How Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers Work (Engineering)
Summary
TLDRThis video offers an insightful exploration into shell and tube heat exchangers, detailing their structure, operation, and the distinction between single and multi-pass models. It highlights the advantages of these heat exchangers, such as cost-effectiveness, simple maintenance, and suitability for high pressures and temperatures, while also addressing their limitations, including lower efficiency and inflexibility in cooling capacity compared to plate heat exchangers.
Takeaways
- 🔧 Shell and tube heat exchangers are crucial in engineering for transferring heat between two fluids.
- 🏭 The video provides an overview of the main components, design features, advantages, and disadvantages of shell and tube heat exchangers.
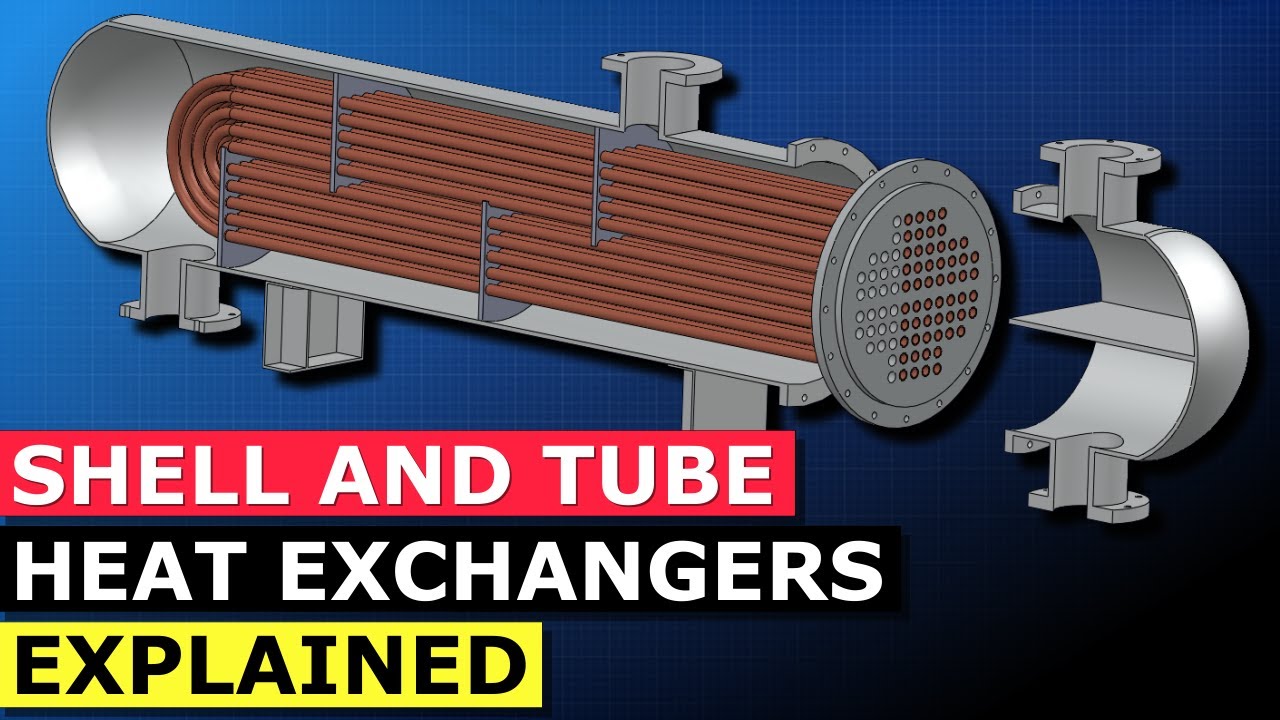
- 🌐 The shell, which acts as a pressure vessel, houses the tubes through which one fluid flows, while the other fluid flows in the shell.
- 💧 Both the tube side fluid and the shell side fluid play integral roles in heat exchange, with their flows being designed for maximum efficiency.
- 🔄 The video explains different types of flow designs, including counter flow, cross flow, and parallel flow, each with its own efficiency and application.
- 🛠️ Maintenance of shell and tube heat exchangers is relatively straightforward due to their simple design and the ease of accessing the tubes.
- 💹 They are cost-effective and suitable for high pressures and temperatures, which are advantages over plate heat exchangers.
- 🚫 However, they are less efficient than plate heat exchangers, require more space, and do not allow for easy adjustments to cooling capacity.
- 🔬 The video uses 3D models to illustrate the internal structure and flow paths, enhancing understanding of how these heat exchangers operate.
- 📚 For further learning, the video suggests visiting the provided website for articles and interactive 3D models, as well as considering online courses for deeper knowledge.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is the shell and tube heat exchanger, discussing its components, design features, advantages, disadvantages, and how it works.
What are the two main fluids involved in a shell and tube heat exchanger?
-The two main fluids involved are the tube side fluid and the shell side fluid, which flow through the tubes and the shell respectively.
What is the purpose of the shell in a shell and tube heat exchanger?
-The shell serves as a pressure vessel that houses the tubes and provides a space for the shell side fluid to flow and exchange heat with the tube side fluid.
Why are baffles used in a shell and tube heat exchanger?
-Baffles are used to create a path for the shell side fluid to flow around the tubes, promoting turbulent flow which enhances heat transfer and helps prevent fouling.
What is the function of tube sheets in a shell and tube heat exchanger?
-Tube sheets are used to hold the tubes in position and seal the inside of the shell to ensure the shell side fluid stays within the space between the two tube sheets.
What is the purpose of turbulators or tube inserts in the tubes?
-Turbulators or tube inserts are used to create turbulent flow within the tubes, which increases the heat transfer capacity and helps keep the tubes clean by reducing the buildup of deposits.
What is the difference between a single pass and a multi-pass heat exchanger?
-In a single pass heat exchanger, the fluid flows through the tubes once before exiting. In a multi-pass heat exchanger, the fluid makes multiple passes over the tubes, enhancing heat transfer.
What is a U-tube shell and tube heat exchanger?
-A U-tube shell and tube heat exchanger is a design where the tubes are bent into a U-shape, allowing for expansion and contraction without stressing the tube sheets.
What are the advantages of shell and tube heat exchangers over plate heat exchangers?
-Shell and tube heat exchangers are generally cheaper, simpler to maintain, suitable for higher pressures and temperatures, have less pressure drop, and are less prone to fouling compared to plate heat exchangers.
What are the disadvantages of shell and tube heat exchangers compared to plate heat exchangers?
-Shell and tube heat exchangers are less efficient, require more space for maintenance, and do not allow for easy adjustment of cooling capacity like plate heat exchangers do.
What type of flow design is the most efficient for a heat exchanger?
-Counter flow design is the most efficient type of flow for a heat exchanger, where the tube side fluid and shell side fluid flow in opposite directions.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)