Fungsi Dari Enzim Pencernaan
Summary
TLDRThis video script explains the role of enzymes in digestion, highlighting their production by various organs such as the salivary glands, pancreas, and liver. It covers how enzymes like amylase, lipase, protease, and nucleases break down carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and nucleic acids. Salivary glands produce ptyalin to begin carbohydrate digestion, while the pancreas releases pancreatic juice containing enzymes that further digest food. The liver produces bile, which helps emulsify fats. The coordinated actions of these enzymes are crucial for efficient digestion and nutrient absorption.
Takeaways
- 😀 Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions in digestion.
- 😀 Salivary glands produce saliva, which contains the enzyme *ptyalin* (amylase) that starts carbohydrate digestion by converting starch to maltose.
- 😀 The pancreas produces digestive juices containing enzymes like amylase, lipase, proteases, and nucleases, which break down carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and nucleic acids respectively.
- 😀 The pancreas secretes amylase to break down starch into maltose and lipase to digest fats into fatty acids and monoglycerides.
- 😀 Proteases such as trypsin and chymotrypsin continue the digestion of proteins by breaking them into amino acids.
- 😀 Carboxypeptidase assists in the hydrolysis of peptides into amino acids.
- 😀 Nucleases break down nucleic acids into nucleotides.
- 😀 Bile, produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder, is released into the duodenum to help emulsify fats, aiding in their digestion.
- 😀 The small intestine absorbs the digested nutrients after enzymes break them down into simpler molecules.
- 😀 The digestive system works with enzymes from different organs—salivary glands, pancreas, and liver—to process and break down food into absorbable nutrients.
- 😀 Each enzyme plays a specific role in digesting different food components: amylase for carbohydrates, lipase for fats, proteases for proteins, and nucleases for nucleic acids.
Q & A
What is the role of enzymes in the digestive system?
-Enzymes play a crucial role in speeding up chemical reactions in the digestive process, helping to break down food into simpler components.
Where are digestive enzymes produced in the human body?
-Digestive enzymes are produced in various organs, including the salivary glands, stomach, pancreas, and small intestine.
What is the function of the salivary glands in digestion?
-The salivary glands produce saliva, which contains the enzyme ptyalin that helps break down carbohydrates into maltose.
How many salivary glands are present in humans, and what are their names?
-Humans have four main salivary glands: the parotid gland, submandibular gland, sublingual gland, and minor salivary glands.
What is the function of the pancreas in digestion?
-The pancreas produces pancreatic juice, which contains enzymes like amylase, lipase, and proteases that assist in digesting carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
What enzymes are found in pancreatic juice, and what are their functions?
-Pancreatic juice contains amylase (which breaks down starch into maltose), lipase (which breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol), and proteases like trypsin and chymotrypsin (which break down proteins).
How does bile contribute to digestion?
-Bile, produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder, emulsifies fats, making them easier to digest by enzymes like lipase.
What is the function of the enzyme amylase?
-Amylase is responsible for breaking down starches into maltose, a simpler form of carbohydrate.
How does lipase aid in fat digestion?
-Lipase breaks down fats into fatty acids and monoglycerides, which can then be absorbed by the body.
What are proteases, and how do they contribute to protein digestion?
-Proteases, including trypsin and chymotrypsin, continue the breakdown of proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids, aiding in protein digestion.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Digestion in Human Beings 3D CBSE Class 7 Science (www.iDaaLearning.com)

Sistema digestório - Brasil Escola

Enzim pada Pencernaan Manusia

Digestive System | Summary

CBSE Class 10 | LIFE PROCESSES | 30 min Series | Exam Winner
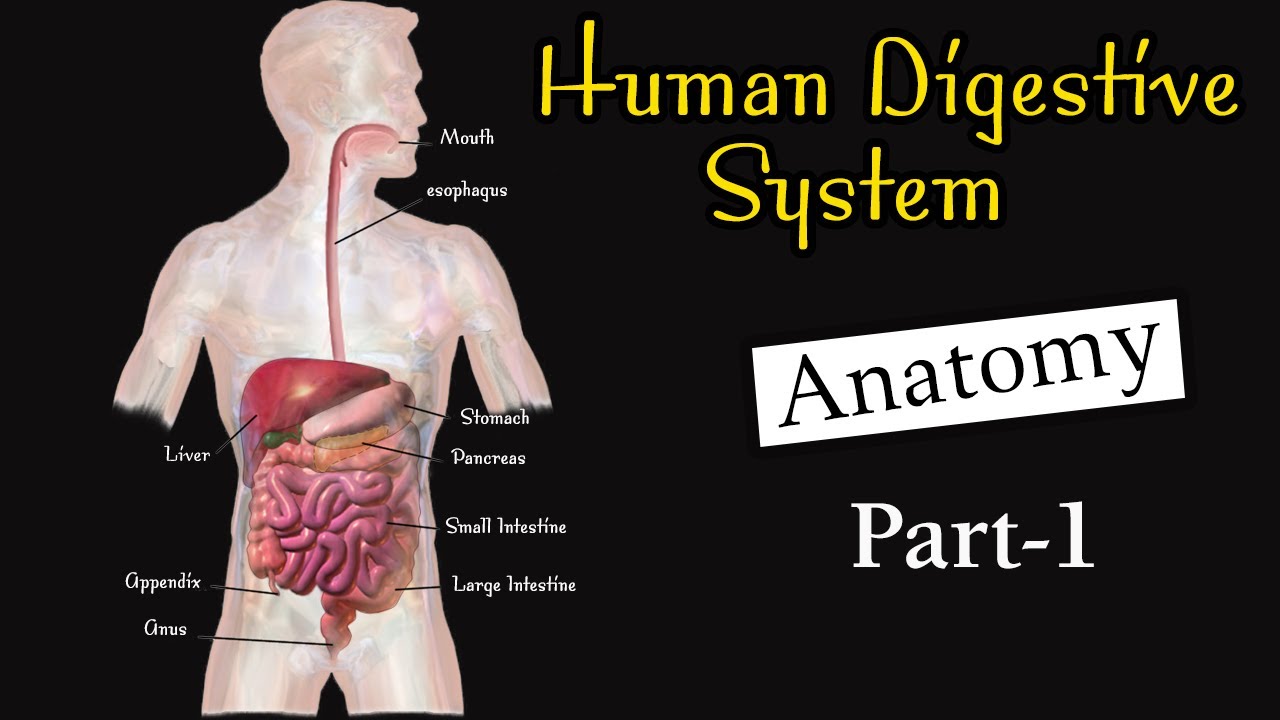
Anatomy of human digestive system I Digestive system I Digestive system class 11
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
