Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) Explained
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson, the concept of Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) is explained in detail, focusing on its application in electrical circuit analysis. KCL states that the total current entering a node is equal to the total current leaving. The video provides clear examples of solving for unknown currents and analyzing circuits with parallel resistors and BJTs. Through step-by-step calculations, viewers learn how to apply KCL to both simple and complex circuits, reinforcing the importance of current conservation in electrical engineering.
Takeaways
- 😀 Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) states that the sum of currents entering a node is equal to the sum of currents leaving the node.
- 😀 KCL can be mathematically expressed as: the sum of all currents in a circuit equals zero (ΣI = 0).
- 😀 KCL is essential for analyzing electrical circuits and helps determine unknown currents by balancing the incoming and outgoing currents at nodes.
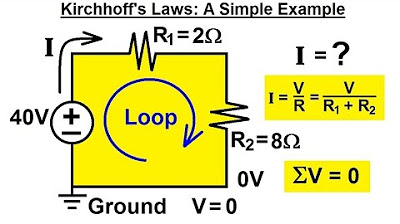
- 😀 In a simple circuit with resistors, the total current is the sum of the currents flowing through each resistor.
- 😀 The current entering a node is considered negative, while the current leaving a node is positive in KCL equations.
- 😀 When currents are unknown, KCL allows you to solve for them by balancing the incoming and outgoing values.
- 😀 Example 1: Given incoming currents (I1 and I2) and outgoing currents (I3 and I4), KCL can help find an unknown current, such as I4.
- 😀 Example 2: In a more complex case, when the direction of an unknown current (I3) is not known, KCL helps determine both the value and the direction of the current.
- 😀 KCL can be applied to circuits with different components, including resistors and transistors, as demonstrated in a BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) circuit.
- 😀 KCL is a fundamental principle not only in basic resistor circuits but also in more advanced electronic circuits such as transistors, where the base current plus the collector current equals the emitter current.
Q & A
What is Kirchhoff's Current Law?
-Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) states that the sum of currents entering a node (junction) is equal to the sum of currents leaving the node. In other words, the algebraic sum of all currents in a circuit is zero.
How can Kirchhoff's Current Law be represented mathematically?
-KCL can be represented as the equation: Σ I_in = Σ I_out, or equivalently, Σ I = 0, where Σ I represents the sum of all currents in the circuit, with incoming currents being negative and outgoing currents being positive.
In the example with the node and currents I1, I2, I3, and I4, what equation does KCL produce?
-According to KCL, the sum of incoming currents (I1 and I2) equals the sum of outgoing currents (I3 and I4). The equation is: I1 + I2 = I3 + I4.
What happens when you rearrange the currents in the KCL equation?
-When you rearrange the currents in the KCL equation, you get an expression where the sum of all currents equals zero. For example, in the equation I1 + I2 = I3 + I4, subtracting I1 and I2 from both sides gives: 0 = -I1 - I2 + I3 + I4.
How do you solve for an unknown current in a KCL equation?
-To solve for an unknown current in a KCL equation, substitute the known values of the currents into the equation and solve for the unknown. For example, if I1 + I2 = I3 + I4 + I5 and some currents are given, you can isolate the unknown current (e.g., I4) and calculate its value.
What does a negative current value indicate in KCL?
-A negative current value indicates that the current is entering the node, as opposed to positive currents which are considered outgoing from the node.
How does KCL help in circuit analysis?
-KCL is fundamental in circuit analysis because it helps determine the unknown currents at different points (nodes) in a circuit. By applying KCL to various nodes, you can solve for the currents in complex electrical circuits.
In the example with the unknown current I3, how is the direction of the current determined?
-The direction of the current is determined by the sign of the result when solving the KCL equation. A positive value for I3 would mean it is leaving the node, while a negative value indicates that I3 is entering the node.
How can KCL be applied to a circuit with resistors in parallel?
-In a parallel resistor circuit, KCL can be used to find the total current (I_T) by summing the currents through each resistor. Since the voltage across all resistors is the same, the total current is the sum of the individual currents through each resistor.
How can Kirchhoff's Current Law be applied to transistor circuits?
-In transistor circuits, KCL is applied to the base (I_B), collector (I_C), and emitter (I_E) currents. The sum of the incoming base and collector currents equals the outgoing emitter current, as per KCL.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)