Atomic Structure & Coulomb's Law - AP Chem Unit 1, Topic 5a
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script explores the history and development of atomic structure theory. It begins with JJ Thompson's discovery of electrons and the plum pudding model, then moves to Rutherford's gold foil experiment revealing the nucleus with protons. Robert Millikan's oil drop experiment determined the charge of an electron, while Niels Bohr introduced energy levels and quantization. James Chadwick discovered neutrons, and the script concludes with a discussion on atomic structure, emphasizing the importance of charge magnitude and distance in understanding electrostatic forces, as explained by Coulomb's law.
Takeaways
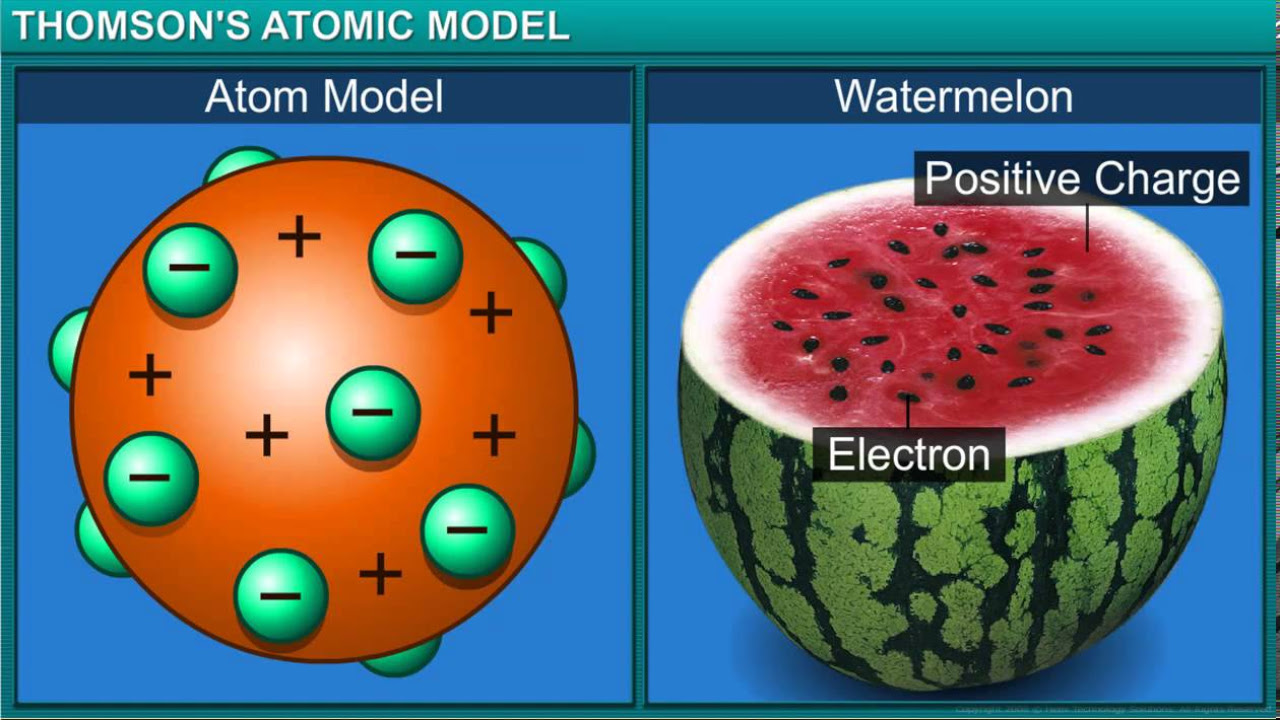
- 🔬 JJ Thompson's cathode ray tube experiment led to the discovery of electrons and the plum pudding model of the atom.
- 🌟 Ernest Rutherford's gold foil experiment with alpha particles resulted in the discovery of the nucleus and the identification of protons.
- 💧 Robert Millikan's oil drop experiment determined the charge of an individual electron to be approximately 1.592 x 10^-19 coulombs.
- 🌌 Niels Bohr proposed that electrons exist in quantized energy levels and can jump between these levels, but cannot exist between them.
- 🚫 James Chadwick discovered neutrons, uncharged particles in the nucleus with a mass similar to protons.
- 💥 The development of atomic theory led to the creation of the first nuclear weapon within 13 years of Chadwick's discovery.
- 🌐 Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, with electrons orbiting in an electron cloud.
- 📏 The majority of an atom is empty space, with the nucleus being extremely small compared to the overall size of the atom.
- 🔐 The ease of removing an electron from an atom is influenced by the magnitude of the positive charge and the distance of the electron from the nucleus.
- 🔗 Coulomb's law explains the attractive force between charged particles, showing that greater charge magnitude and shorter distances result in stronger forces.
Q & A
What did JJ Thompson discover about atoms using a cathode ray tube?
-JJ Thompson discovered that atoms contained negatively charged particles, which he called electrons, using a cathode ray tube. He observed that these particles were deflected towards a positively charged metal plate.
What is the Plum Pudding model of the atom?
-The Plum Pudding model, proposed by JJ Thompson, suggested that electrons were randomly distributed within a positively charged 'gel' that made up the rest of the atom, similar to plums in a plum pudding.
What was Ernest Rutherford's contribution to atomic theory?
-Ernest Rutherford proposed the existence of a dense, positively charged nucleus within the atom after observing that alpha particles were deflected when shot at a thin gold foil.
What did Rutherford's gold foil experiment reveal about the structure of atoms?
-Rutherford's gold foil experiment revealed that atoms have a dense, positively charged nucleus, which contradicted the Plum Pudding model and led to the Rutherford model of the atom.
What was Robert Millikan's contribution to understanding the charge of electrons?
-Robert Millikan determined the charge of an individual electron through his oil drop experiment, calculating it to be approximately 1.592 x 10^-19 coulombs.
How did Niels Bohr's theory differ from the Plum Pudding model regarding electron behavior?
-Niels Bohr theorized that electrons existed in specific energy levels and orbited the nucleus in a manner similar to planets around the sun, which was a significant departure from the random distribution suggested by the Plum Pudding model.
What is the concept of quantization in relation to electron energy levels?
-Quantization refers to the idea that electrons can only exist in specific, discrete energy levels and cannot exist in between these levels, similar to steps on a staircase.
Who discovered neutrons and how did this impact our understanding of the atom?
-James Chadwick discovered neutrons, uncharged particles in the nucleus with similar mass to protons. This discovery led to the understanding that atoms consist of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Why is it easier to remove an electron from hydrogen compared to helium?
-It is easier to remove an electron from hydrogen because there is only one proton attracting the electron, resulting in a weaker electrostatic force compared to helium, which has two protons attracting its electrons.
How does Coulomb's law relate to the attraction between charged particles in an atom?
-Coulomb's law states that the attractive force between charged particles is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them, helping to explain why electrons are held in the atom.
Why is it easier to remove an electron from lithium compared to helium, even though both have a +2 charge?
-It is easier to remove an electron from lithium because the outermost electron in lithium is farther from the nucleus, resulting in a weaker attractive force compared to the outermost electron in helium.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

STRUKTUR ATOM PART 1 PARTIKEL SUB ATOM DAN NOTASI ATOM

GCSE Chemistry - History of the Model of the Atom #7

TEORI MODEL ATOM | Fisika Atom #1 - Fisika Kelas 12

2.1 History of the Atom

Tudo se Transforma, História da Química, História dos Modelos Atômicos
Chemistry_Class 9th_Chapter 4_Structure of the Atom_Module-Thomson's Atomic Model
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
