PEMERIKSAAN FISIK ABDOMEN
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, a medical professional named Azizah conducts a physical examination of the abdomen. She explains the procedure, which includes inspecting for any abnormalities, auscultating for bowel sounds, and performing percussion to detect organ status and ascites. The examination also involves palpation to assess the liver, spleen, and kidneys, ensuring the patient's comfort throughout. The video serves as a practical guide for medical students and professionals, highlighting the importance of a systematic approach in abdominal examinations.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script is a detailed account of a physical examination of the abdomen, conducted by a medical professional named Azizah.
- 🕵️♂️ The examination is intended to identify any abnormalities or discomfort in the patient's abdomen, following the patient's complaint of pain.
- ⏱ The process is expected to take approximately 10 minutes, as mentioned in the script.
- 👕 The patient is asked to expose the abdominal area by lifting their shirt for the examination.
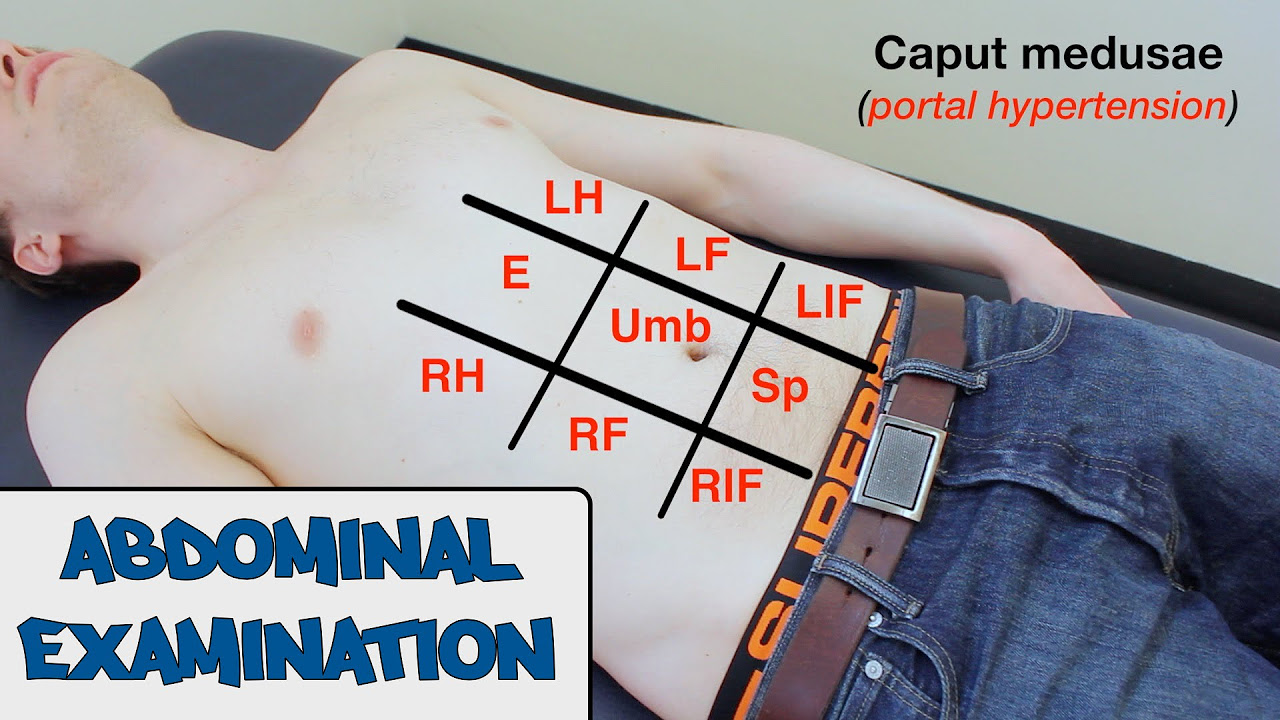
- 🔍 The abdomen is divided into quadrants for systematic inspection, which includes observing for any movements, wounds, skin color, or hair distribution.
- 👂 Auscultation is performed to listen for bowel sounds, with the expectation of hearing them 5 to 35 times per minute.
- 👊 Percussion is used to determine the presence of air or organs in the abdominal area, with different sounds indicating various conditions.
- 🤲 Palpation is conducted gently to assess the texture and any tenderness in the abdominal region, with specific attention given to the liver and spleen.
- 🩺 The script describes a methodical approach to examining for ascites, which includes shifting the patient's position to observe changes in sound during percussion.
- 🧪 The examination concludes with a check for the presence of any masses or fullness in the abdominal area, and a check for aortic pulsation.
- 📝 The script emphasizes the importance of a systematic approach to abdominal examination, with inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation being the key steps.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the physical examination described in the script?
-The purpose of the physical examination is to determine if there are any abnormalities in the abdominal area of the patient, as the patient had complained of abdominal pain the previous day.
How long is the physical examination expected to take?
-The physical examination is expected to take approximately 10 minutes.
What is the first step in the examination process as described in the script?
-The first step in the examination process is to have the patient expose the abdominal area by lifting the shirt and to ensure the patient is comfortable and lying down.
How is the abdominal area divided for inspection in the script?
-The abdominal area is divided into four quadrants by drawing a horizontal line across the abdomen and a vertical line from the sternum to the pubis, creating the right upper, left upper, right lower, and left lower quadrants.
What is the significance of observing the movement of the abdominal area during the examination?
-Observing the movement of the abdominal area helps to assess the presence of any swelling, pulsations, or asymmetry that may indicate an underlying issue.
What does the script mention about the patient's last meal before the examination?
-The patient had their last meal in the morning, a few hours before the examination.
What is auscultation and why is it performed during the abdominal examination?
-Auscultation is the act of listening to sounds within the body, such as bowel sounds, to detect any abnormalities. It is performed to listen to the sounds produced by the intestines and to count the frequency of bowel sounds, which can indicate the presence of bowel obstruction or other issues.
What is the significance of percussing the abdomen during the examination?
-Percussion is used to determine the presence of fluid or air in the abdominal cavity by listening to the sound produced. It helps to identify the location of organs and detect conditions like ascites or organ enlargement.
How is the liver examined for percussion in the script?
-The liver is examined by percussing from the lower edge of the ribcage towards the pelvis, listening for a change in sound from dull (indicating a solid organ) to resonant (indicating air in the stomach).
What is palpation and how is it performed in the abdominal examination?
-Palpation is the process of examining the abdomen by touch, feeling for tenderness, masses, or organ enlargement. It is performed gently with the fingertips, starting from the non-dominant hand and moving to the dominant hand for deeper palpation.
What is the final step in the abdominal examination as described in the script?
-The final step in the abdominal examination is to palpate the aorta and the kidneys, assessing for any tenderness or abnormalities.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)