The Brain—Lesson 2—How Neurotransmission Works
Summary
TLDRThe communication between neurons begins when an electrical impulse, called an action potential, travels along the axon of a presynaptic neuron. Upon reaching the axon terminal, the impulse causes vesicles to release neurotransmitters into the synaptic space. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, triggering an action potential that moves toward the cell body. After signaling, neurotransmitters are either broken down by enzymes or reabsorbed into the presynaptic neuron for future release. This process repeats with each action potential, enabling continuous communication between neurons.
Takeaways
- 😀 Communication between neurons starts when an action potential travels along the axon of a presynaptic neuron.
- 😀 The action potential cannot cross the synaptic space and triggers vesicles to move towards the axon terminal.
- 😀 Vesicles fuse with the axon terminal membrane, releasing neurotransmitters into the synaptic space.
- 😀 Neurotransmitters are chemicals that bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron.
- 😀 The binding of neurotransmitters to receptors can trigger an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron.
- 😀 The electrical signal moves toward the cell body of the postsynaptic neuron after triggering an action potential.
- 😀 After releasing its message, the neurotransmitter detaches from the receptor and returns to the synaptic space.
- 😀 Enzymes in the synaptic space break down some neurotransmitters, while others are reabsorbed into the presynaptic neuron.
- 😀 Transporter proteins in the presynaptic neuron carry the neurotransmitter back into the cell.
- 😀 The reabsorbed neurotransmitter is repackaged into vesicles for future release during subsequent action potentials.
- 😀 This entire process repeats every time an action potential reaches the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron.
Q & A
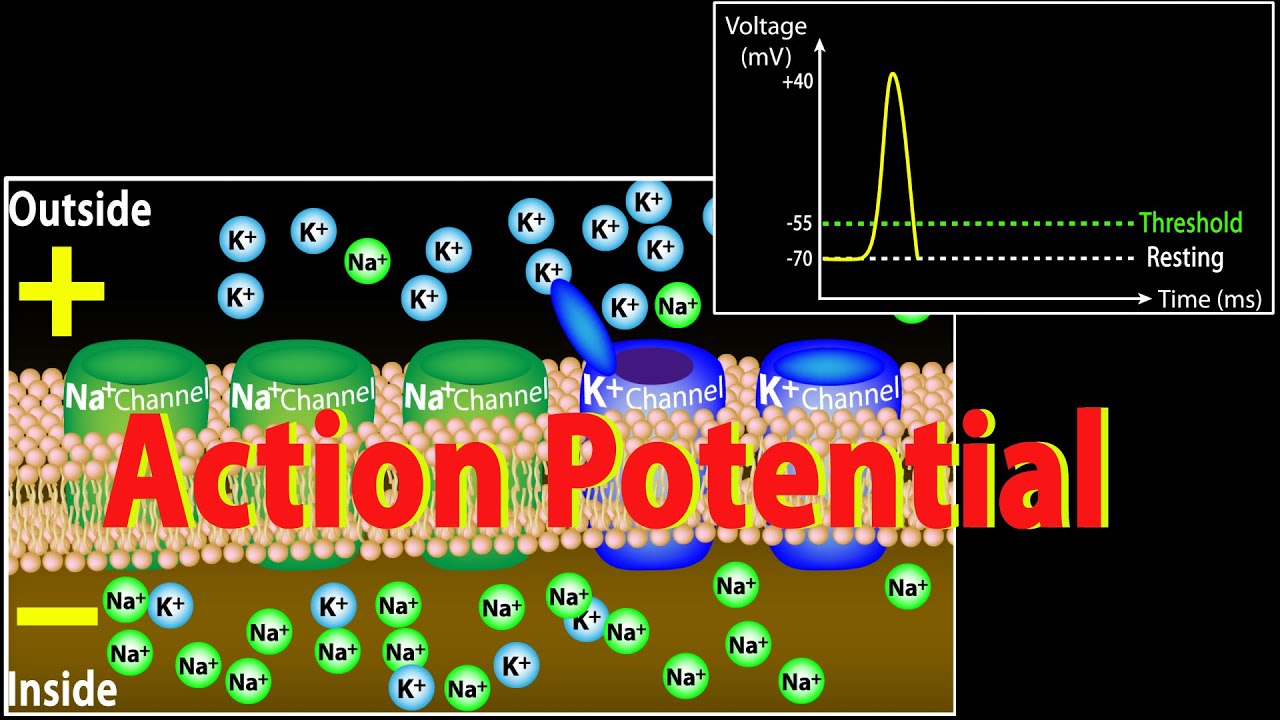
What is an action potential, and what role does it play in neuron communication?
-An action potential is an electrical impulse that travels along the axon of a presynaptic neuron. It plays a crucial role in initiating the process of communication between neurons by triggering the release of neurotransmitters at the axon terminal.
What happens when an action potential reaches the axon terminal?
-When an action potential reaches the axon terminal, it causes vesicles containing neurotransmitters to move toward and fuse with the terminal membrane, releasing their contents into the synaptic space.
What are neurotransmitters, and how do they function in neuron communication?
-Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers released from vesicles at the axon terminal. They travel across the synaptic space and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, which can trigger an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron.
How do neurotransmitters interact with the postsynaptic neuron?
-Neurotransmitters bind to special proteins called receptors on the postsynaptic neuron. This binding can trigger an electrical signal, or action potential, in the postsynaptic neuron, moving it toward the cell body.
What happens to neurotransmitters after they release their message?
-After releasing their message, neurotransmitters detach from the receptors and are either broken down by enzymes in the synaptic space or taken back into the presynaptic neuron through transporter proteins.
What role do transporter proteins play in the communication process?
-Transporter proteins help take neurotransmitters back into the presynaptic neuron, where they are repackaged into vesicles to be used again in future communications.
Why is it important for neurotransmitters to be recycled?
-Recycling neurotransmitters ensures that they are readily available for release the next time an action potential reaches the axon terminal, maintaining efficient and continuous communication between neurons.
What happens to neurotransmitters that are not taken back into the presynaptic neuron?
-Neurotransmitters that are not taken back are typically broken down by enzymes present in the synaptic space, preventing them from interfering with further signaling.
What is the role of the synaptic space in neuron communication?
-The synaptic space is the small gap between two neurons where neurotransmitters travel to communicate between the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons. It is essential for the transmission of signals from one neuron to another.
How does the entire process of neurotransmitter release and uptake repeat?
-The process repeats each time an action potential reaches the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron. The neurotransmitters are released, bind to receptors, and then are either broken down or recycled, enabling continuous neuron communication.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Video Pembelajaran Biologi Impuls Lewat Sel Saraf - Materi Pelajaran Sistem Saraf

Structure and Function of a Neuron

Sinapse Química: Animação | Anatomia e etc

NEW: INTERACTIVE Animation: Action Potential in Neurons, Animation with Quiz

Overview of neuron function | Nervous system physiology | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy
Action Potential in Neurons, Animation.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
