August 26, 2024
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the concept of ions and ionic bonds. It explains that ions are atoms or molecules with a positive or negative charge resulting from gaining or losing electrons. The script highlights the role of the periodic table in predicting ion formation, with noble gases being stable due to full outer electron layers. Cations are positively charged ions that have lost an electron, while anions are negatively charged ions that have gained an electron. The video further discusses ionic bonding, which typically occurs between metals and non-metals, forming ionic compounds like table salt. These compounds are characterized by their ability to form large crystal structures, dissolve in water, conduct electricity when dissolved, and have high boiling points.
Takeaways
- 📘 Ions are atoms or molecules with a positive or negative charge, created when atoms gain or lose electrons.
- ⚡ Cations are positively charged ions that have lost an electron, while anions are negatively charged ions that have gained an electron.
- 🔋 In an atom's inner shell, there can be up to 2 electrons, while the second and third layers can hold up to 8 electrons each.
- 🧪 Noble gases are stable atoms because they have a full outer electron layer, making them non-reactive.
- 👍 Cations can be remembered by associating the 'T' in cation with a '+' symbol (positive charge), while anions sound like 'negative' (negative charge).
- ⚛️ Atoms want to have full electron rings, as this makes them stable and less reactive.
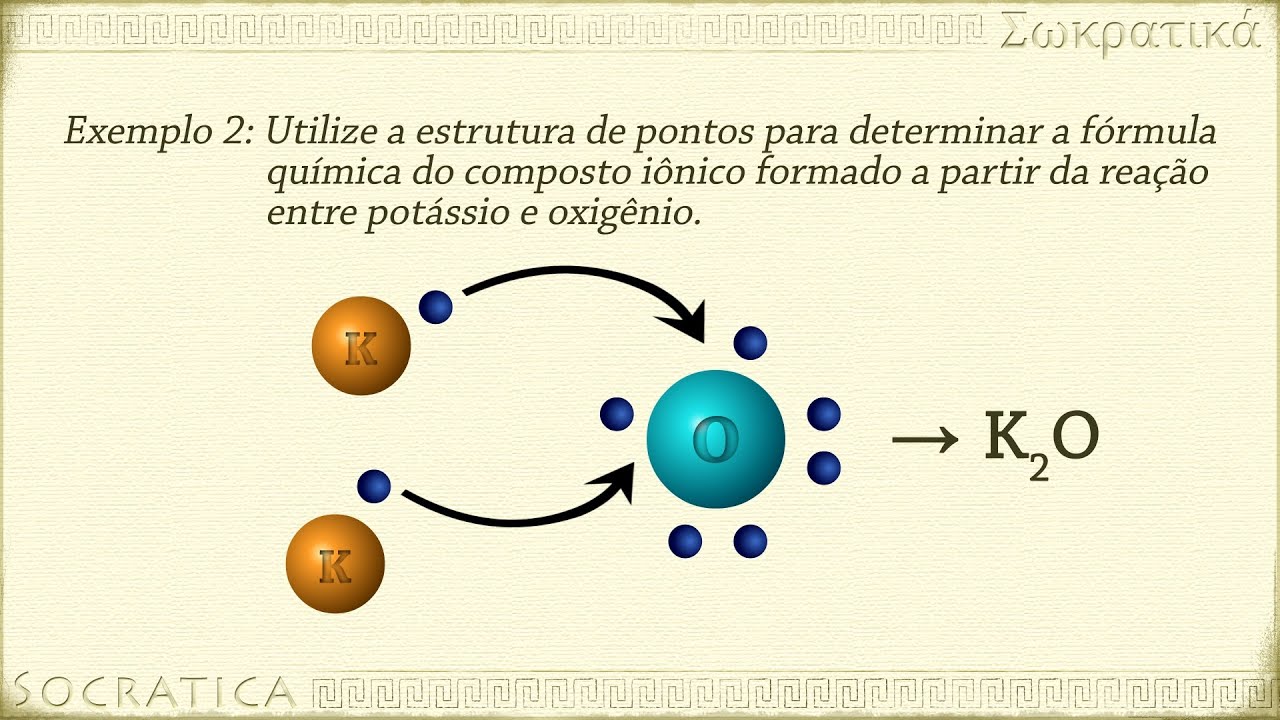
- 🔄 Ionic bonds are formed between oppositely charged ions (cations and anions) and typically occur between metals and non-metals.
- 🧂 Sodium atoms, for example, can lose an electron to become a sodium ion (Na+), forming an ionic bond with other elements.
- 🔬 The periodic table helps predict how atoms will react, with certain columns forming specific types of ions.
- 💧 Ionic compounds, like table salt (NaCl), form crystal structures, dissolve in water, have high boiling points, and can conduct electricity when dissolved.
Q & A
What is an ion?
-An ion is an atom or molecule with a positive or negative charge, created when atoms gain or lose electrons.
How do cations and anions differ?
-Cations are positively charged ions that have lost one or more electrons, while anions are negatively charged ions that have gained one or more electrons.
What is the significance of a full electron shell in atoms?
-Atoms with a full electron shell, like the noble gases, are very stable and non-reactive because their outer electron layer is complete, making them 'happy' or stable.
How can the periodic table help predict ion formation?
-The periodic table helps predict ion formation by indicating how many electrons an atom needs to gain or lose to achieve a stable, full outer electron shell.
Why do atoms in column 1 of the periodic table typically form cations?
-Atoms in column 1 have only one electron in their outer shell, making it easier for them to lose that electron and form a cation with a positive charge.
What happens when a sodium atom loses an electron?
-When a sodium atom loses an electron, it becomes a sodium ion (Na+) with a positive charge because it now has more protons than electrons.
What is ionic bonding?
-Ionic bonding is the strong attraction between oppositely charged ions, typically between metals and non-metals, where one atom gives away an electron and another atom gains it.
What are some properties of ionic compounds?
-Ionic compounds often form large crystal structures, dissolve easily in water, have high boiling points, and conduct electricity when dissolved in water.
Why are noble gases non-reactive?
-Noble gases are non-reactive because their outer electron shells are fully filled, making them stable and not inclined to gain or lose electrons.
How do sodium chloride and other ionic compounds demonstrate ionic bonding?
-In sodium chloride (table salt), sodium gives up an electron to chlorine, forming a strong ionic bond between the positively charged sodium ion (Na+) and the negatively charged chloride ion (Cl-), creating a stable compound.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Química: Ligações Iônicas

IKATAN KIMIA || SUBMATERI KESTABILAN ATOM DAN IKATAN ION || FASE E KELAS X SMA #abadi2024

Series 11 Soil Colloids IX Anion Exchange & chelation

GCSE Chemistry - What is Ionic Bonding? How Does Ionic Bonding Work? Ionic Bonds Explained #14

Legame Ionico - Legami Chimici | Lezioni di Chimica

Soal-soal Ikatan Kimia Kelas 10 dan 11 SMA/MA Pilihan
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)