Sistema digestório - Brasil Escola
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Fred, a biology teacher, explains the digestive system's structure and functions in a clear and engaging manner. He covers the role of various organs, including the mouth, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine, as well as the digestive processes such as peristalsis, enzymatic breakdown, and nutrient absorption. Fred also discusses the importance of accessory organs like the pancreas, liver, and salivary glands, and how they assist in digestion. The video combines anatomy and physiology to give a comprehensive overview of digestion, from food intake to nutrient absorption and waste elimination.
Takeaways
- 😀 The digestive system is essential for absorbing nutrients and producing energy to keep the body alive.
- 😀 The basic function of the digestive system is to break down larger molecules into smaller particles for easy absorption.
- 😀 The autonomic nervous system controls the digestive system, except for chewing and swallowing.
- 😀 Physical processes in digestion include chewing, swallowing, and peristalsis, while chemical processes involve enzymatic breakdown.
- 😀 The digestive system starts in the mouth, where chewing and the release of saliva begin the breakdown of food.
- 😀 Salivary glands in the mouth release saliva containing enzymes like salivary amylase, which helps digest carbohydrates.
- 😀 The epiglottis plays a crucial role in ensuring food travels to the esophagus, not the trachea, to avoid choking.
- 😀 The stomach has two main functions: producing hydrochloric acid for protein digestion and secreting mucus to protect its lining.
- 😀 The chyme, formed in the stomach, enters the small intestine where the pH is adjusted for further digestion and nutrient absorption.
- 😀 The large intestine is responsible for absorbing water and minerals, forming feces, and hosting bacteria that aid in digestion and produce vitamins.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the digestive system?
-The primary function of the digestive system is to break down larger molecules into smaller particles, allowing the body to absorb nutrients and produce energy for the cells.
How is the digestive system controlled?
-The digestive system is primarily controlled by the autonomic nervous system, with the exception of chewing and swallowing, which are voluntary actions.
What are the two main types of processes in digestion?
-The two main types of processes in digestion are physical processes (such as chewing, swallowing, and peristalsis) and chemical processes (primarily involving digestive enzymes).
What role do the salivary glands play in digestion?
-The salivary glands produce saliva, which contains the enzyme salivary amylase that begins the digestion of starch in the mouth, turning it into smaller, digestible particles.
Why is the pH of saliva around 7 important?
-A pH of around 7 is essential for the optimal functioning of salivary amylase, the enzyme responsible for breaking down starch into simpler sugars.
What happens during swallowing, and what role does the epiglottis play?
-During swallowing, the tongue and epiglottis work together to ensure food moves into the esophagus and not the trachea. The epiglottis closes to prevent food from entering the respiratory system, guiding it into the esophagus.
What is the role of hydrochloric acid and pepsin in the stomach?
-In the stomach, hydrochloric acid creates an acidic environment that activates pepsin, an enzyme responsible for digesting proteins into smaller peptides. The acid also helps in breaking down food particles.
How does bile aid in digestion?
-Bile, produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder, emulsifies fats in the small intestine, breaking them into smaller droplets to make them easier to digest by enzymes.
What are the three parts of the small intestine, and what role do they play in digestion?
-The small intestine is divided into the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum neutralizes stomach acid and receives digestive enzymes, while the jejunum and ileum are involved in nutrient absorption.
What is the role of the large intestine in digestion?
-The large intestine absorbs water and mineral salts from the remaining undigested food. It also compacts waste into feces, assisted by bacteria that produce vitamins like B12 and K.
How does fiber help with digestion?
-Fiber cannot be digested by the human body but helps maintain healthy digestion by keeping feces moist and facilitating peristalsis, thus preventing constipation.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
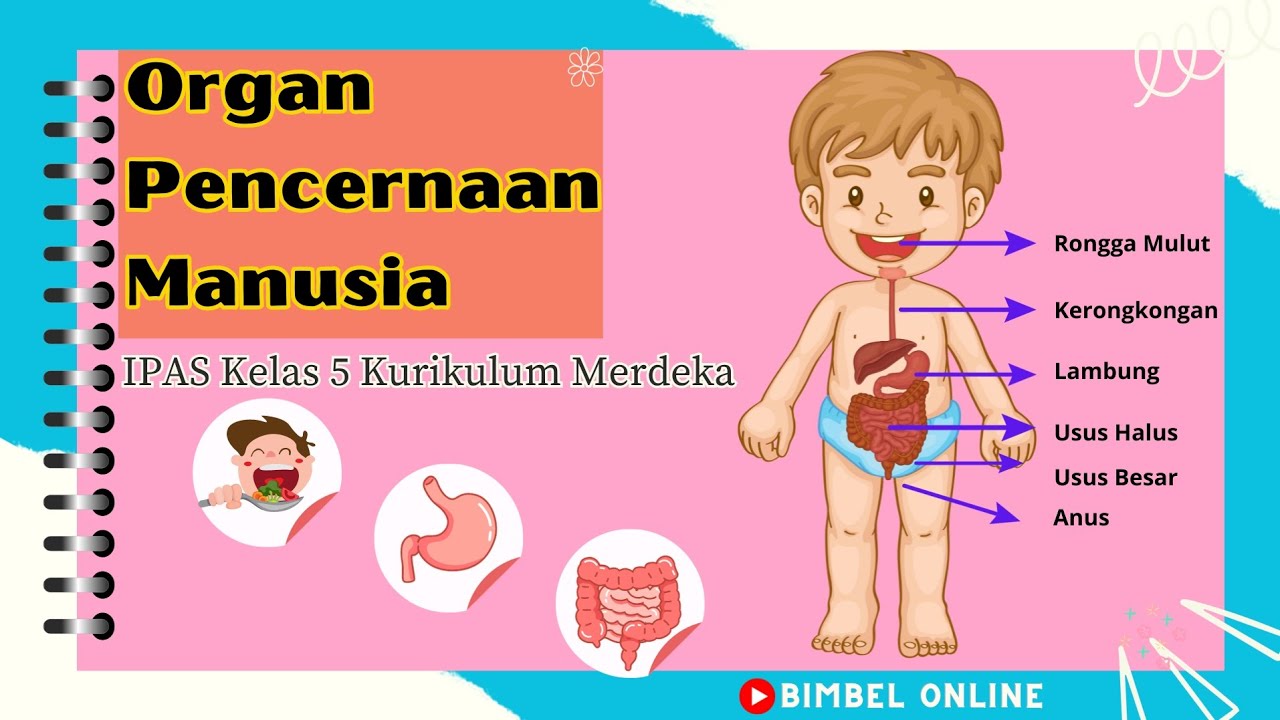
Organ Percernaan Manusia - IPAS Bab 5 Topik B || Kurikulum Merdeka

aula DNA RNA 4

for+2 & 5th Semester CLASS | MOLECULAR BIOLOGY|Nucleic Acid,Nucleotide,Nucleoside|Pratikshya Mishra

Video Microteaching Pembelajaran IPA MI/SD materi " Sistem Pencernaan Manusia"

[Part-1] Jaringan Tumbuhan

The Human Body | Facts About the Parts of the Human Body System
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)