LA CELLULE : UNE VILLE MAGNIFIQUE - BMShow
Summary
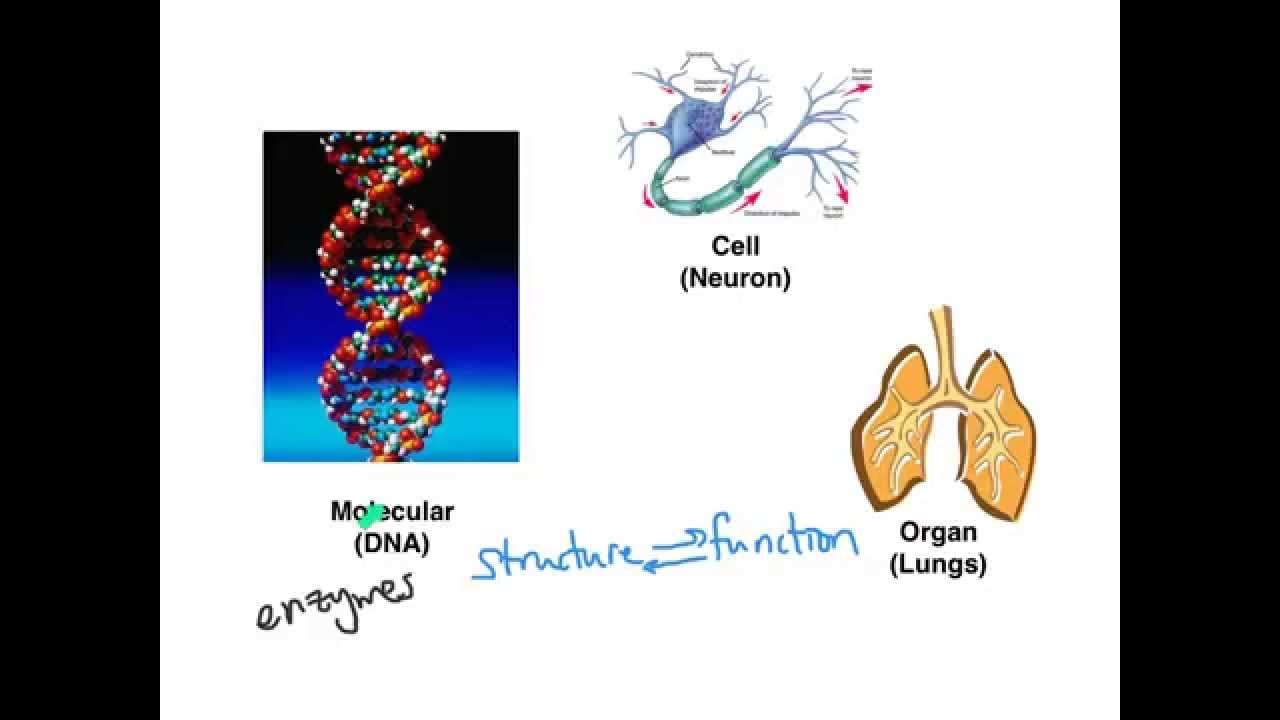
TLDRWelcome to the Boring Medical Show, where the host, BMS, creatively likens the human body to a world with continents, countries, and cities, each representing different levels of biological organization. The video dives into cellular biology, highlighting the vast number of cells (over 100,000 billion) and proteins (250,000 billion billion) in the human body. It differentiates between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, focusing on eukaryotes as they are the cells of our body. The host introduces 'Cellulia,' a model cell, and explains its protective barriers, the membrane, and its organelles, which are like tiny organs within the cell. The video promises future episodes exploring each element in more detail.
Takeaways
- 🌍 The human body is metaphorically described as a world with continents, countries, and cities, where cells are the cities and proteins are the inhabitants.
- 🔍 There are over 100,000 billion cells in the human body, each containing more than 2.5 billion proteins, illustrating the vast complexity of our biological systems.
- 🧬 Cells are categorized into two types: prokaryotes, which lack a nucleus, and eukaryotes, which have a nucleus and include the cells of our body.
- 🏙️ The 'city' of Cellulia, a model for understanding cells, is surrounded by a membrane that acts as a barrier, protecting the cell's contents.
- 🛡️ The cell membrane consists of two layers: the exoplasmic layer (E) and the protoplasmic layer (P), with lipids forming the physical barrier and proteins facilitating communication.
- 🏢 Organelles are specialized structures within the cell that perform essential functions, likened to tiny organs within the city of Cellulia.
- 🏛️ The nucleus is a significant organelle, considered the 'government' or 'town hall' of the cell, playing a central role in cellular activities.
- 💧 The cytoplasm, which includes everything inside the cell except the nucleus, is analogous to the 'cities' within the barriers of Cellulia.
- 🌊 The cytosol, a liquid within the cell, supports the organelles and is compared to the water upon which Venice rests, highlighting the cell's fluid environment.
- 🔬 Each element of the cell, including the membrane and organelles, will be explored in more detail in future videos, indicating a series that delves deeper into cellular biology.
Q & A
What is the analogy used to describe the human body in the script?
-The human body is compared to a world with continents, countries, and cities, where continents are body parts like the head, thorax, abdomen, and limbs, countries are organs or tissues, and cities are cells.
How many cells are estimated to be in the human body according to the script?
-The script estimates that there are more than 10 to the 14th power different cells, which translates to over 100,000 billion cells.
What is the significance of the number of proteins in each cell as mentioned in the script?
-Each cell contains more than 2.5 billion proteins, which, when multiplied by the number of cells, results in a staggering quantity of proteins in the human body.
What are the two types of cells distinguished by the presence or absence of a nucleus?
-The two types of cells are Prokaryotes, which do not have a nucleus, and Eukaryotes, which have evolved with a nucleus.
Why is the theory of evolution mentioned in the context of medicine?
-The theory of evolution is mentioned because it serves as a framework for understanding the development and function of cells in the human body, despite it not being perfectly accurate.
What is the term used to describe the city in the script that represents a typical cell?
-The term used is 'Cellulia,' which is a model that describes the majority of cells in terms of structure and function.
What are the barriers that protect the inside of the cell, as described in the script?
-The barriers that protect the inside of the cell are the cell membrane, which is composed of two layers: the exoplasmic layer (E layer) and the protoplasmic layer (P layer).
What is the term for the liquid on which Cellulia, the cell city, rests according to the script?
-The liquid on which Cellulia rests is called 'the Cytosol.'
What is the role of the proteins in the cell membrane as described in the script?
-The proteins in the cell membrane act like the TSA of Cellulia, allowing the cell to communicate with other cells and control the passage of substances in and out of the cell.
What is the term for the structures within the cell that have an important role, as mentioned in the script?
-The term for these structures is 'Organelles,' which are likened to the tiny organs of the cell, each with a specific function.
What is the role of the nucleus in the cell, as described in the script?
-The nucleus is described as the government or town hall of the cell, indicating its central role in controlling the cell's activities and containing genetic information.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)