Types of Heat Exchanger
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the four most common types of heat exchangers: shell and tube, plate, spiral, and double pipe heat exchangers. Shell and tube exchangers are ideal for applications where water is unavailable or specific temperatures are needed. Plate heat exchangers use flat plates to maximize heat transfer, while spiral exchangers utilize concentric spiral flows for efficient heat exchange in compact spaces. Lastly, double pipe exchangers consist of a smaller pipe within a larger one, providing an easy-to-use, effective solution for simpler needs. Each type has its unique advantages for different industrial applications.
Takeaways
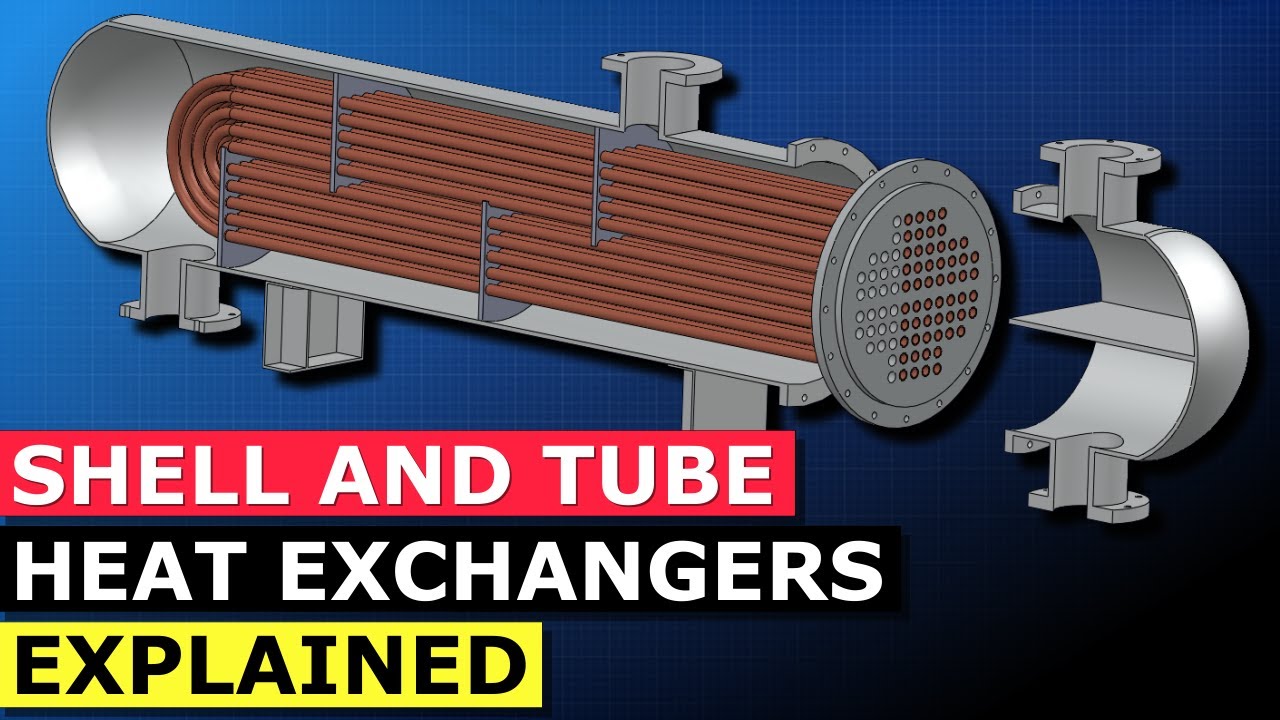
- 😀 Shell and tube heat exchangers are one of the most commonly used types, where one fluid runs through the tubes while another flows over the tubes for heat transfer.
- 😀 Air-cooled heat exchangers are used in places where water is not available or where the outlet temperature must meet specific requirements.
- 😀 Plate heat exchangers use plates to transfer heat, providing a larger surface area for heat exchange, which enhances their efficiency.
- 😀 Spiral heat exchangers have concentric spiral flow passages, keeping the fluids separate and preventing bypassing or mixing.
- 😀 Spiral heat exchangers are designed by rolling metal plates to form these concentric flow paths, offering a unique design for heat transfer.
- 😀 Tube-in-tube heat exchangers (also known as concentric pipe heat exchangers) have one pipe inside another, allowing heat transfer between the two fluids flowing inside the pipes.
- 😀 Heat exchangers are widely used across various industries to manage heat in processes where cooling or heating is essential.
- 😀 Shell and tube heat exchangers are effective for handling high-pressure fluids and are often used in applications requiring robust designs.
- 😀 Plate heat exchangers offer flexibility in terms of modular design, making them easy to expand or modify for different applications.
- 😀 Tube-in-tube heat exchangers are especially useful in compact spaces and are designed for efficient thermal exchange between two fluids.
Q & A
What is a shell and tube heat exchanger?
-A shell and tube heat exchanger is a type of heat exchanger where one fluid runs through tubes, while another fluid flows over the tubes, transferring heat between the two fluids.
What are the common applications of shell and tube heat exchangers?
-Shell and tube heat exchangers are commonly used in applications where water is not available or when the design process requires achieving outlet temperatures given specific maximum temperatures for the fluids involved.
What is a plate heat exchanger?
-A plate heat exchanger is a type of heat exchanger that uses plates to transfer heat between two fluids. The plates provide a larger surface area for heat exchange, improving efficiency compared to traditional tube heat exchangers.
How do plate heat exchangers provide a surface area advantage over shell and tube heat exchangers?
-Plate heat exchangers have the advantage of providing a much larger surface area for heat exchange because the plates are spread out, allowing for more efficient heat transfer.
What is a spiral heat exchanger?
-A spiral heat exchanger consists of two concentric spiral flow passages made by rolling long metal sheets into spiral shapes. One flow passage is for each fluid, ensuring that there is no bypassing or intermixing of fluids.
Why are spiral heat exchangers effective?
-Spiral heat exchangers are effective because they minimize fluid bypassing and intermixing, ensuring efficient heat transfer between the two fluids.
What is a double-pipe heat exchanger?
-A double-pipe heat exchanger, also known as a concentric pipe heat exchanger, consists of a single tube within another, with fluid flowing through the inner pipe and a separate fluid flowing through the outer pipe.
How does the design of a double-pipe heat exchanger work?
-In a double-pipe heat exchanger, one fluid flows through the inner pipe, while the other fluid circulates through the outer pipe, allowing heat transfer between the two fluids. The design is simple and often used for smaller heat exchange tasks.
What is the function of the outer pipe in a double-pipe heat exchanger?
-The outer pipe in a double-pipe heat exchanger serves as the surrounding conduit through which one of the fluids circulates, allowing heat transfer to or from the fluid inside the inner pipe.
How does a spiral heat exchanger prevent fluid intermixing?
-A spiral heat exchanger prevents fluid intermixing by maintaining separate flow passages for each fluid within the concentric spiral design, ensuring that each fluid remains isolated and does not mix with the other.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)