Phylogeny | Evolutionary Relationship | Tree Diagram
Summary
TLDRThis script explains how scientists use tree diagrams to illustrate the evolutionary relationships among living organisms. By organizing creatures into branching patterns, the diagrams show a best guess of how they are related through reproductive lineages. The branching points represent common ancestors, and the order of traits along branches indicates the sequence of evolutionary changes. The script emphasizes that tree diagrams are hypotheses based on available evidence, which can be revised with new data, such as fossils, and that the key information lies in the branch points rather than the order of organisms at the top.
Takeaways
- 🌳 Humans naturally organize things by similarities and differences, but evolutionary relationships require a different approach, using branching tree diagrams.
- 🔍 Tree diagrams represent the evolutionary relationships among living organisms, assuming a common ancestry and showing how they diverged over time.
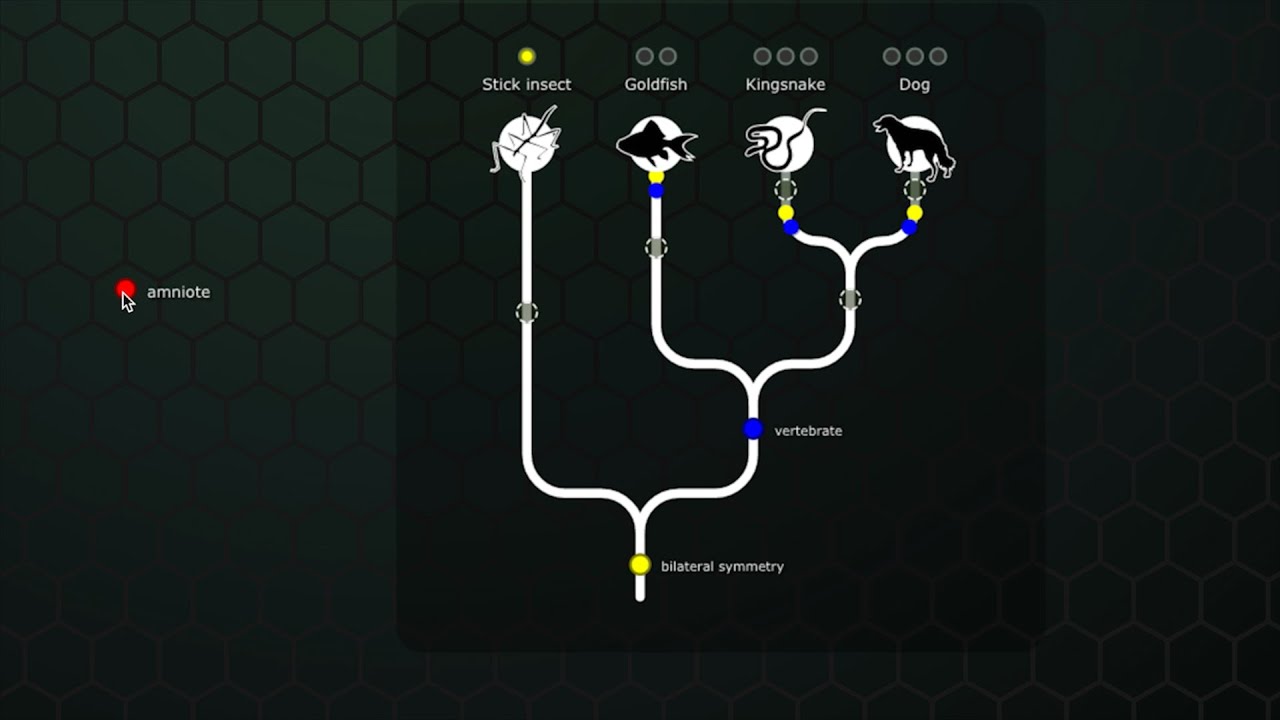
- 🌱 The base of the tree diagram symbolizes a hypothetical common ancestor, with the tips representing current living descendants.
- 🔗 Branches in the tree diagram represent reproductive lineages, showing how species diverged from one another.
- 🔄 The order of traits along the branches indicates the sequence in which evolutionary changes occurred.
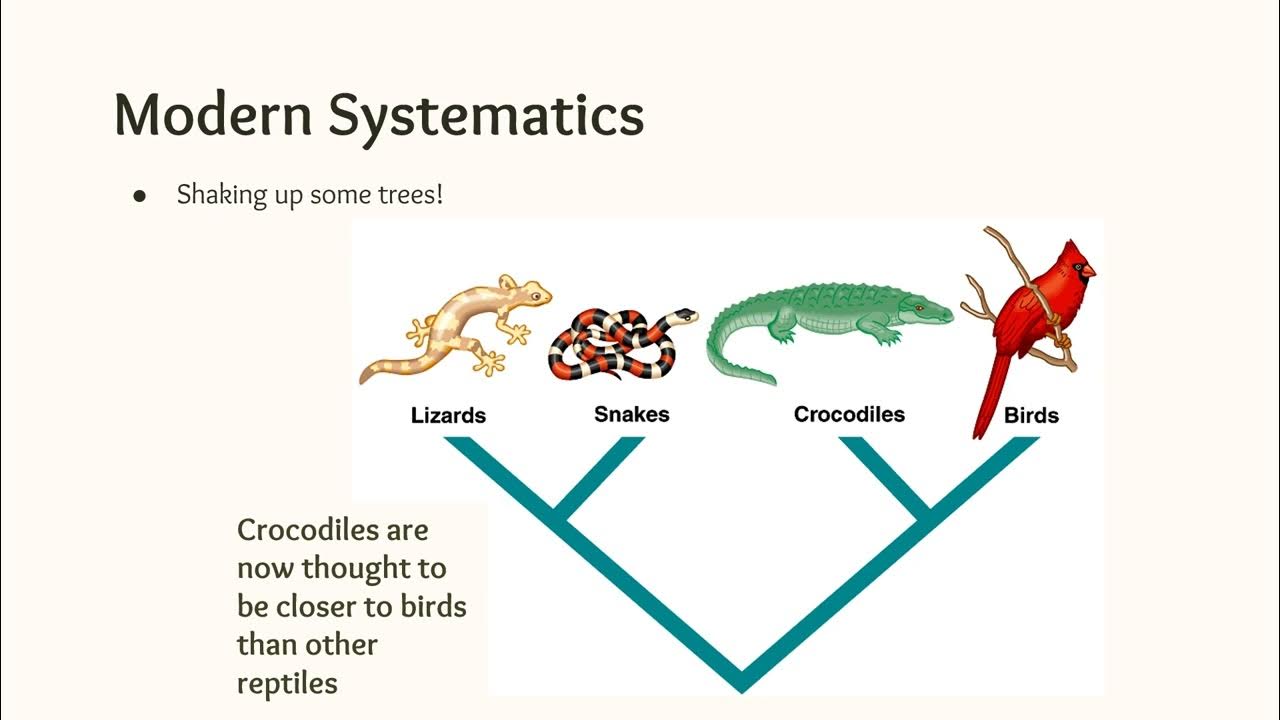
- 🔎 Branch points or nodes in the tree represent common ancestors, with the most recent common ancestor shared by all branches beyond it.
- 🔑 The closeness of relatedness between species can be inferred from the number of traits they share and the recency of their common ancestor.
- 🔄 The order of organisms across the top of the tree diagram is not significant; the key information lies in the branch points.
- 💠 Tree diagrams are hypotheses based on available evidence and can be revised with new data, such as fossils.
- 🧬 Scientists use multiple lines of evidence, including anatomy, fossils, embryonic development, and DNA and amino acid sequences, to construct these diagrams.
- 🌐 Despite the variety of ways tree diagrams can be drawn, they adhere to consistent organizational rules to represent evolutionary relationships.
Q & A
How do humans naturally organize things?
-Humans naturally organize things by grouping them based on their similarities and differences.
What makes evolutionary relationships different from other types of organization?
-Evolutionary relationships are different because they depict how living things are related through their shared ancestry, typically represented in tree diagrams.
What is the underlying assumption when organizing living things into tree diagrams?
-The underlying assumption is that all living things descended from a common ancestor.
How do the branches in a tree diagram represent the evolutionary relationships?
-The branches in a tree diagram represent the reproductive lineages of organisms and how they split over time.
What does the base of a tree diagram symbolize?
-The base of a tree diagram symbolizes a hypothetical common ancestor from which all the organisms at the tips of the branches are descended.
How do branch points or nodes in a tree diagram relate to common ancestors?
-Branch points or nodes in a tree diagram represent common ancestors, with the most recent common ancestor being the one that is shared by all branches beyond it.
What does the order of organisms across the top of a tree diagram indicate?
-The order of organisms across the top of a tree diagram does not indicate anything; the key information is in the branch points.
How can the arrangement of branches around a node affect the interpretation of a tree diagram?
-Rotating the branches around a node does not change the relationships shown in the tree, as long as the nodes are in the same relative order.
What evidence could support the direction of evolution depicted in a tree diagram?
-Fossils found in layers of rock can provide evidence for the direction of evolution, suggesting whether lineages evolved from simple to complex or vice versa.
What other types of evidence do scientists use to organize real organisms in tree diagrams?
-Scientists use characteristics from anatomy, fossils, embryonic development, and DNA and amino acid sequences to organize real organisms in tree diagrams.
Why might a tree diagram be redrawn?
-A tree diagram might be redrawn when new evidence comes to light, as tree diagrams are hypotheses based on the best available evidence at the time.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)