6.3 Ionic Bonding and Ionic Compounds
Summary
TLDRThis video explains ionic bonding and ionic compounds, focusing on how positive and negative ions form stable structures. Using examples like sodium chloride (NaCl) and calcium fluoride (CaF2), it explores the ratio of ions that balance charges, the formation of crystalline solids, and how these lattices result in compounds with high melting points and brittleness. The video also contrasts ionic and covalent bonds, discusses lattice energy, and explains how ionic compounds can conduct electricity when melted or dissolved. Lastly, it introduces polyatomic ions, including ammonium and sulfate, highlighting their significance in chemistry.
Takeaways
- 🧲 Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond formed by the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
- 🌏 Most of the Earth's rocks and minerals are held together by ionic bonds, such as common table salt (NaCl).
- 🔄 Ionic compounds form when positive and negative ions combine in a ratio that balances the overall charge.
- 📏 The chemical formula of an ionic compound, like NaCl, represents the simplest whole-number ratio of ions in the compound.
- 🔬 A formula unit is the simplest collection of atoms that can represent the formula of an ionic compound.
- 🔬 Ionic compounds form crystalline solids that are hard and brittle, unlike molecules that share covalent bonds.
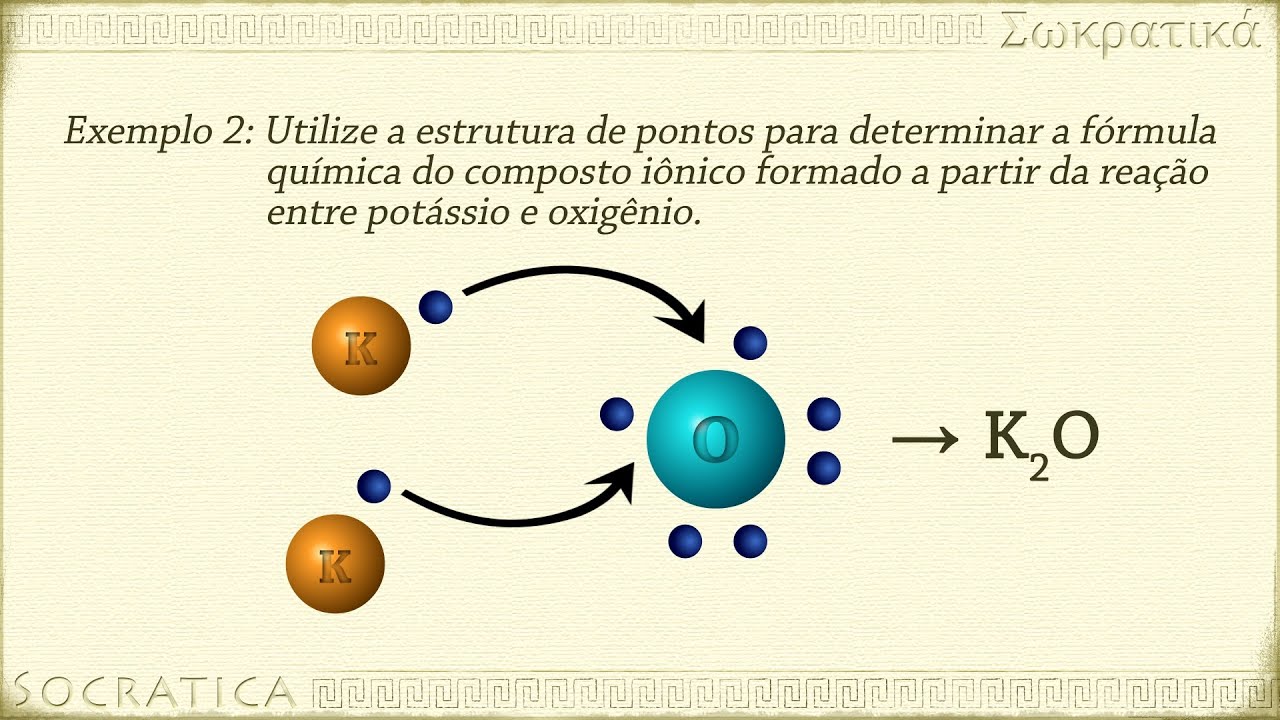
- 🔄 The formation of ionic compounds involves the transfer of electrons from metal atoms (like sodium) to non-metal atoms (like chlorine).
- 💠 Ionic compounds arrange themselves in a three-dimensional crystal lattice structure to maximize attraction and minimize repulsion between ions.
- ⚖️ Lattice energy is a measure of the strength of the ionic bond within a compound, determined by the energy released when the lattice is broken down into gaseous ions.
- 🌡 Ionic compounds typically have high melting and boiling points due to their strong ionic lattice structure.
- 💧 When ionic compounds are dissolved in water, they dissociate into free ions, which allows them to conduct electricity.
Q & A
What are ionic bonds and ionic compounds?
-Ionic bonds are formed by the attraction between positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions). Ionic compounds are formed by the combination of these ions in a specific ratio to balance the overall charge.
What is an example of an ionic compound found in nature?
-A common example is sodium chloride (NaCl), also known as table salt, which consists of sodium (Na) as a cation with a +1 charge and chlorine (Cl) as an anion with a -1 charge.
What is a formula unit in ionic compounds?
-A formula unit is the simplest collection of atoms from which the formula of an ionic compound can be established. For example, the formula unit of sodium chloride is NaCl.
How do calcium and fluorine combine to form an ionic compound?
-Calcium (Ca) has a +2 charge, while fluorine (F) has a -1 charge. To balance these charges, two fluorine atoms are needed for each calcium atom, resulting in the formula CaF₂.
What is electron dot notation and how is it used to illustrate ionic bonding?
-Electron dot notation represents the valence electrons of atoms using dots. It can be used to show the transfer of electrons during ionic bonding, such as sodium losing an electron to chlorine, resulting in Na⁺ and Cl⁻.
Why do ionic compounds form crystal lattices?
-Ionic compounds form crystal lattices to maximize the attraction between oppositely charged ions while minimizing repulsion between like charges. This results in a stable, three-dimensional structure.
What is lattice energy in the context of ionic compounds?
-Lattice energy is the energy released when one mole of an ionic lattice is formed from its constituent gaseous ions. It measures the strength of the bonds within the ionic lattice.
How do ionic compounds differ from molecular compounds in terms of physical properties?
-Ionic compounds generally have high melting and boiling points due to strong ionic bonds, and they form hard but brittle solids. Molecular compounds, on the other hand, often have lower melting and boiling points and can exist as liquids or gases at room temperature.
Why are ionic compounds good conductors when melted or dissolved in water?
-When ionic compounds are melted or dissolved in water, their ions are free to move, allowing them to conduct electricity by carrying electric charges through the solution or molten state.
What are polyatomic ions, and can you provide an example?
-Polyatomic ions are charged species consisting of multiple atoms bonded together. An example is ammonium (NH₄⁺), which has a net positive charge because it has lost one electron to achieve stability.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)