The Sci Guys: Science at Home - SE2 - EP11: Gay-Lussac's Law of Ideal Gases
Summary
TLDRIn this S guys video, hosts Ryan and Adam explore Gay-Lussac's Law, which states that temperature and pressure of an ideal gas are directly proportional. They demonstrate this through an experiment involving candles, water, food coloring, and a beaker. As the candles burn, the air molecules' temperature increases, raising the pressure and causing the water level to rise. The experiment visually illustrates the law, showing how changes in temperature affect pressure in a closed system.
Takeaways
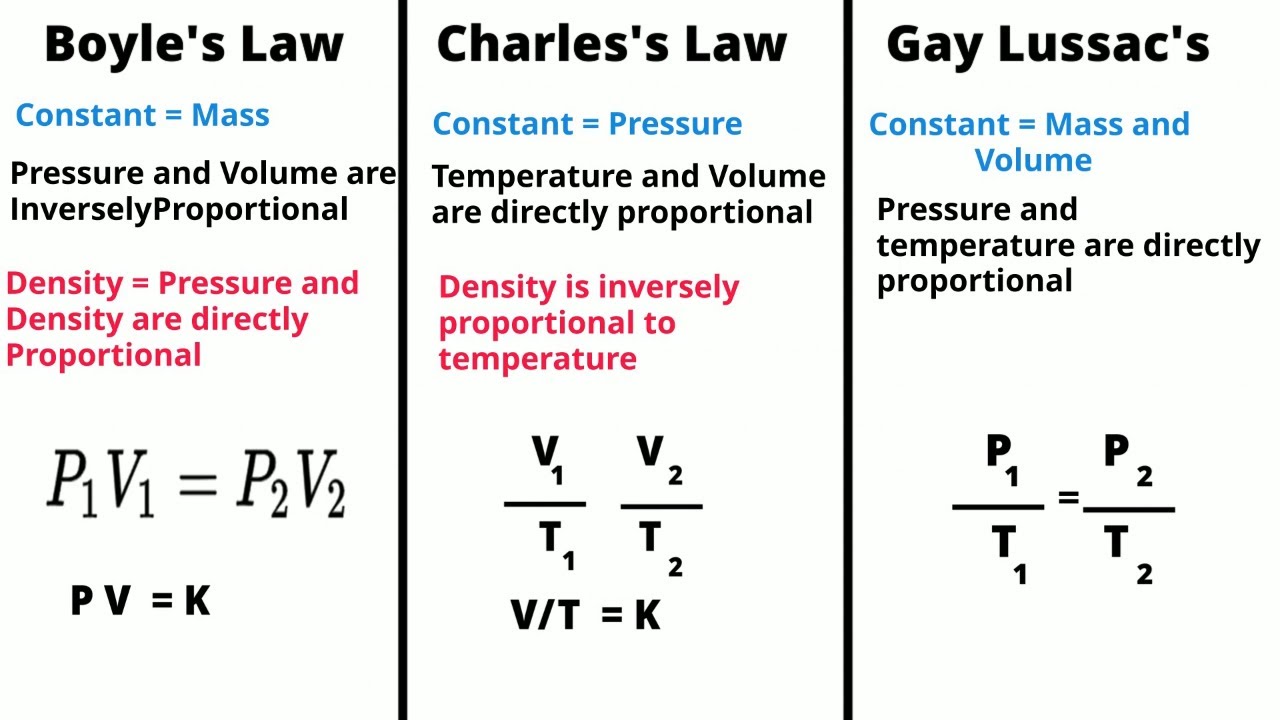
- 🔍 The video discusses Gay-Lussac's Law, which states that the temperature and pressure of an ideal gas are directly proportional.
- 🧪 The experiment involves using candles, a beaker, water, food coloring, and a butane lighter to demonstrate the law.
- 👔 Safety precautions are emphasized, including wearing protective gear and ensuring adult supervision when dealing with fire.
- 🔥 The candles' flames decrease as the air inside the beaker heats up, causing the water level to rise due to increased pressure.
- 🌡️ Gay-Lussac's Law applies to a fixed amount of gas at a constant volume in a closed system, where temperature and pressure are directly related.
- 🌌 Ideal gases, like oxygen and hydrogen, behave according to gas laws such as Gay-Lussac's, assuming particles are non-interacting and randomly moving.
- 🔑 The experiment shows that as the air molecules' temperature increases, so does the pressure, pushing the water level up.
- 🔄 The combustion of candles produces carbon dioxide and water vapor, which displace oxygen and lead to the candles' extinguishment.
- ♨️ After the candles are out, the air molecules cool, decreasing the pressure and causing the water level to rise to equalize the pressure.
- 📚 The video concludes by reinforcing the observable relationship between temperature and pressure in an ideal gas as described by Gay-Lussac's Law.
Q & A
What is the main concept discussed in the video?
-The main concept discussed in the video is Gay-Lussac's Law, which states that the temperature and pressure of an ideal gas are directly proportional.
What equipment is needed for the experiment demonstrated in the video?
-The equipment needed includes candles, a beaker or glass, water, a shallow dish, food coloring, and a butane lighter or matches.
Why is it important to wear an apron or lab coat during the experiment?
-Wearing an apron or lab coat is important to protect from spills and splashes, and it's also a safety measure to prevent any hazards associated with fire.
How does the experiment demonstrate Gay-Lussac's Law?
-The experiment demonstrates Gay-Lussac's Law by showing that as the temperature of the gas inside the beaker increases due to the burning candles, the pressure also increases, causing the water level to rise.
What happens to the candles when the beaker is placed over them?
-The candles' flames get smaller and eventually extinguish as the oxygen in the beaker is consumed and the pressure increases due to the heat.
Why does the water level rise under the beaker after the candles are extinguished?
-The water level rises because the pressure under the beaker decreases as the air molecules cool down and lose pressure, causing the water to be pulled up into the beaker to equalize the pressure.
What is an ideal gas according to the script?
-An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of randomly moving, non-interacting particles that follow the laws of gases such as Gay-Lussac's Law.
What happens to the air molecules in the beaker when the candles are lit?
-The air molecules in the beaker get excited and try to spread further apart due to the increase in temperature from the burning candles.
What are the products of the combustion reaction that occurs when the candles burn?
-The products of the combustion reaction are carbon dioxide gas and water vapor.
Why do the candles eventually go out in the experiment?
-The candles go out because the oxygen in the beaker is consumed, and the increasing levels of carbon dioxide and water vapor produced by the combustion reduce the available oxygen needed for the candles to burn.
How does the experiment relate to the real-world behavior of gases?
-The experiment relates to real-world behavior of gases by illustrating how gases behave under changes in temperature and pressure, which is a fundamental concept in understanding gas laws and their applications.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)