM only considers events with negative consequences as risks, while ISO 31,000 considers both events with positive and negative consequences as risks. Additionally, Koso focuses on risk controls to mitigate negative risks, while ISO allows for a broader range of risk responses, including increasing risk in certain contexts.
What is the key distinction in how Koso ERM and ISO 31,000 approach risk responses?
-Koso ERM mainly focuses on reducing the likelihood or impact of risks, whereas ISO 31,000 provides a broader range of responses, including changing the likelihood or consequences of risks (not just reducing them), depending on the context.
What does ISO 31,000 provide that Koso ERM does not?
-ISO 31,000 provides more extensive coverage of defining and maintaining the ERM framework, risk management policy, and includes a detailed guide on risk assessment techniques. It also defines terms like risk appetite, tolerance, and vulnerability, which Koso does not.
Why does the session suggest organizations should consider using both Koso ERM and ISO 31,000 frameworks?
-The session suggests using both frameworks because no single framework or standard will cover all the needs of an organization’s ERM. By integrating elements from both, an organization can build a more comprehensive and tailored ERM framework.
What is the difference between 'inherent risk analysis' and 'residual risk analysis' as discussed in the session?
-Inherent risk analysis, which is covered by Koso ERM, refers to the level of risk before controls are applied, while residual risk analysis, emphasized in ISO 31,000, assesses the remaining risk after controls have been implemented. ISO 31,000 does not cover inherent risk analysis.
How do Koso ERM and ISO 31,000 differ in their analysis of likelihood and consequences in risk assessment?
-Koso ERM analyzes likelihood at the event level, while ISO 31,000 recommends conducting likelihood analysis at the consequence level. ISO's approach provides a more detailed analysis of potential outcomes and their likelihood.
What caution does the session give regarding the use of external frameworks like Koso ERM and ISO 31,000?
-The session cautions that external frameworks often reflect widely adopted practices and consensus, which means they may not include new or innovative ideas in risk management. Organizations aiming for best-in-class risk management may need to develop their own innovative practices, which could later influence future revisions of external standards.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Utilising ChatGPT To Evaluate Operational Risk Knowledge

Generative AI vs. Conventional AI: Introduction For Operational Risk Professionals

SML Talks Reza Abdulmajid Preview 3

67. Is Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) overrated? | A critical look at ERM methodologies

CORPORATE RISK MANAGEMENT
SI GRC VHD M08 141021 V01 UP
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
