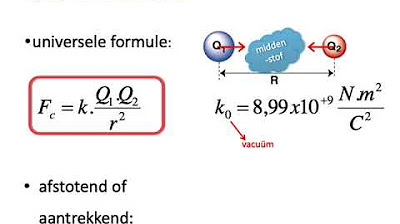
Force électromagnétique - 1: Force de Lorentz
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the concept of electromagnetic forces, specifically the Lorentz force, and its impact on charged particles moving through magnetic fields. It explains how the force depends on the charge, velocity, and magnetic field, and introduces the right-hand rule to determine its direction. The video also covers practical applications, such as particle accelerators and cancer treatment, and how Earth's magnetic field protects us from harmful solar particles. Additionally, it links these concepts to natural phenomena like the aurora borealis, demonstrating the profound influence of electromagnetism in both science and daily life.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Lorentz force is the force experienced by a charged particle moving through both an electric and magnetic field.
- 😀 The force on a moving particle is perpendicular to both its velocity and the magnetic field.
- 😀 The strength of the Lorentz force depends on the charge of the particle, its velocity, and the intensity of the magnetic field.
- 😀 The Lorentz force is maximized when the velocity and magnetic field are perpendicular to each other.
- 😀 The force becomes zero when the velocity is aligned with the magnetic field.
- 😀 The right-hand rule is used to determine the direction of the Lorentz force for positive charges: the thumb points in the direction of the force when the index finger points in the velocity direction and the middle finger in the direction of the magnetic field.
- 😀 For negative charges, like electrons, the Lorentz force acts in the opposite direction of what is indicated by the right-hand rule.
- 😀 In particle accelerators, magnetic fields are used to bend the paths of charged particles, allowing them to reach high speeds.
- 😀 Electric fields are also used in particle accelerators to increase the speed of charged particles, which can be used for treatments like cancer therapy.
- 😀 The Earth’s magnetic field helps protect life on Earth by deflecting high-energy particles from the Sun, which could otherwise be harmful, and creating the auroras as these particles interact with the atmosphere.
Q & A
What is the Lorentz force?
-The Lorentz force is the force exerted on a charged particle moving through a magnetic field. It is perpendicular to both the velocity of the particle and the magnetic field, and its magnitude depends on the charge, the velocity, and the strength of the magnetic field.
How is the strength of the Lorentz force determined?
-The strength of the Lorentz force is directly proportional to the charge of the particle (q), its velocity (v), and the magnetic field strength (B). The force is calculated as F = q(v x B), where 'x' represents the vector cross product.
Why does the Lorentz force depend on the angle between the velocity and magnetic field?
-The Lorentz force depends on the angle between the velocity and the magnetic field because the force is maximized when the velocity is perpendicular to the magnetic field (90 degrees), and minimized (zero) when the velocity is parallel to the magnetic field (0 or 180 degrees).
What happens when the direction of a charged particle’s motion is parallel to the magnetic field?
-When the velocity of a charged particle is parallel to the magnetic field, the Lorentz force becomes zero. This is because the cross product of the velocity and magnetic field vectors is zero when they are aligned.
What is the right-hand rule and how is it used in this context?
-The right-hand rule helps determine the direction of the force on a positive charge moving through a magnetic field. Point your index finger in the direction of the particle's velocity, your middle finger in the direction of the magnetic field, and your thumb will point in the direction of the force.
What happens if the charged particle is negatively charged, like an electron?
-If the charged particle is negative, such as an electron, the direction of the Lorentz force is opposite to what the right-hand rule indicates for a positive charge. Some people use the left-hand rule for negative charges to easily determine the force direction.
What role does the Lorentz force play in particle accelerators?
-In particle accelerators, the Lorentz force is used to steer charged particles in circular paths with magnetic fields, while electric fields are used to accelerate them. This combination allows particles to gain high speeds, which is useful for various applications like cancer treatment.
How do magnetic fields help protect Earth from harmful solar particles?
-Earth's magnetic field deflects charged solar particles, known as the solar wind, protecting life on Earth. These particles are redirected around the planet, especially at the poles, where they interact with the atmosphere and produce the auroras.
What causes the auroras seen at Earth's poles?
-The auroras are caused by charged particles from the solar wind colliding with Earth's atmosphere. As these particles spiral along the magnetic field lines, they excite atmospheric molecules, causing them to emit light, which we see as auroras.
How can the Lorentz force be used in medical applications, like cancer treatment?
-In medical applications, such as proton therapy for cancer, the Lorentz force is used to guide charged particles (like protons) at high speeds toward tumors. This allows the particles to target and destroy cancerous cells while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)