Introduction to Relations
Summary
TLDRIn this presentation, Ajay introduces the concept of relations in mathematics, focusing on defining relations and their graphical representation. He explains key terms such as Cartesian products, subsets, and how elements relate to sets. Ajay also touches on finding the number of relations and discusses different types of relations. Throughout, he emphasizes the importance of understanding relations, using various examples to clarify the concepts. The presentation wraps up with a note on further discussion about types of relations in future sessions.
Takeaways
- 📚 The speaker is presenting a new chapter on relations and introducing key concepts.
- 🔍 Definition of relations is the primary focus, starting with explaining a subset of A across B.
- 🧮 The concept of Cartesian product is discussed, including its application to sets and subsets.
- 👥 Examples of sets and their elements are given, like sets A and B representing people or other objects.
- ✏️ The speaker explains how elements belong to specific sets using mathematical notation.
- 📈 The graphical representation of relations is mentioned as a key way to visualize sets and their connections.
- ⚙️ The speaker delves into power sets, which are sets that include all subsets of a particular set.
- 🎯 The goal is to understand how to define relations between elements of different sets and find the number of possible relations.
- 🧑🏫 Specific types of relations, like one-to-one and many-to-one, are introduced.
- 🎓 The session concludes with a promise to further discuss types of relations in future presentations.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the presentation?
-The main topic of the presentation is 'Relations', which involves introducing and explaining the concept of relations and their properties.
What is the definition of a relation in the context of sets?
-A relation from set A to set B is defined as a subset of the Cartesian product of A and B, which means it pairs elements from A with elements from B.
What is a Cartesian product in the context of relations?
-A Cartesian product of sets A and B, denoted as A × B, is the set of all ordered pairs (a, b) where 'a' is an element of A and 'b' is an element of B.
How is the notation of a relation typically represented?
-A relation is typically represented as R ⊆ A × B, where R is a subset of the Cartesian product of sets A and B.
What does it mean for an element to belong to a relation?
-An element (a, b) belongs to a relation R if 'a' from set A is related to 'b' from set B according to the relation R, meaning (a, b) is an element of R.
What is the importance of understanding relations in mathematics?
-Understanding relations is crucial in mathematics because they help describe connections between elements of different sets and are foundational to functions, graphs, and other advanced concepts.
What is an example of a relation given in the presentation?
-One example given involves sets containing elements like {0, 1, 2, 3} and relations defined as subsets of their Cartesian products, such as {(0, 1), (2, 3)}.
What are the possible types of relations that can exist between sets?
-Possible types of relations include reflexive, symmetric, transitive, and equivalence relations, each having distinct properties regarding how elements relate within a set.
How can one find the number of possible relations between two sets?
-The number of possible relations between two sets A and B is 2 raised to the power of the product of the number of elements in A and the number of elements in B, which corresponds to the number of subsets of A × B.
What is the next focus after the introduction to relations in the presentation?
-After the introduction, the next focus of the presentation will be on discussing the different types of relations and their properties in detail.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
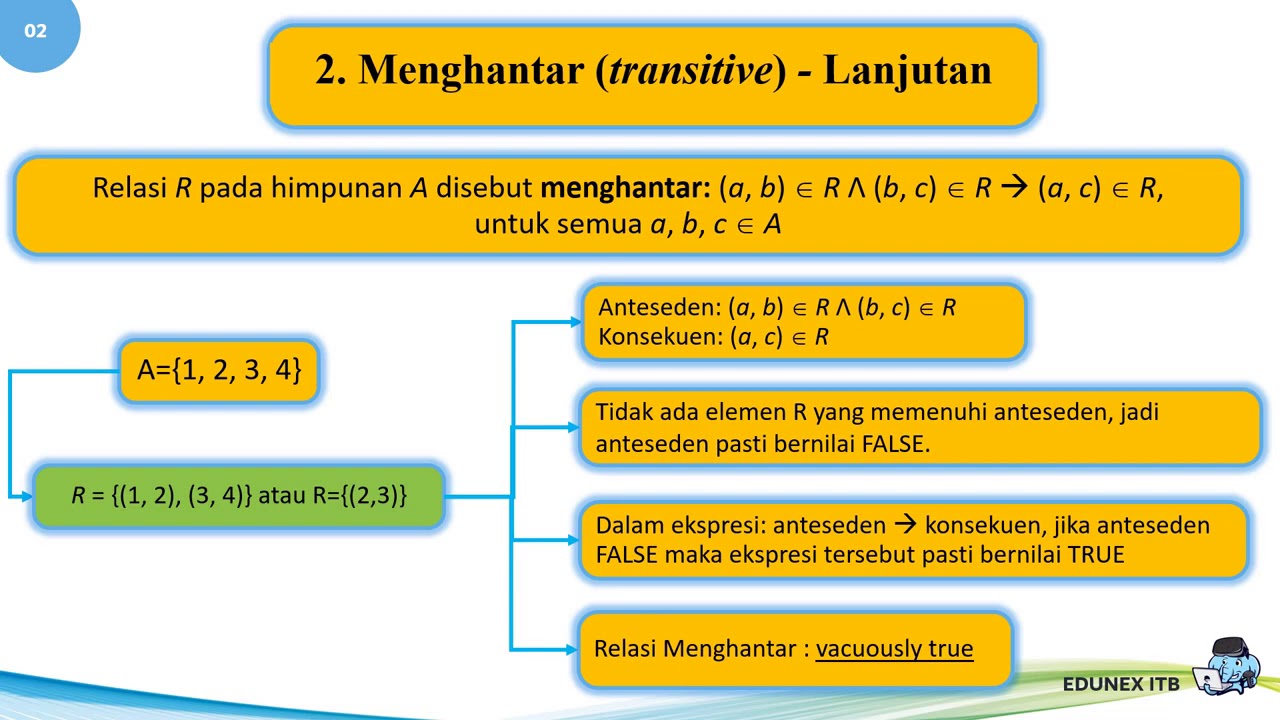
Matdis 06 : Relasi&Fungsi (Segmen 3: sifat-sifat relasi)

Understanding Relations I Señor Pablo TV
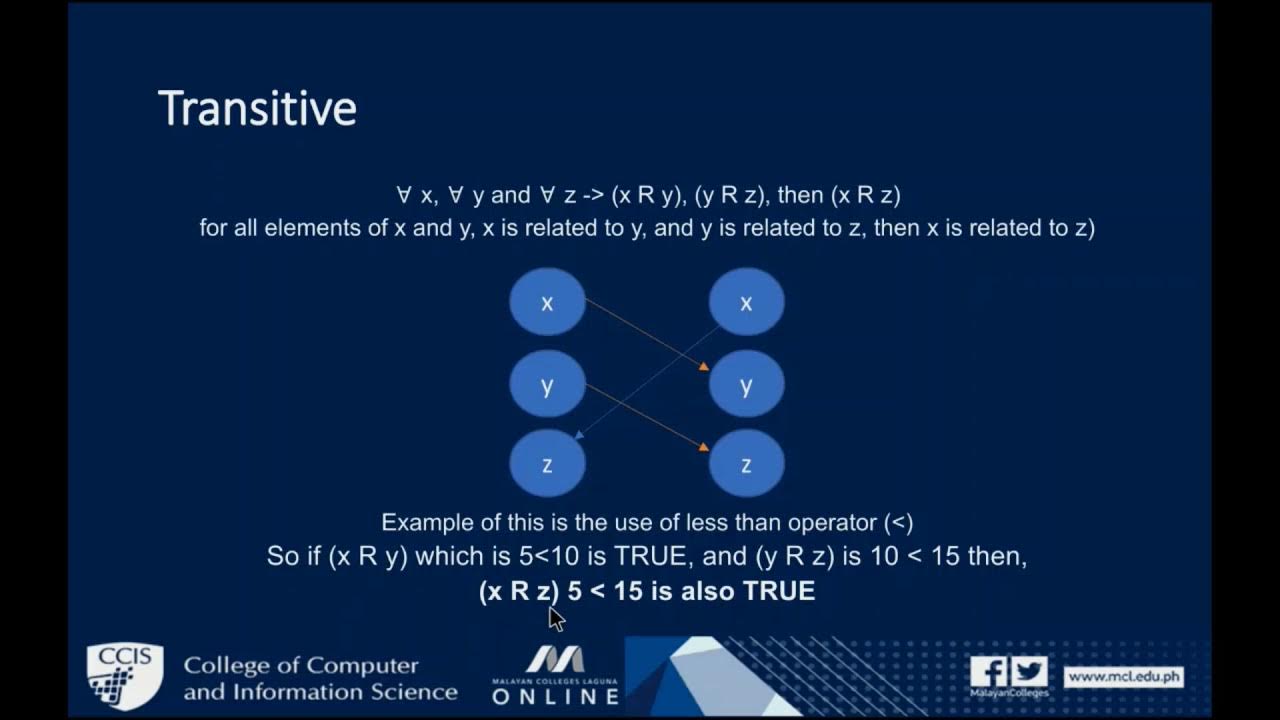
CS101 2 Module 3 Relations and their Properties PART1

CBSE Class 11 Maths Project-Relations & Functions

Learn Functions – Understand In 7 Minutes

Matdis 07: Relasi & Fungsi (Segmen 4: Relasi Inversi, Kombinasi dan Komposisi Relasi)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
