Dividend Discount model (multistage) || Equity || CFA Level-1
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the multi-stage growth dividend model, a financial approach used to estimate the present value of dividends when growth rates change over different time periods. The model is broken down into stages, where dividends grow at different rates initially before stabilizing to a constant growth rate. The speaker demonstrates the steps to calculate dividends for each year using different growth rates and applies the Gordon Growth Model for stable growth. The video provides a detailed example and formula to help viewers understand how to estimate a company's value through this model.
Takeaways
- 😀 Multi-Stage Dividend Growth Model applies different growth rates over multiple years, before transitioning to a constant growth rate.
- 😀 The process involves calculating expected dividends for each year, factoring in variable growth rates.
- 😀 The present value of dividends is calculated by adjusting for the growth rate using formulas like D1/(1+k), where k is the discount rate.
- 😀 The model accounts for cases where a company has non-constant growth in the early years, transitioning to a stable growth rate later on.
- 😀 Growth rates in the model can be applied year by year, e.g., 25% for the first few years, then dropping to a lower rate in subsequent years.
- 😀 The value of a company's shares can be determined by calculating the present value of expected future dividends using the Multi-Stage Dividend Growth Model.
- 😀 When different growth rates are used for various years, individual cash flows must be calculated for each year before applying the constant growth rate for the long term.
- 😀 The model helps estimate the value of stocks where dividends change over time, reflecting more accurate future expectations.
- 😀 The transition from non-constant to constant growth rates in dividend calculation is key for estimating long-term stock value.
- 😀 The methodology ensures that as growth rates stabilize, the model can seamlessly calculate the present value of future dividends using a constant growth rate formula.
Q & A
What is a multi-stage growth model in finance?
-A multi-stage growth model is a financial model that assumes a company’s dividend growth rate will change over time. Initially, the company may experience higher growth rates, which gradually stabilize into a constant rate after several years.
Why would a company have different growth rates at different stages?
-A company may have different growth rates at various stages due to market conditions, product life cycles, or changes in the business environment. Early years might show rapid growth, while later years experience stabilization or a slower, constant growth rate.
How is the present value of dividends calculated in a multi-stage growth model?
-In a multi-stage growth model, the present value of dividends is calculated by discounting each year’s expected dividends individually. For each stage with different growth rates, the expected dividends are calculated and then discounted to the present using the appropriate discount rate (cost of equity).
What happens when a company transitions from a high growth phase to a constant growth phase?
-When a company transitions from a high growth phase to a constant growth phase, the growth rate of dividends stabilizes. At this point, a constant growth rate is applied to future dividends, and the valuation uses a standard dividend discount model to estimate the company’s value.
Can a multi-stage growth model have more than two stages of growth?
-Yes, a multi-stage growth model can have more than two stages. For example, a company may experience different growth rates for each year in the first few years (e.g., 20% in year 1, 25% in year 2, etc.), followed by a final constant growth phase.
What is the formula used to calculate the present value of dividends for each year in the multi-stage model?
-The formula to calculate the present value of dividends for each year in a multi-stage model is P0 = D1 / (1 + ke), where D1 is the dividend in the first year, and ke is the required rate of return or discount rate. For subsequent years, the dividends are adjusted for the expected growth rate.
How do you handle different growth rates in each stage of the model?
-Each stage with a different growth rate is handled by calculating the dividend for that specific year using the respective growth rate. The present value of those dividends is then discounted to the present, and the final value is obtained by summing these discounted dividends.
What is the role of the cost of equity (ke) in the multi-stage growth model?
-The cost of equity (ke) represents the required return for investors, which is used as the discount rate to bring future dividends back to their present value. It is crucial for determining the valuation of the company in the model.
Why is it important to use a multi-stage growth model instead of a constant growth model?
-A multi-stage growth model is more realistic in cases where a company’s growth rate changes over time. Unlike the constant growth model, which assumes a fixed growth rate, the multi-stage model accounts for varying growth rates at different stages of the company’s life cycle.
What are the potential disadvantages of using a multi-stage growth model?
-One disadvantage is the complexity of the model, as it requires careful estimation of multiple growth rates and the corresponding dividends for each stage. This can lead to errors or uncertainty if growth rates are difficult to predict accurately.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
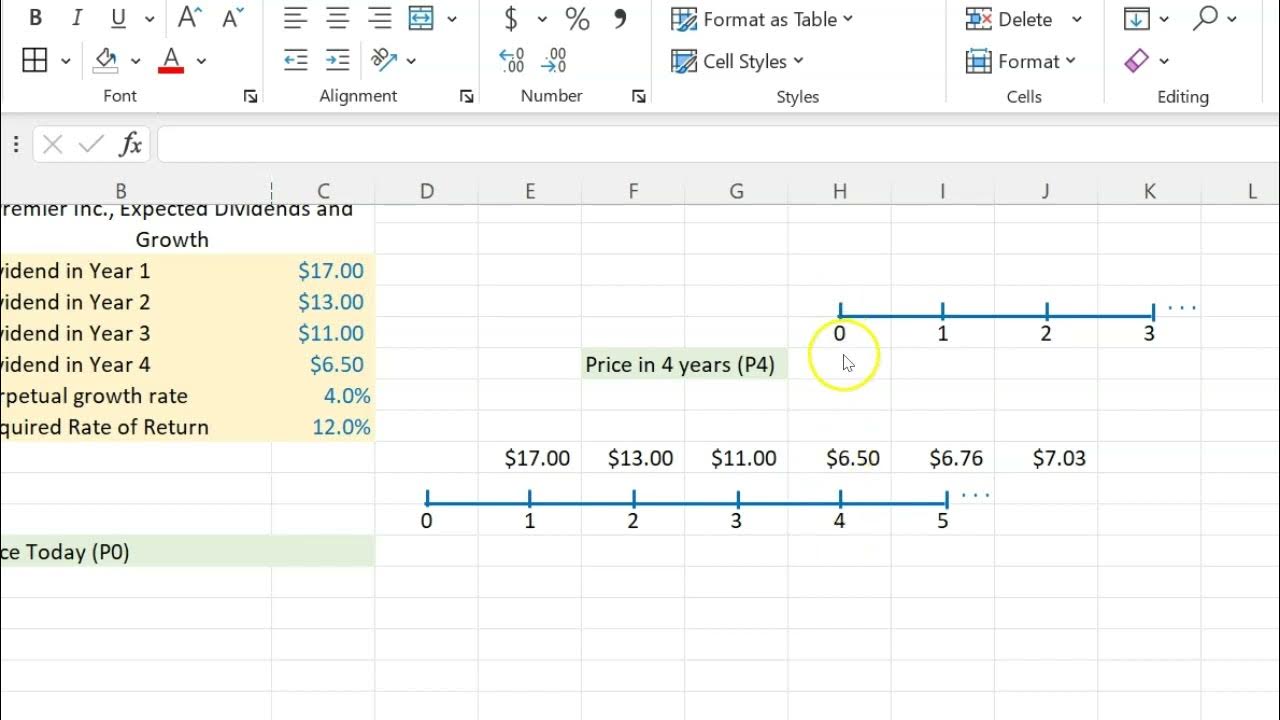
Stock Valuation With Non-Constant Dividends (Using Excel)

Dividend Discount Model (DDM)

Dividend Discount Gordon Model || CFA Level-1 || Equity

Dividend Discount Model || Equity || CFA Level-1

Introduction to Equity Valuation || CFA Level-1 || Equity

Should You BUY a HOUSE or RENT? Check with this EXCEL SHEET! | Ankur Warikoo Hindi
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
