11AS01 - History of the atom - WACE Chemistry Year 11
Summary
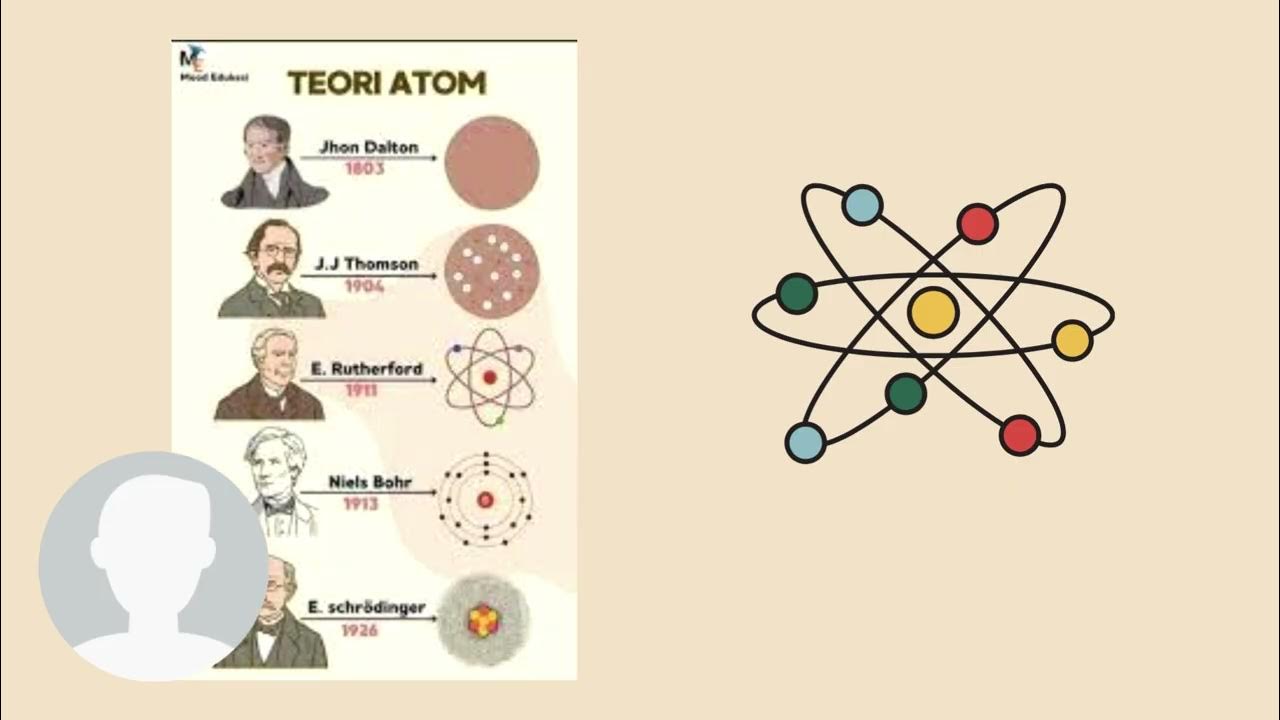
TLDRThis video introduces Year 11 students to the history of atomic structure, covering key scientists and their contributions. It starts with Dalton's ideas about atoms and compounds, followed by Thomson's discovery of electrons using the cathode ray tube. Rutherford's gold foil experiment reveals the dense atomic nucleus, while Bohr introduces electron orbits and energy levels. Lastly, Chadwick discovers the neutron, completing the modern atomic model. The video emphasizes the importance of understanding these concepts for grasping atomic structure in chemistry.
Takeaways
- 🧑🏫 Dalton introduced the idea that all matter is made up of atoms, indivisible units with identical mass and properties within each element.
- ⚖️ Dalton also proposed that compounds are combinations of atoms in fixed ratios, leading to different substances with unique properties.
- 🔄 Chemical reactions, according to Dalton, are simply rearrangements of atoms, adhering to the law of conservation of mass and constant composition.
- 🔬 Thompson's cathode ray experiment led to the discovery of the electron, a small negatively charged particle, part of every element.
- 🍪 Thompson developed the 'plum pudding' model, where electrons are embedded in a positively charged 'soup,' balancing out the atom.
- 🏹 Rutherford's gold foil experiment revealed that atoms are mostly empty space, with a dense, positively charged nucleus at the center.
- 🌍 Bohr expanded the model, suggesting that electrons orbit the nucleus in defined paths and jump between orbits when energy is absorbed or emitted.
- 💡 Bohr's model also explained that electrons emit specific wavelengths of light when transitioning between energy levels.
- ⚛️ Chadwick discovered the neutron, a neutral particle within the nucleus, explaining why atomic mass didn't match the number of protons alone.
- 📜 The video emphasizes that understanding the history of atomic theory is key but not a major part of exams, advising students to focus on grasping the core concepts.
Q & A
What was John Dalton's main contribution to atomic theory?
-Dalton proposed that all matter is made of indivisible atoms, and that atoms of a given element have the same mass and properties. He also introduced the idea that compounds are combinations of atoms in fixed ratios.
What are the two key laws Dalton's atomic theory is based on?
-Dalton's theory is based on the Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that mass is conserved in chemical reactions, and the Law of Constant Composition, which says that compounds have a consistent composition throughout.
How did J.J. Thomson's cathode ray experiment change the understanding of the atom?
-Thomson discovered the electron, a small, negatively charged subatomic particle, through his cathode ray experiment. This led to the understanding that atoms are divisible and contain smaller particles.
What was the significance of Thomson's plum pudding model?
-Thomson's plum pudding model suggested that atoms consist of negatively charged electrons embedded within a positively charged 'soup,' similar to plums in a pudding, which explained the overall neutrality of atoms.
What did Rutherford's gold foil experiment reveal about the atom's structure?
-Rutherford's experiment showed that atoms have a dense, positively charged nucleus at their center. This was inferred when some alpha particles bounced back after hitting the nucleus, while most passed through the atom's mostly empty space.
How did Bohr's model of the atom differ from previous models?
-Bohr's model proposed that electrons orbit the nucleus in distinct energy levels or shells. When electrons gain energy, they move to higher energy levels, and when they return to lower levels, they emit light of specific wavelengths.
What is the concept of energy quantization in Bohr’s atomic model?
-In Bohr’s model, electrons can only occupy specific energy levels. The energy released or absorbed by an electron when moving between these levels is quantized, meaning it comes in fixed amounts corresponding to specific wavelengths of light.
What discovery did James Chadwick make about the atom?
-Chadwick discovered the neutron, a neutral subatomic particle found in the nucleus of atoms. This helped explain why the mass of atoms did not correspond directly to the number of protons, as neutrons contribute to atomic mass but have no charge.
How did Chadwick’s discovery solve the issue of mismatched atomic mass?
-Chadwick's discovery of the neutron explained why the atomic mass was higher than the mass of just the protons, as neutrons add mass without affecting the atom’s charge.
What role do neutrons play in the atomic nucleus?
-Neutrons help stabilize the nucleus by providing a buffer between the positively charged protons, which would otherwise repel each other due to their like charges.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

8th Science | Chapter 5 | Inside the Atom | Lecture 1 | Maharashtra Board |
stuktur atom

GCSE Physics - Development of the model of the atom #31

Atomic Structure: The Basics

IPA Kelas 9 Semester 2 : Partikel Penyusun Materi (Part 1 : atom dan molekul)

Perkembangan Teori Atom dan Penemuan Partikel Penyusun Atom Disertai Animasi - Kimia X
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
