6.2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses covalent bonding and molecular compounds, explaining how atoms rarely exist independently and instead form molecules through covalent bonds. The video highlights key concepts such as molecular formulas, bond energy, the octet rule, Lewis structures, and multiple bonds. Examples like hydrogen, fluorine, and nitrogen bonding are provided, illustrating single, double, and triple bonds. The video also explains how resonance structures, such as ozone, exist as hybrids of multiple possible structures. Overall, it focuses on the principles that govern the formation and stability of molecular compounds.
Takeaways
- 😀 Covalent bonds involve atoms sharing electrons to form molecules, which are electrically neutral.
- 🔬 Molecular compounds consist of atoms bonded together, and they are represented by molecular formulas.
- 💧 Diatomic molecules are made of two atoms, like hydrogen (H2) and fluorine (F2).
- ⚛️ Atoms bond to reduce their potential energy, forming stable compounds at a specific bond length.
- 🌱 Bond energy refers to the energy required to break chemical bonds and is measured in kilojoules per mole.
- 🔋 The octet rule states that atoms tend to form compounds to achieve eight electrons in their outermost shell.
- 🧪 Single bonds involve one pair of electrons, while double and triple bonds involve multiple electron pairs, making them stronger and shorter.
- 📐 Lewis structures represent the arrangement of electrons in a molecule, showing bonded and unbonded electron pairs.
- 🧬 Resonance structures exist when a molecule can be represented in multiple ways, as with ozone (O3).
- 💥 Multiple bonds (double or triple) are shorter and stronger than single bonds due to closer nuclei in shared orbitals.
Q & A
What is a covalent bond?
-A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond where two or more atoms share electrons, creating a molecule that is electrically neutral.
What is a molecular compound?
-A molecular compound consists of molecules formed by atoms that are bonded together through covalent bonds. It has a specific molecular formula that indicates the number and type of atoms in the compound.
What is a diatomic molecule, and can you give an example?
-A diatomic molecule is composed of only two atoms, which can be of the same or different elements. For example, hydrogen gas (H₂) and fluorine gas (F₂) are diatomic molecules.
Why do atoms form molecules instead of existing as standalone atoms?
-Atoms tend to form molecules because bonded atoms have lower potential energy compared to standalone atoms. Lower potential energy makes the molecules more stable, which is a preferred state in nature.
What is bond energy, and why is it important?
-Bond energy is the energy required to break a chemical bond and separate atoms in a molecule. It is important because it represents the strength of the bond; the same amount of energy is released when the bond is formed as is required to break it.
What is the octet rule?
-The octet rule states that atoms tend to form bonds in such a way that each atom has eight electrons in its outer shell, achieving the same electron configuration as a noble gas, which is a stable, low-energy state.
How does the bonding in hydrogen differ from the bonding in larger atoms like fluorine?
-Hydrogen forms a covalent bond by sharing its single electron with another atom, aiming to achieve a stable 1s² configuration (like helium). Fluorine, however, shares electrons to complete its octet, filling its 2s and 2p orbitals.
What is the significance of bond length, and what is the bond length for hydrogen?
-Bond length is the distance between two bonded atoms at their lowest potential energy. For hydrogen, the bond length is about 75 picometers, where the attractive forces between electrons and nuclei balance the repulsive forces.
What are multiple bonds, and how do they differ from single bonds?
-Multiple bonds are covalent bonds where two or more pairs of electrons are shared between atoms. A double bond shares two pairs, and a triple bond shares three pairs. Multiple bonds are shorter and stronger than single bonds, which share only one pair of electrons.
What is resonance, and why does it occur in molecules like ozone?
-Resonance occurs when a molecule cannot be represented by a single Lewis structure because the real structure is a hybrid of two or more forms. In ozone (O₃), the bonds between oxygen atoms exist as a blend of single and double bonds, leading to resonance.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

What Are Covalent Bonds | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool

IPA Kelas 9 Semester 2 : Partikel Penyusun Materi (Part 3: Ikatan Kimia)

IKATAN KIMIA : IKATAN KOVALEN | KIMIA SMA KELAS 10

6.1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding

5 Covalent Bonding Intro
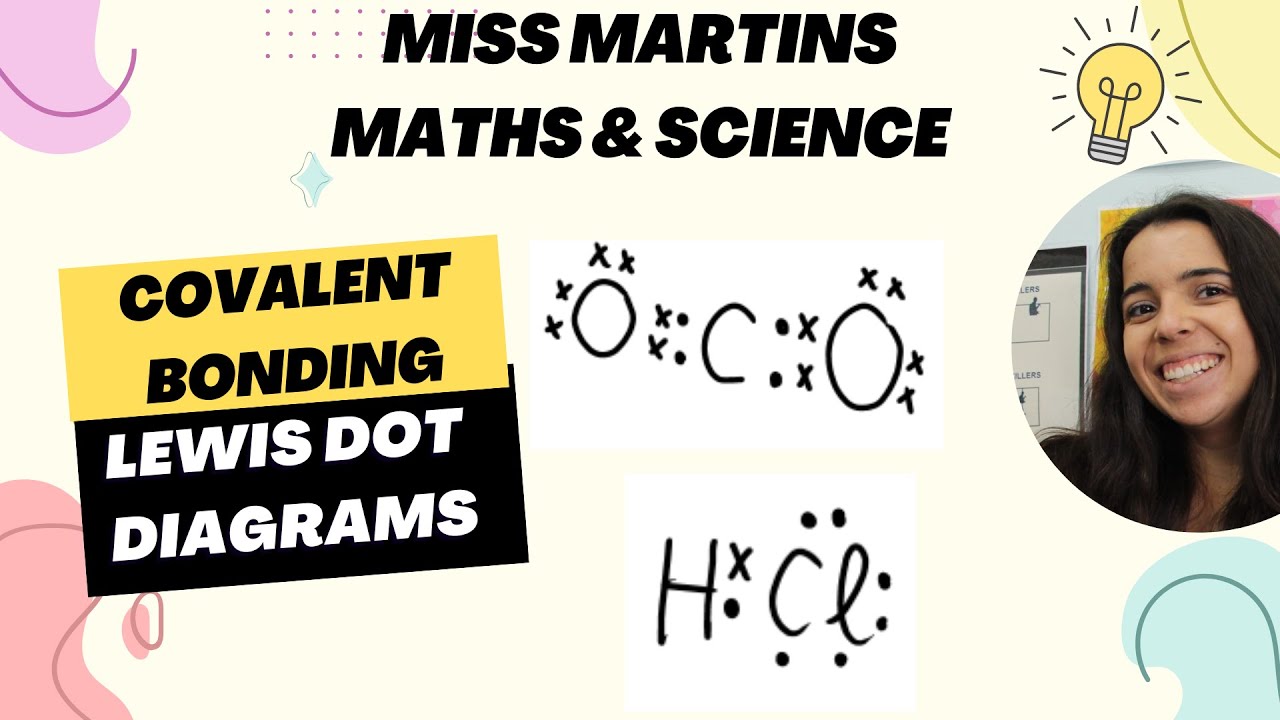
Chemical Bonding: Covalent Bonding Lewis Dot Diagrams
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
