Chapter 5 - Service vs Merchandisers EXPLAINED!
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Else explores merchandising operations, contrasting them with service companies that focus on providing services rather than managing inventory. She highlights the significance of merchandising in driving GDP growth, noting that personal consumption fuels retail sales, which accounted for approximately $5 trillion in North America in 2012. The complexity of merchandising lies in managing inventory, which shifts from an asset to an expense once sold. The video sets the foundation for understanding the accounting practices related to inventory, paving the way for future discussions on the topic.
Takeaways
- 😀 Service companies focus on providing services rather than selling products, making their operating cycle straightforward.
- 😀 Examples of service companies include accounting firms like KPMG, banks like the Bank of Montreal, and shipping companies like FedEx.
- 😀 The main revenue source for service companies comes from the services they provide, not from product sales.
- 😀 GDP (Gross Domestic Product) growth is a crucial indicator of economic health, heavily influenced by personal consumption.
- 😀 Personal consumption accounts for two-thirds of household spending and over 70% of total economic output (GDP).
- 😀 Retail sales are the primary component of personal consumption, reflecting consumer buying habits.
- 😀 The North American merchandising industry is significant, with retail sales reaching approximately $5 trillion in 2012.
- 😀 Merchandising operations encompass a wide range of businesses, including auto dealerships, grocery stores, clothing stores, and more.
- 😀 The operating cycle of merchandising companies is more complex due to the need to purchase, sell, and replenish inventory.
- 😀 Inventory is considered a current asset for merchandising companies, transitioning to an expense (cost of goods sold) once sold.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video series introduced by Else?
-The main focus of the video series is on merchandising operations, expanding beyond the simpler context of service companies.
Why are service companies considered simpler in terms of accounting?
-Service companies are simpler because they do not deal with inventory; they provide services, pay employees, and collect cash from customers without the complexities of buying and selling products.
What is GDP and why is it important in the context of merchandising?
-GDP, or Gross Domestic Product, measures the economic health of a country and its growth. It is important in merchandising because personal consumption, a key driver of GDP, heavily relies on retail sales.
What percentage of total economic output does personal consumption account for?
-Personal consumption accounts for more than 70% of total economic output (GDP).
Can you list some examples of merchandising operations?
-Examples of merchandising operations include auto dealerships, online retailers, department stores, grocery stores, restaurants, gas stations, clothing stores, and appliance stores.
How does the operating cycle of merchandising companies differ from service companies?
-Merchandising companies have a more complex operating cycle, involving purchasing inventory, selling it, collecting cash, and then reinvesting in more inventory, whereas service companies simply provide services.
What constitutes inventory for merchandising companies?
-Inventory is made up of finished goods that merchandising companies buy to resell to their customers.
Why is inventory classified as a current asset?
-Inventory is classified as a current asset because it is expected to be sold within a year or within the operating cycle of the business.
What happens to inventory when it is sold?
-When inventory is sold, it moves from being an asset on the balance sheet to an expense on the income statement called Cost of Goods Sold (COGS).
What will the next video in the series cover?
-The next video will cover the accounting systems used to record the purchase and sale of inventory.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Accounting Cycle Merchandising Company u
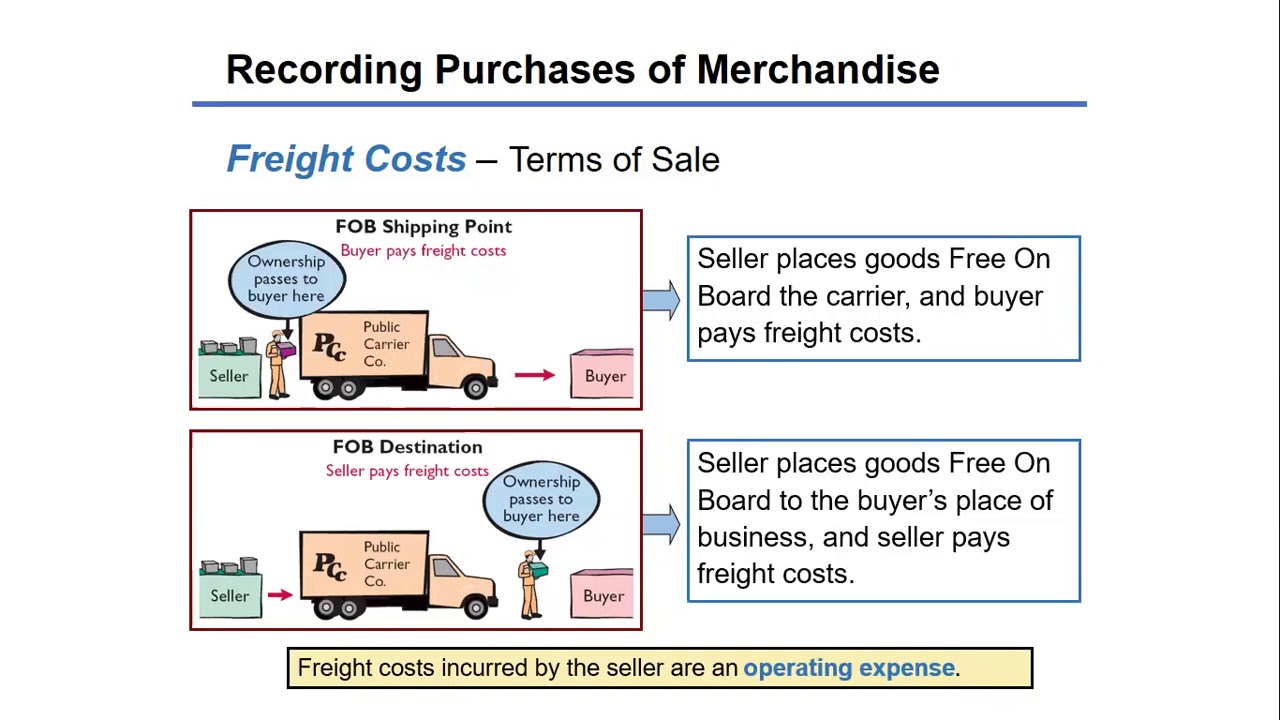
Accounting for Merchandising Operations Recording Purchases of Merchandise

Accounting for Merchandising operation

Citron Hygiene

Financial Accounting - Lesson 6.1 - Service vs Merchandisers

Lesson 027 - Accounting for Merchandising Operations 1: Sales and Purchases
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
